There are various ways in which one can go about accessing the different floors in a building, stairs being the most common means. Therefore, this makes stairs a vital design element for any multi-storeyed building. However, just because the utility of the stairs is high, doesn’t mean that it cannot look stylish and chic.
Stairs can, sometimes, be the most attractive feature in an empty foyer, depending on how they are constructed. Thus the materials you use to construct a staircase is important. To make a staircase look appealing, materials like metals, wood, concrete, bricks, and stone are used. Of these, a metal staircase is one of the most popular choices among a maximum number of architects, builders, and designers.
Metal stairs are independent of the building structure. They are structurally supported on each floor or the landings, if provided. The fact that the metal stair is a self-supporting stair system means that it can be installed independently of the floor structure. One of the main advantages that the metal stair has over the other types of stairs is that the different segments can be fabricated at the metal shop and then assembled at the site.
Metal stairs are made using different kinds of metals. So, let us take a look at all the different metals that are used to make these wonderful stairs.
Types of Metals Used in Metal Stairs
The various types of metals used in metal stairs are as listed below:01. Steel
02. Aluminum
03. Iron
04. CopperNow, let us go in-depth into each metal used in the manufacture of metal stairs.
01. Steel Stairs and Their Components
Steel is the most widely used metal in the construction industry because it is extremely strong, highly durable, and rust-resistant. Steel is also an ideal metal for the fabrication of spiral metal stairs because it is malleable, which means that it can be bent and shaped without it losing its strength. The various uses of steel in the fabrication of a metal stair are listed below:
a) Steel Stair Treads:
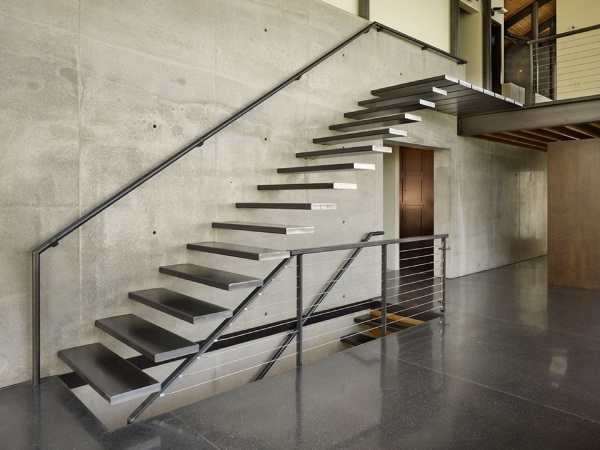
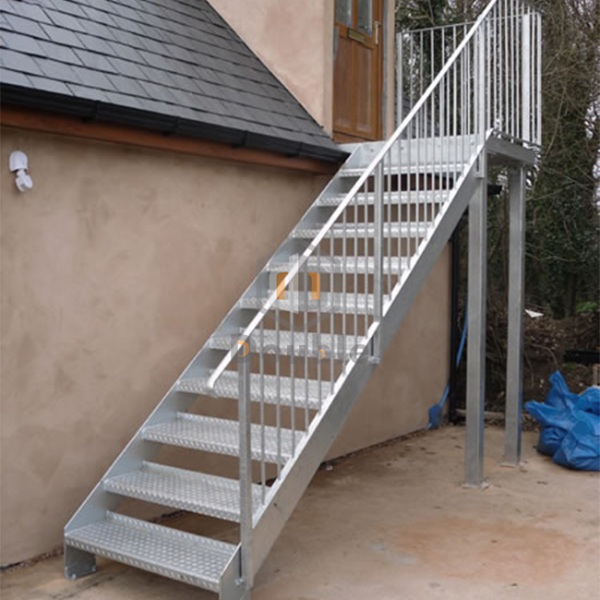
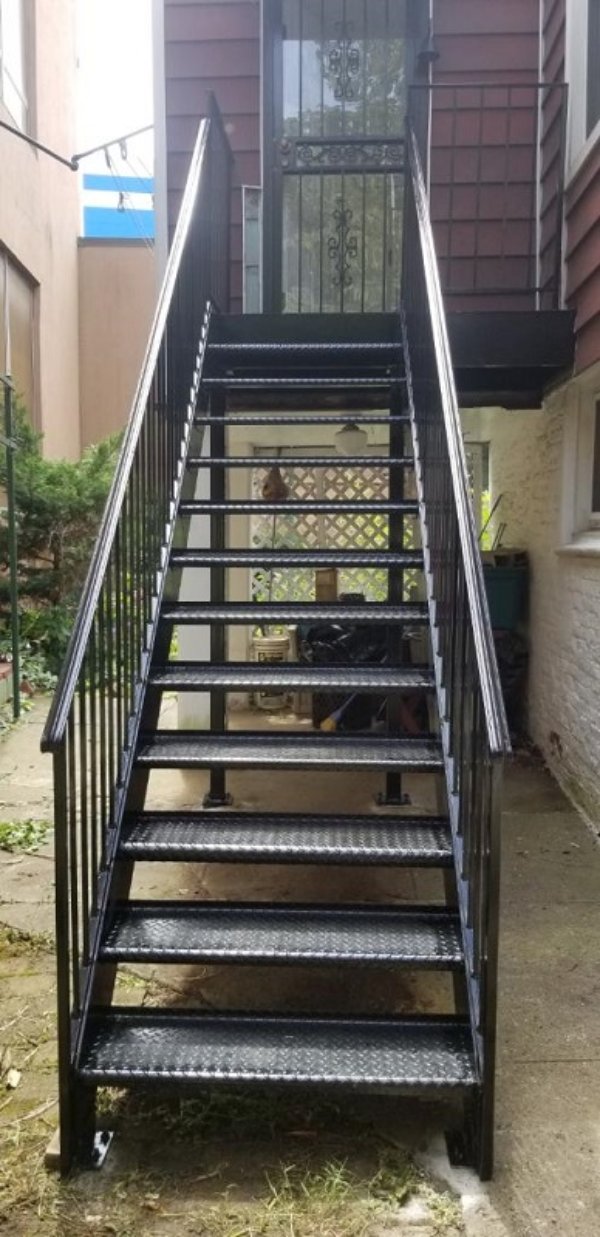



