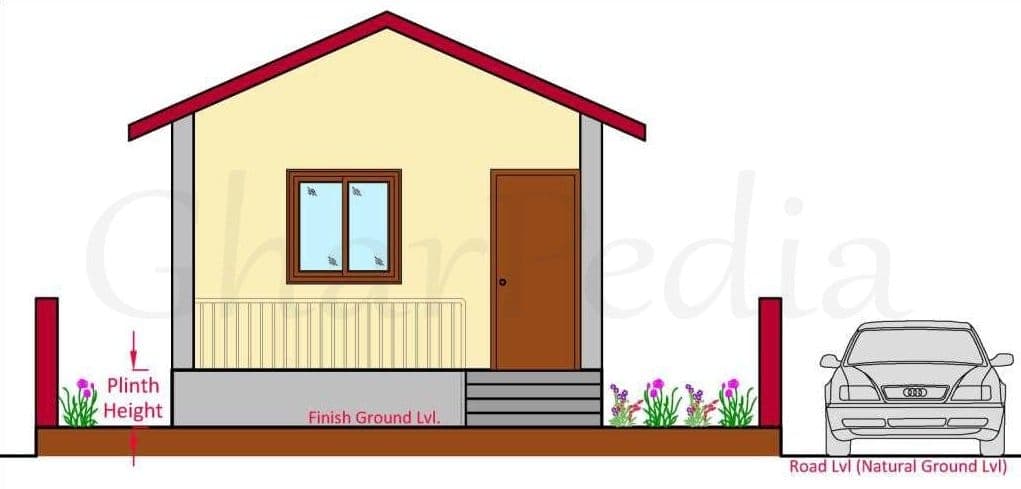
In architecture, a plinth is the base or platform upon which a column or structure rests and it is normally constructed just above the ground level and immediately after the foundation. It raises the floor above the ground level and herewith prevents surface water from entering the building.
There are various reasons that govern while deciding the ideal plinth height of the house. The plinth height is provided essentially to protect the superstructure from dampness which may seep in due to direct contact from the ground level. The top of plinth level is provided with damp proof course which is an additional protection against dampness.
Plinth height also prevents stormwater or overflowing drainage from directly entering the building in case of heavy rainfall. If the ground level is lower than the adjoining road level and if there are no public stormwater drains under the public road adjoining your property you would not be able to discharge stormwater during rain from your plot. The water would get collected in the plot and the land would remain submerged till the water dries out. Hence under all circumstances, the plot must be minimum 6 inches or 150 mm above from the road level. It is also advisable to keep the land sloping downwards towards the road so that water will drain out fast. The plinth level therefore also should be provided accordingly i.e. minimum 1’-6” or 450 mm above final ground level. Better if it is 600 to 900 mm above finished ground level.

Sometimes on busy roads the municipality will recarpet the roads every 3 to 5 years. In such cases over a period, the level of the road would go up considerable and even by 300 mm i.e. 1 ft. It is therefore advisable to have the level of plot minimum 1 ft or 300 mm higher so that when the level of the road goes up you will not face problem. The plinth therefore would be Height of filling + minimum 450 or 600 to 900 mm.
Plinth height includes plinth wall & plinth beam depending on the height of plinth and filled with compacted soil. The plinth beam is constructed which braces the plinth level. i.e upon substructure to take up load of walls and transfer the same to the footings and further to hard strata.
The Functions of the Plinth are:
- Provided plinth beam can transfer the load from the superstructure to the foundation.
- It can provide the damp proof course to the house for preventing dampness.
- It can support the backfilling of the earth as a retaining wall.
- Providing plinth to the house can also increase the aesthetical look of the building.