b) Stair with Steel Plate:
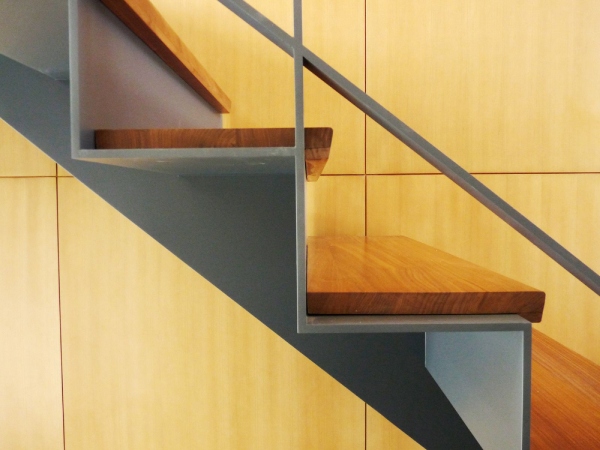
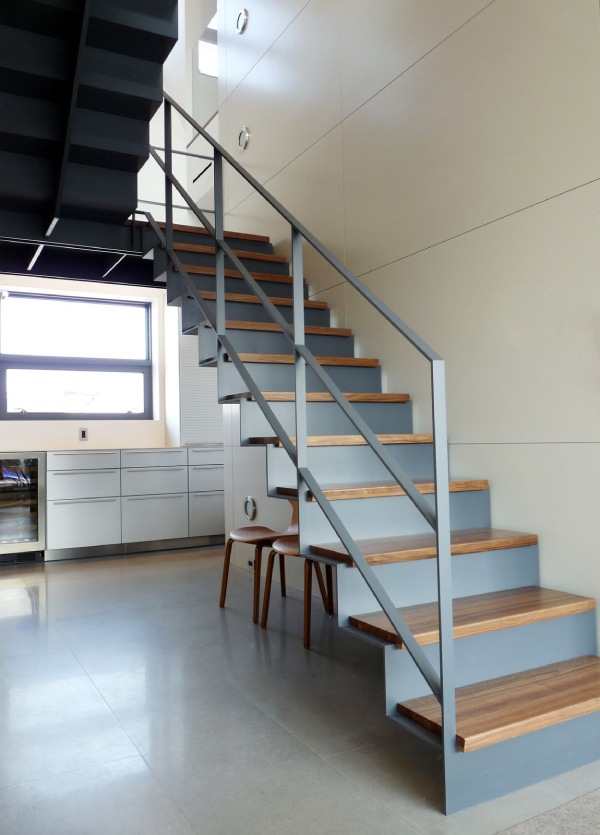
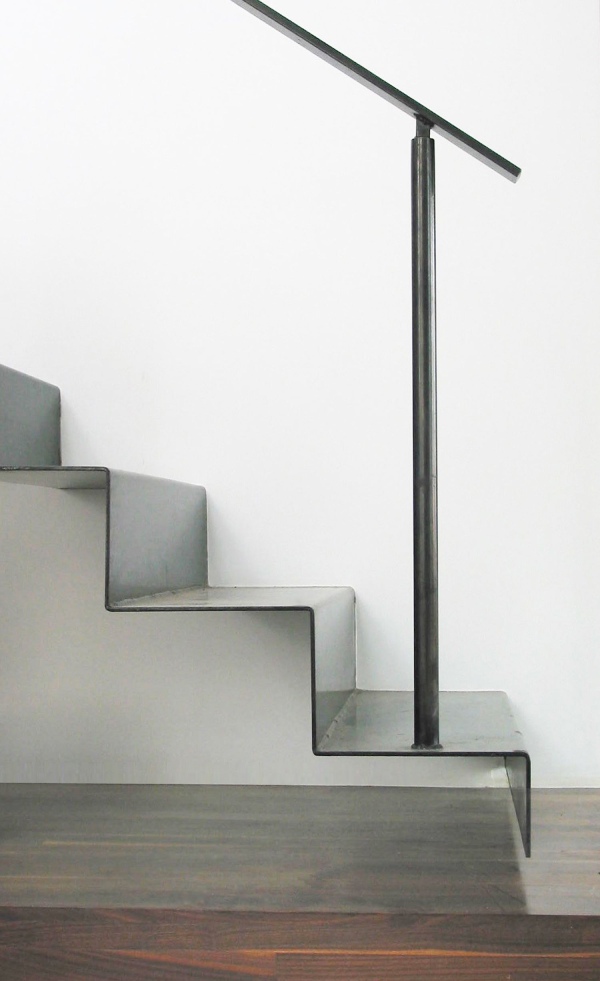



c) Steel Stair Railing:
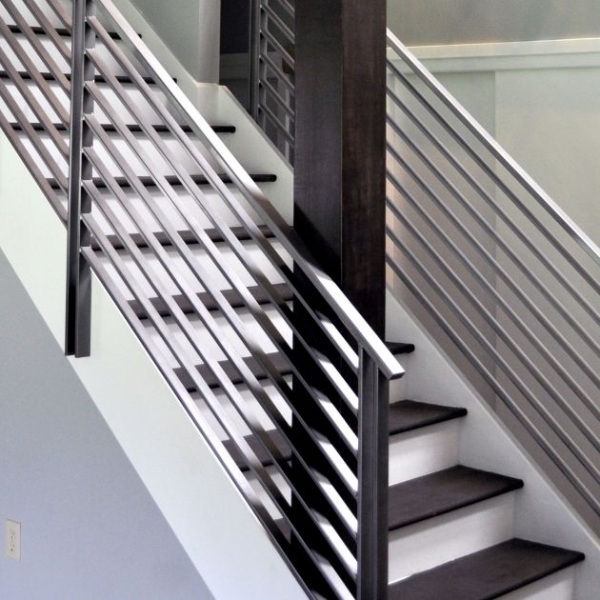
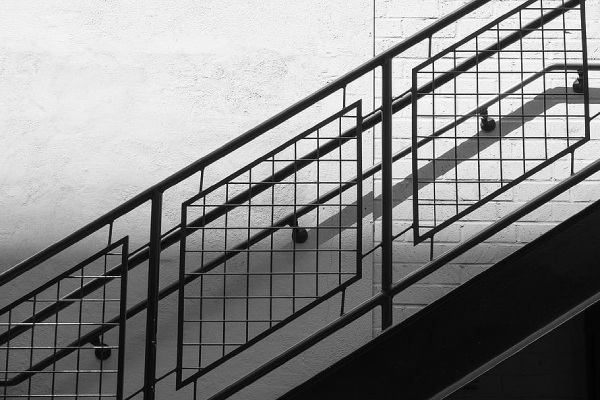
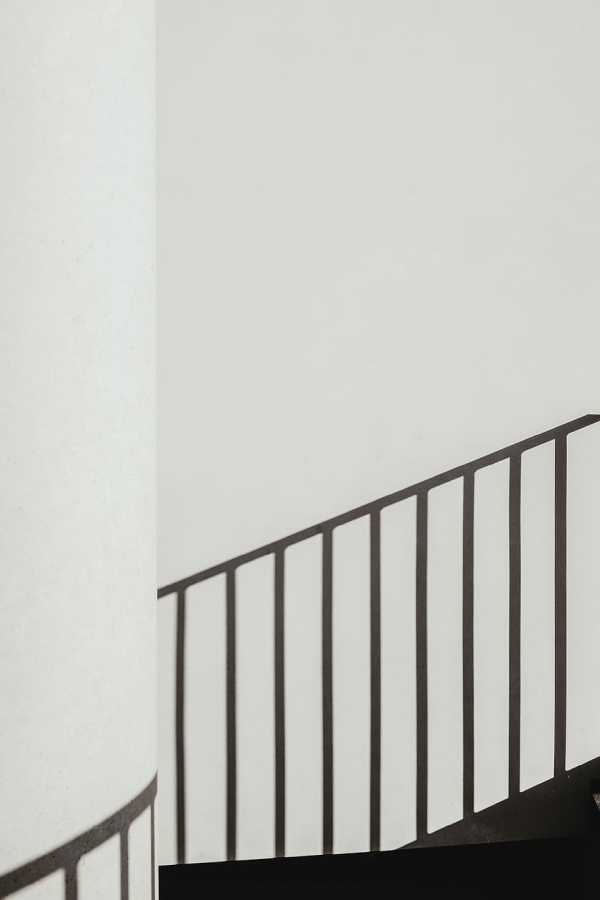



d) Steel Handrail:
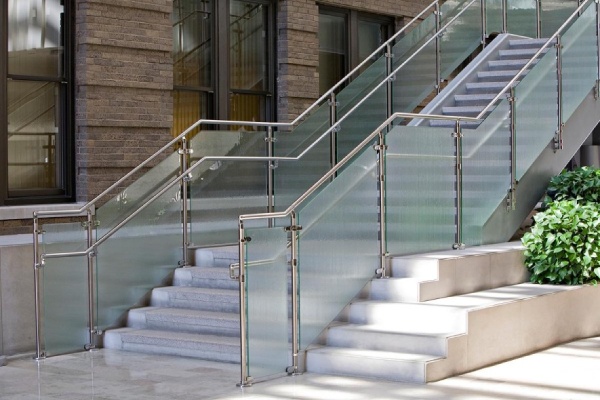
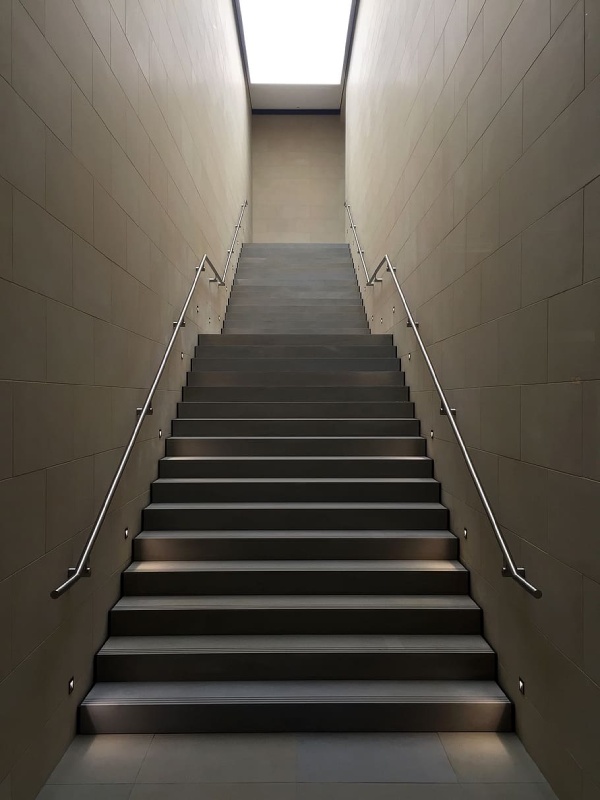
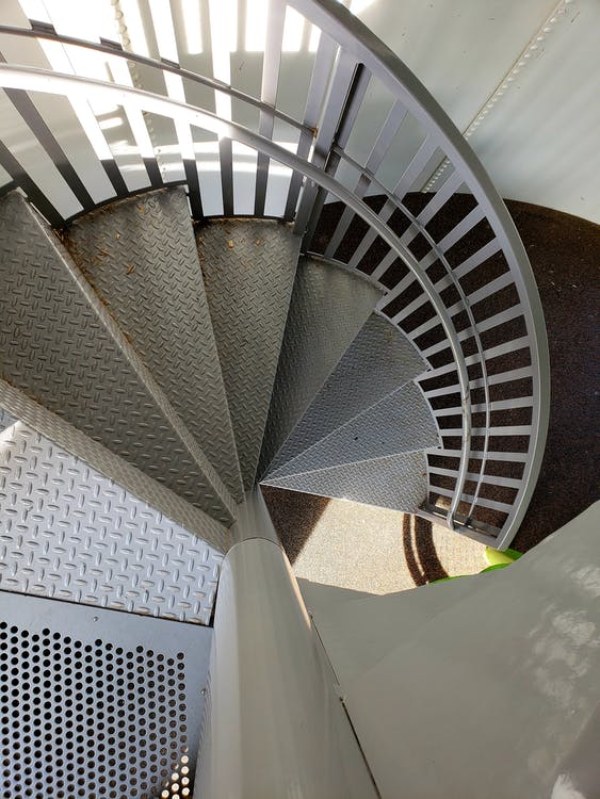



e) Steel Stringers:
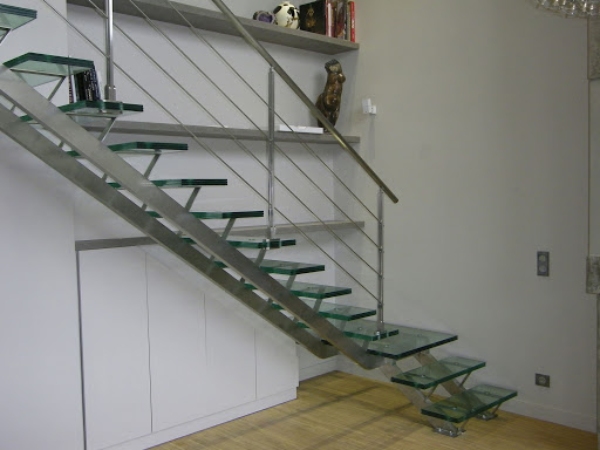
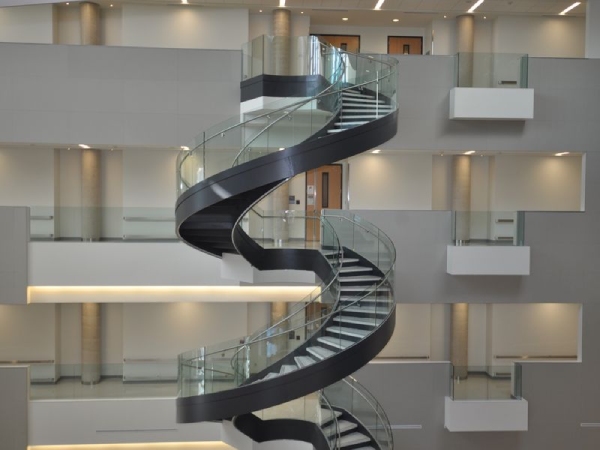



f) Stair with Steel Brackets:
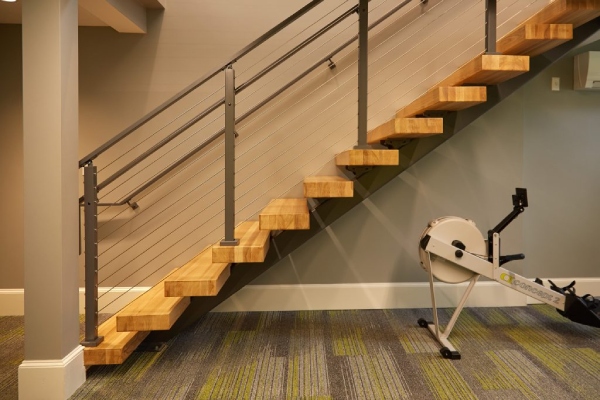
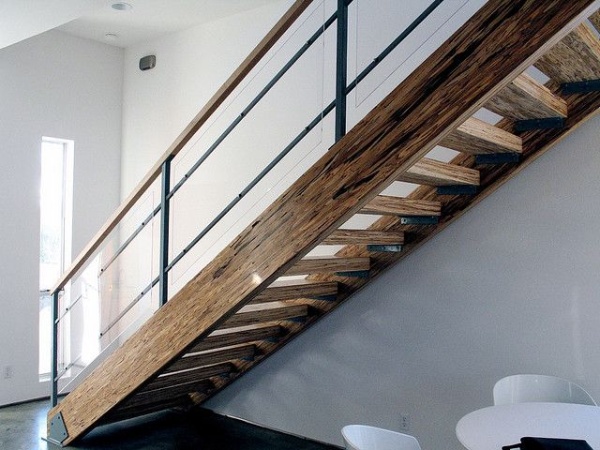
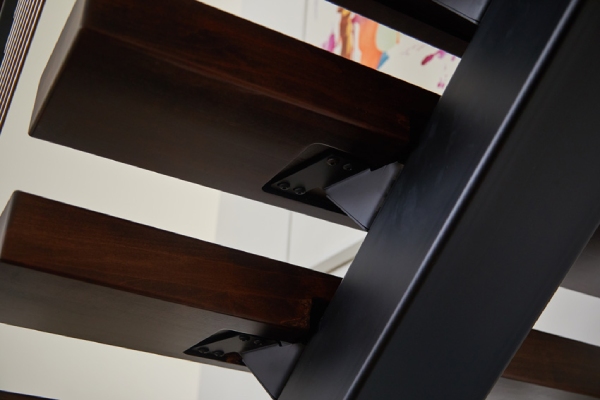



02. Aluminum Stairs and Their Components
Aluminum is a light-weight, anti-corrosive, and affordable metal used in the fabrication of metal stairs. Aluminum is a good metal for spiral metal stairs, however, it is more brittle than steel as it does not absorb vibrations as steel does. Aluminum is more likely to break under high pressure.
The various uses of aluminum in the fabrication of a metal stair are as follows:
a) Aluminium Stringer:
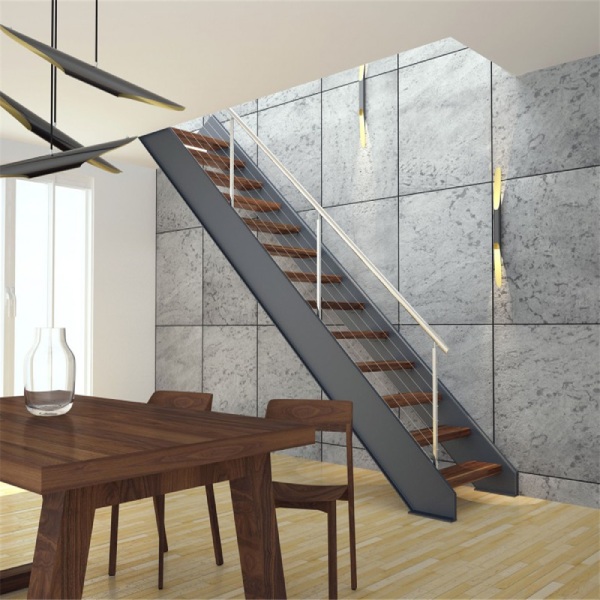
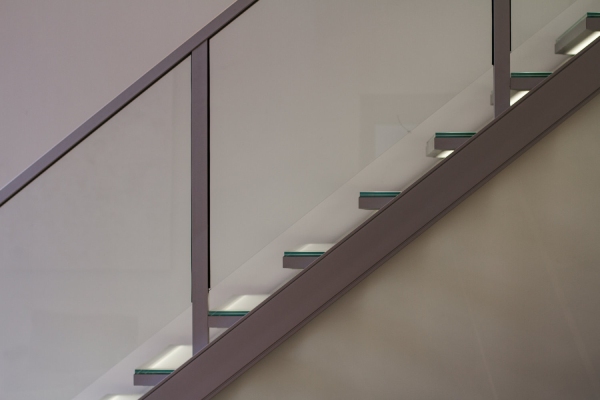



b) Aluminium Railing and Handrail:
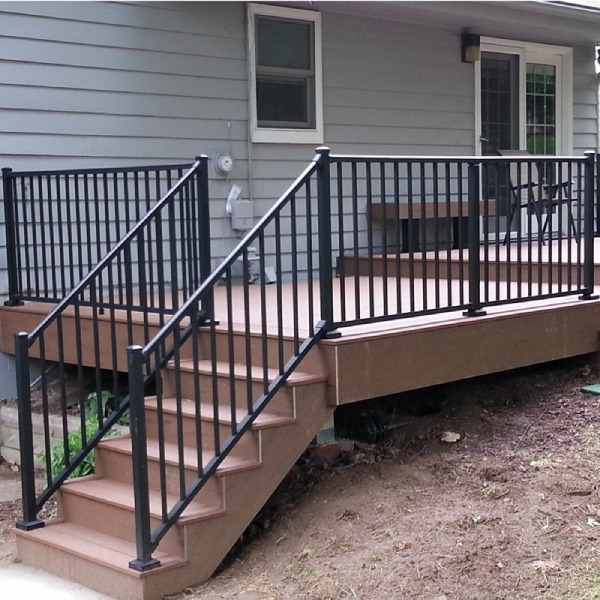
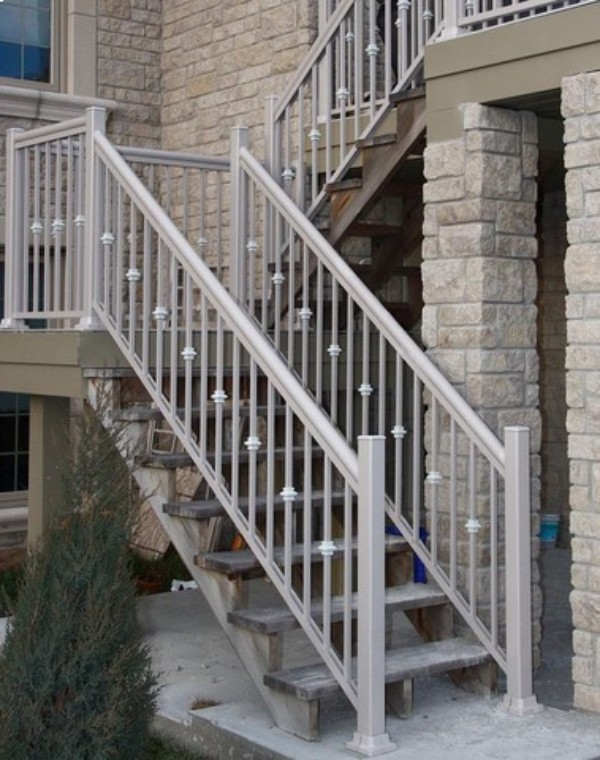



03. Iron Stairs and Their Components
There are two types of iron used in the fabrication of metal stairs:
01. Cast Iron and
02. Wrought Iron
Cast Iron is melted, poured, and molded, whereas, for wrought iron, the rolling takes place in the final stages of its production. The various uses of iron in the fabrication of a metal stair are as follows:
a) Cast Iron Treads:
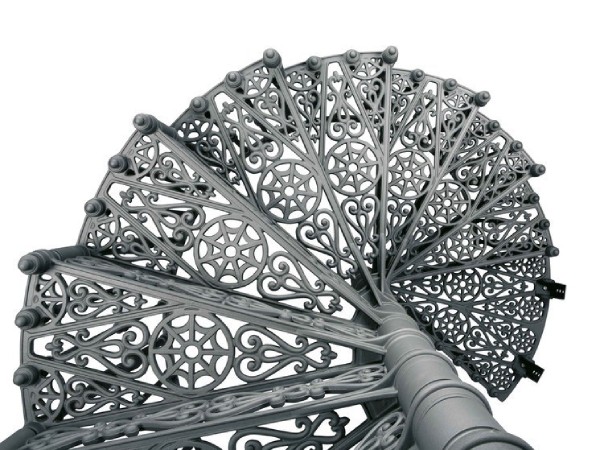
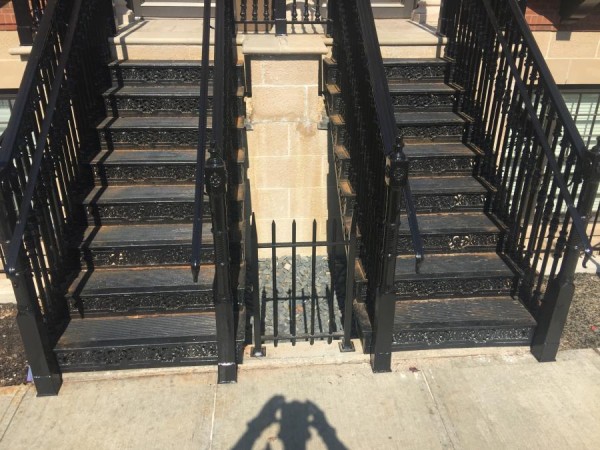

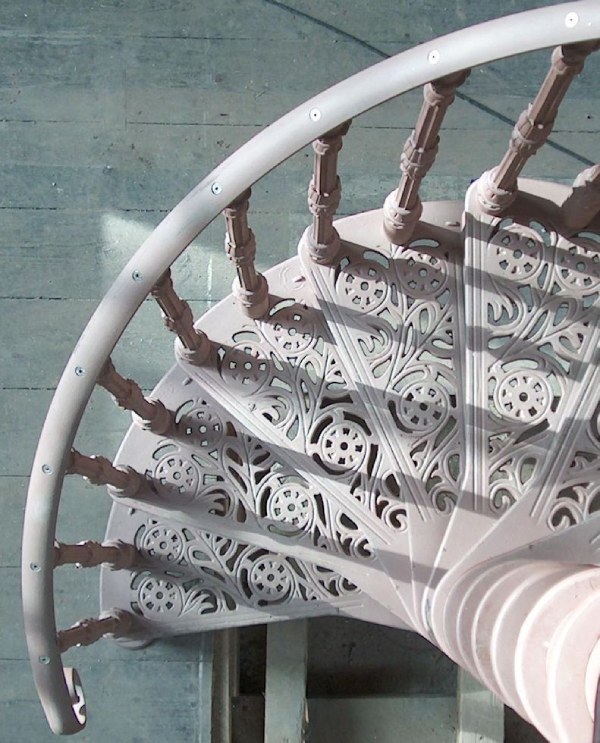

b) Cast Iron Handrail and Railing:
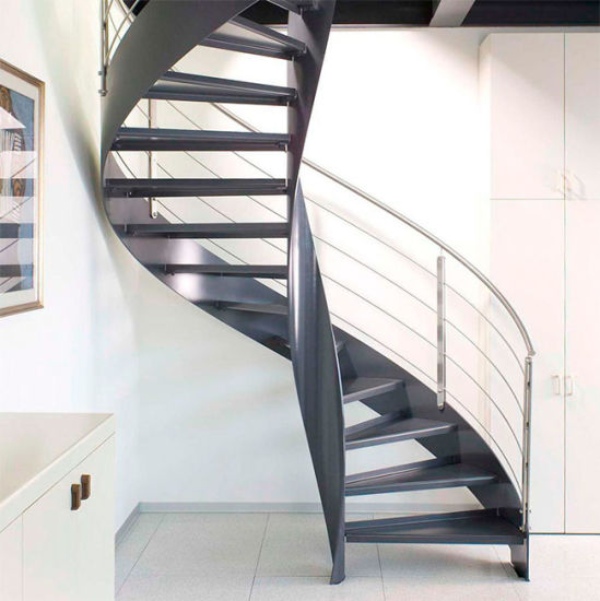
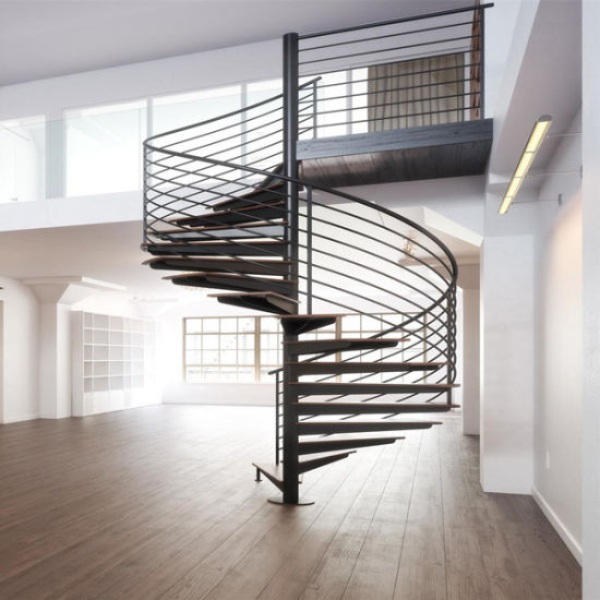
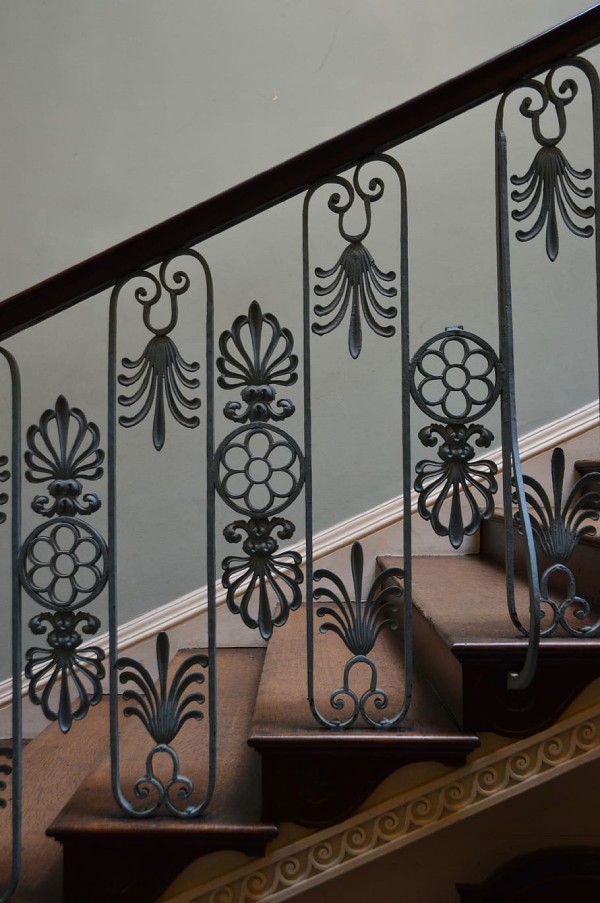



c) Cast Iron Spindles:

d) Wrought Iron Railing:
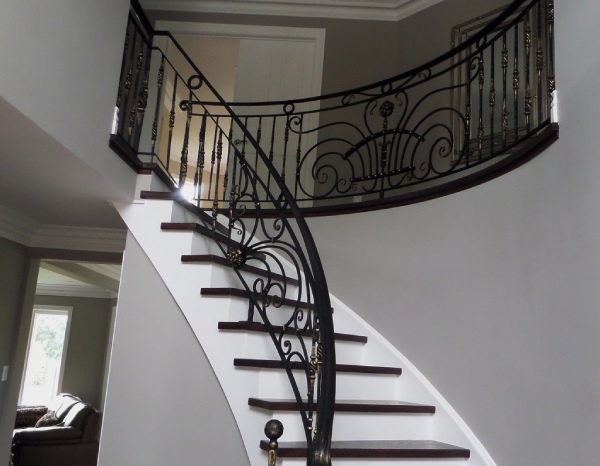
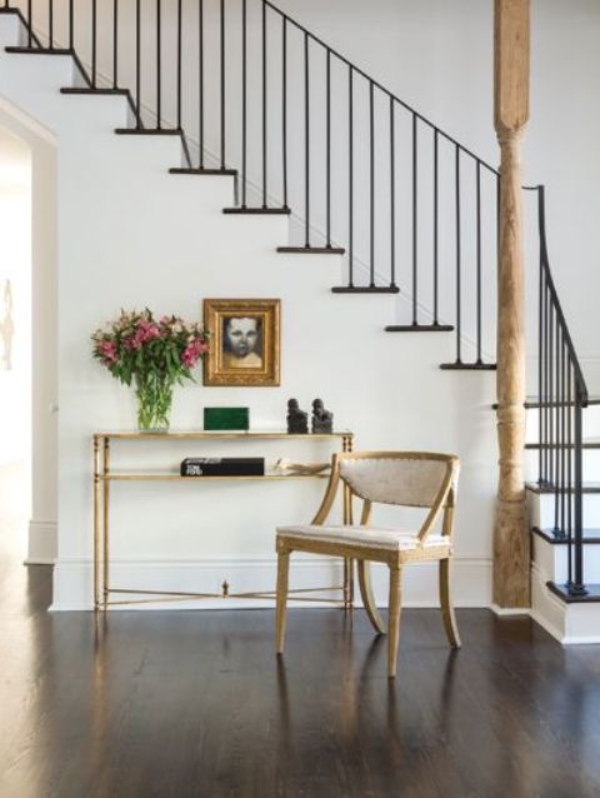



e) Wrought Iron Spindles:

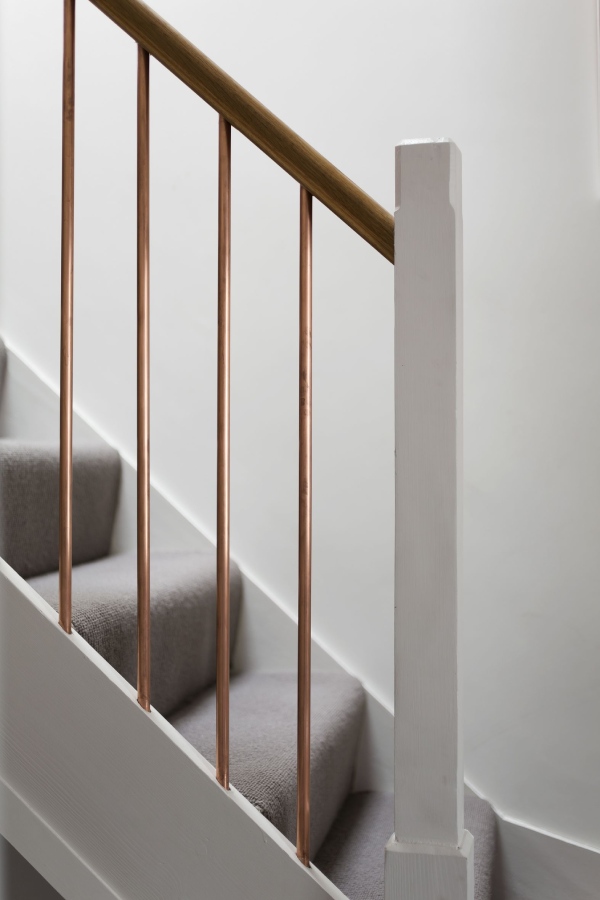
04. Copper Stairs and Their Components
Copper railings are the only form of copper stair component used as it is durable, rust-free, and easy to install.
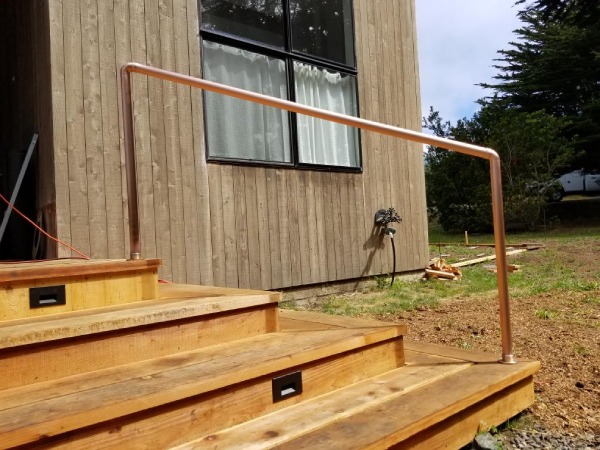
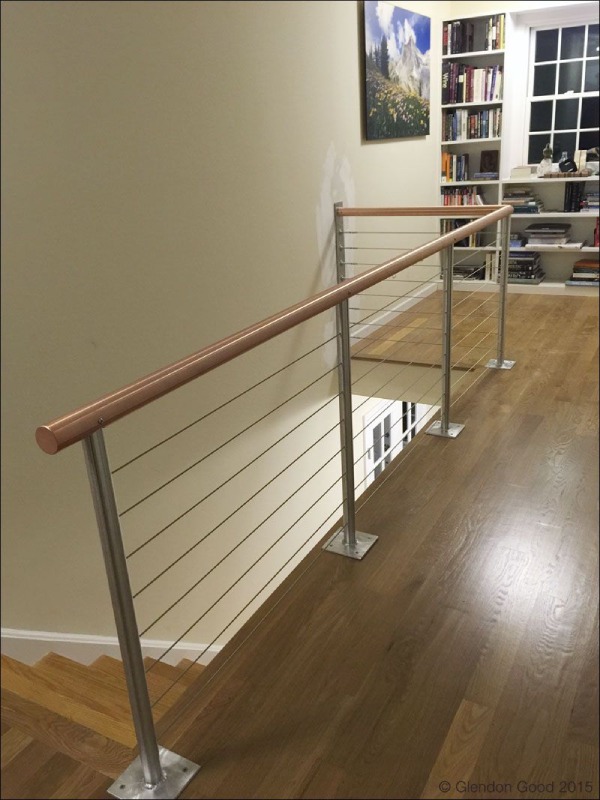



Now that we have seen all the kinds of metals used in the fabrication of a metal stair, let us see how these metals come together to form a staircase through multiple components.
Components of a Metal Stair
Various components, when joined together, form a stair. The various components that make up a metal stair are:
01. Metal Step – Combination of Tread and Riser
02. Metal Stringers
03. Metal Landing
01. Metal Step – Combination of Tread and Riser
A. Types of metal steps:
A metal step comprises metal treads and metal risers. This combination is responsible for carrying the gravity loads between the stringers. The primarily used options for metal steps are:
- Integral light gauge metal tread and riser
- Metal plate
- Prefabricated metal grating treads
- Non-metal options for treads and risers (e.g., wooden treads, precast concrete treads, etc.)
Let us have a quick look at these four types of metal steps:
Integral light gauge metal tread and riser:
In this type of metal step, a light gauge metal that easily bends and takes the shape of the geometry we require for the treads and risers is used. Then, concrete is poured in the formed pan tread, and as a result, we get a step.
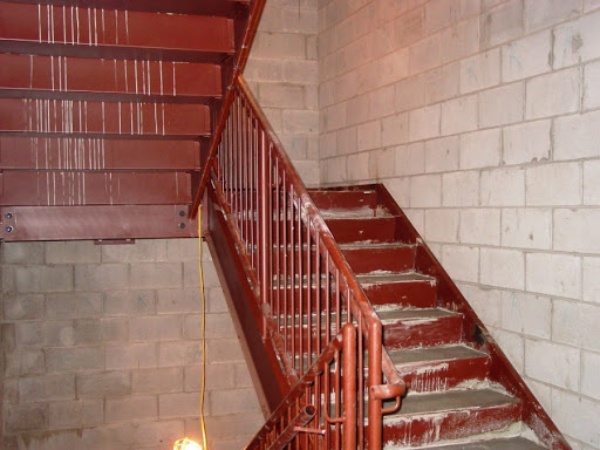

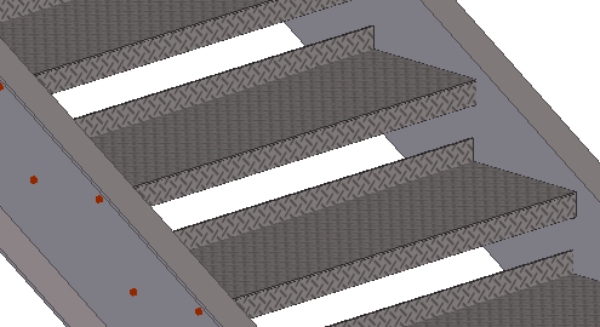
Metal Plate:
A diamond or chequered plate is typically used as a walking surface because these plates have adequate strength, and they provide a surface with good traction.
Prefabricated metal grating treads:
This type of metal step is used in a wet environment or for an exterior metal stair that is receives a lot of rain. It is even used for architectural purposes as this grating allows small objects and liquids to pass through.
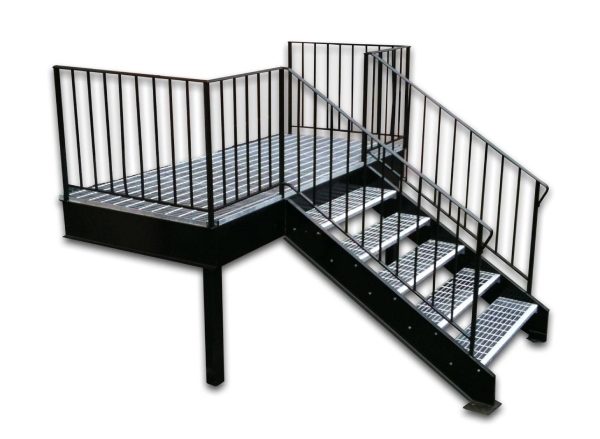

Non-metal options for treads and risers:
Depending on how the non-metal materials (pre-cast concrete, wood, glass, plastic, or stone) interact with metal as per the design, we can use an appropriate material for this tread-riser combination.
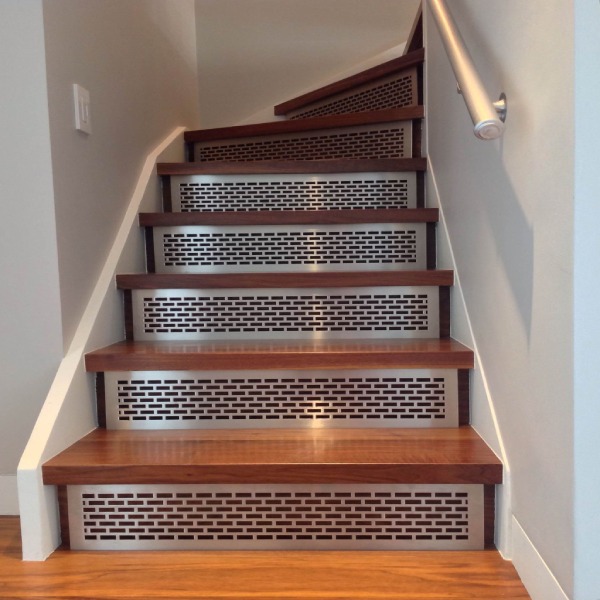
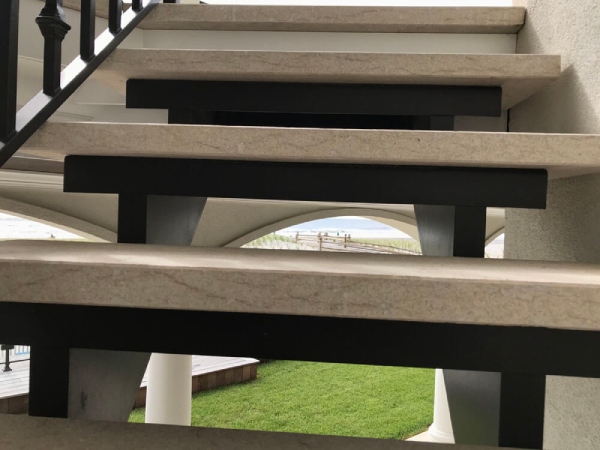
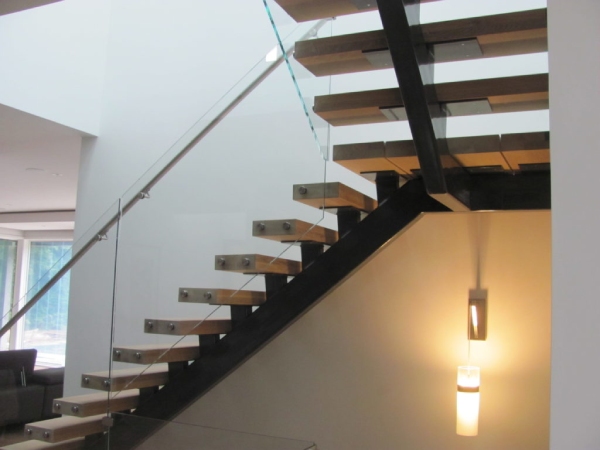




These were the four types of metal steps used in metal stairs. Now, let us look at how the components of steps, i.e., the tread and risers are connected.
B. Tread and Riser Connections:
Depending on the type of metal step used in the metal stair, a different type of tread and riser connection can be used. We can even use this connection for the bracing of a metal stringer, and it can also provide diaphragm rigidity to the stairway and the metal landing of the metal stair.
There are mostly three types of connections used:
- Direct Welding
- Carrier Angle or Plate
- Other Connection Options
Let’s see which type of connection is suitable for various types of tread and riser combinations.
Direct Welding:
In this type of connection, there is direct welding between the treads, risers and metal stringers. Mostly, this procedure takes place in the shops. Direct Welding connections are used are for the following combinations of tread and risers:
- Integral light gauge metal tread and riser
- Metal plate
Carrier Angle or Plate:
Carrier Angle or a plate is an alternative to direct welding. In this type of connection, there is welding between carrier angle/plate and stringers. Then the carrier angle or a plate supports the tread. Various uses of Carrier Angle or plate connection is used for following combination of tread and riser:
- Integral light gauge metal tread and riser
- Metal plate
- Some Non-Metal options for treads and risers
Other Connection Options:
We can directly bolt some tread options, like grating treads, to the metal stringers.
02. Metal Stringers
Metal stringers are that part of a metal stair that spans from the lower floor to the upper floor to provide support to the treads and risers. A majority of the times, steel stair stringers are used because of their properties, as discussed earlier in the article. The various types of metal stringers used in metal stairs are:
a) Plate Stringer
b) Saw-tooth Stringer
c) Double Plate or H Stringer
d) Channel Stringer
e) Box Stringer
Let us have a quick look at these types of stringers.
a) Plate Stringer:
Plate stringers either utilize the standard flat bar steel sections or a profile cut in the required size and shape from a metal plate.
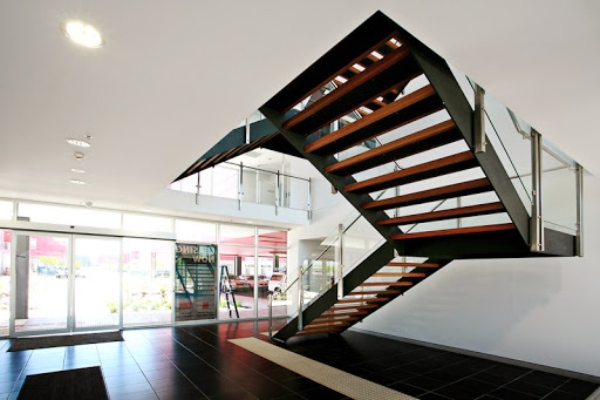

b) Saw-tooth Stringer:
Saw-tooth stringer is a type of plate stringer that gets cut from a metal plate as per the shape and size required.
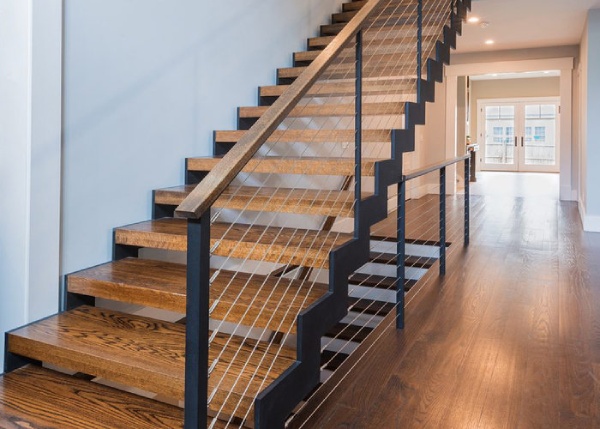

c) Double Plate or H Stringer:
Double plate or H stringer is another type of plate stringer where there is a use of two metal plates with a continuous pocket between both the plates for grouting a glass pane.
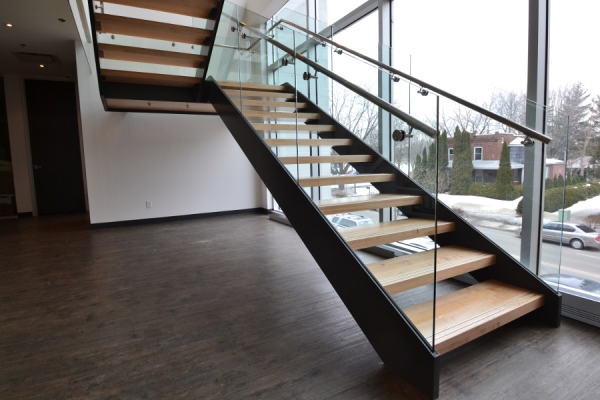

d) Channel Stringer:
Channel stringer is a prevalent and robust design that is either kept exposed or plated to form a hollow section.
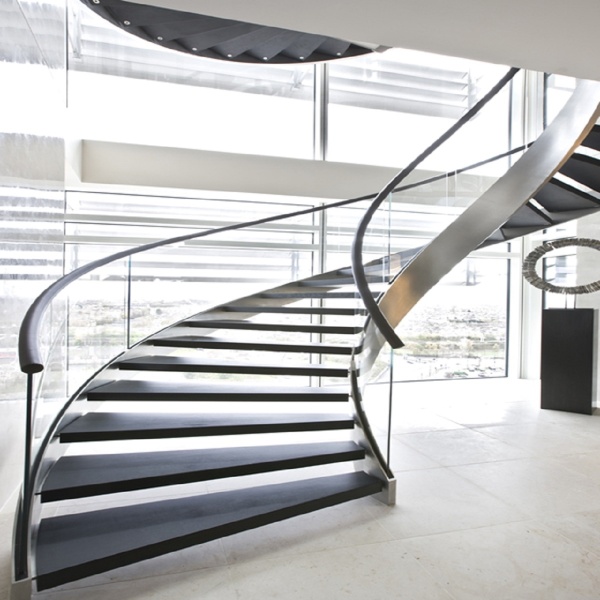

e) Box Stringer:
Box stringer is also a popular and robust design available in either square or rectangular shape.
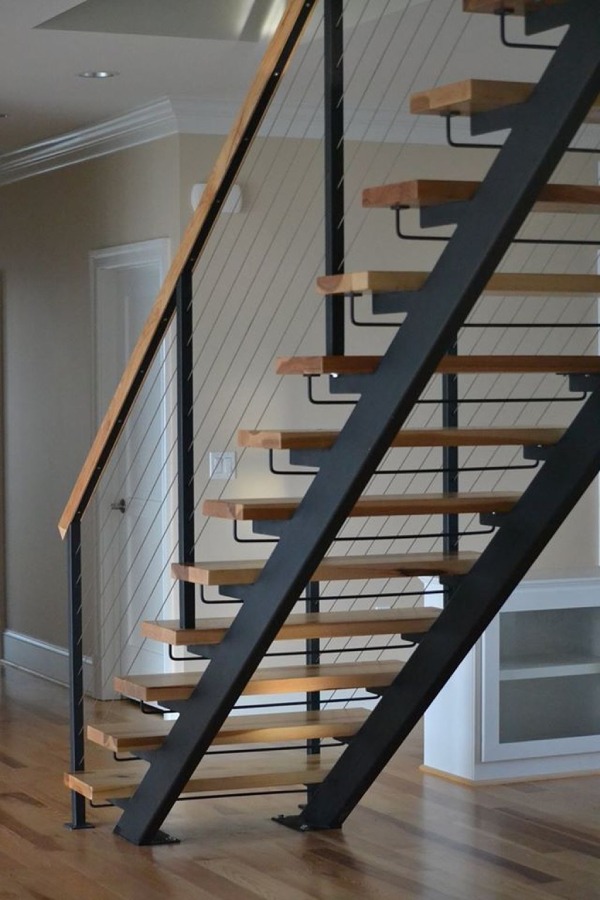

03. Metal Landing
Metal landing serves as a resting area for a user while ascending or descending a stairway. The classifications of metal landings as per the architectural requirements are:
a) Cast-in-place concrete over the metal deck on the landing steel framing
b) Cast-in-place concrete over the stiffened plate on the landing steel framing
c) Landing with chequered plate flooring on landing steel framing
d) Landing with steel grating on landing steel framing
e) Landing with any pre-cast, masonry or non-steel flooring on landing steel framing
Now that we have seen the major components of a metal stair, let us take a look at its various types
Types of Metal Stairs
Let us divide the metal stairs into two major categories depending on their use in a residence:
Case 1: Types of metal stairs based on functional requirement
Case 2: Types of metal stairs based on on-going trends
Case 1: Types of metal stairs based on functional requirement
Depending on the access to the required spaces on upper floors, metal stairs can be classified based on the functional requirements of the spaces. So, let us have a quick look at the types of metal stairs based on their functional requirement.
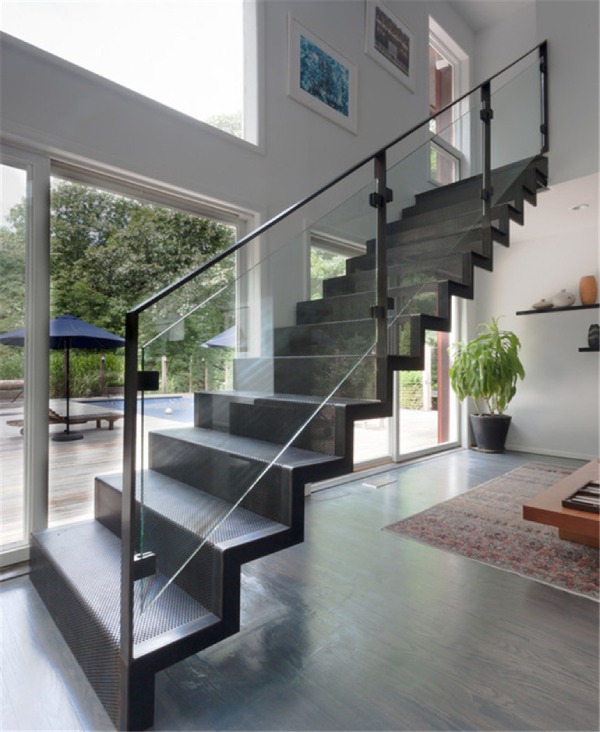
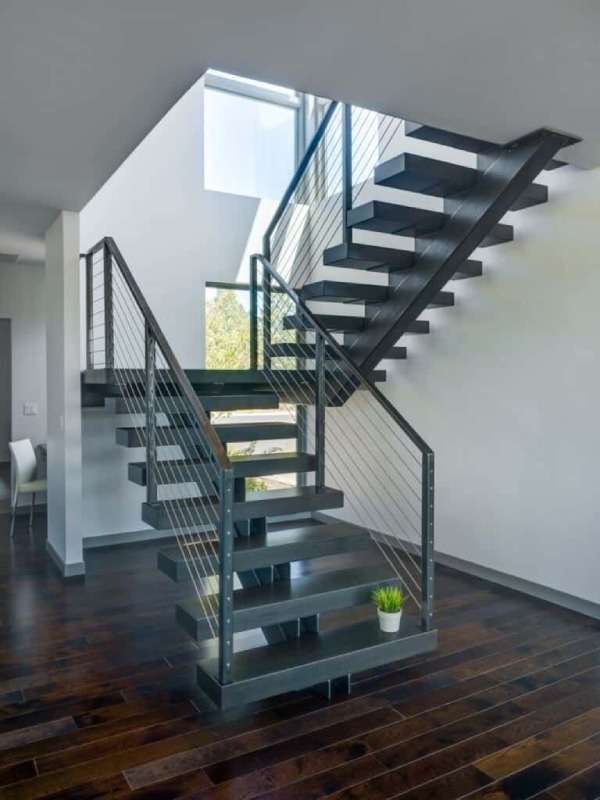
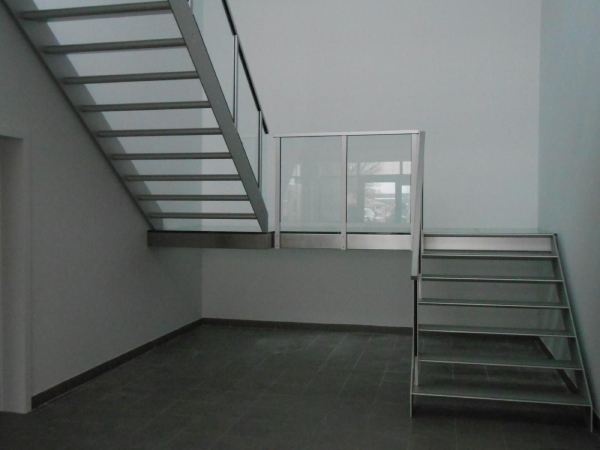
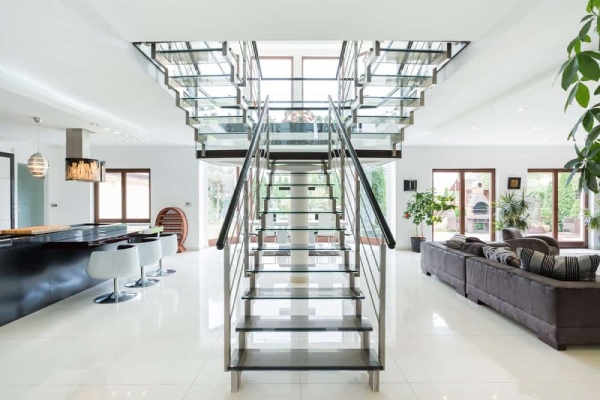
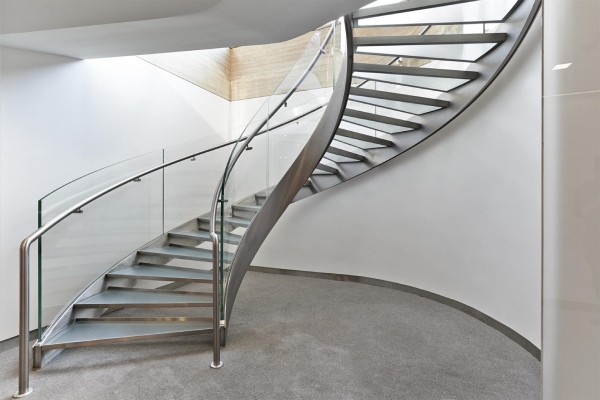
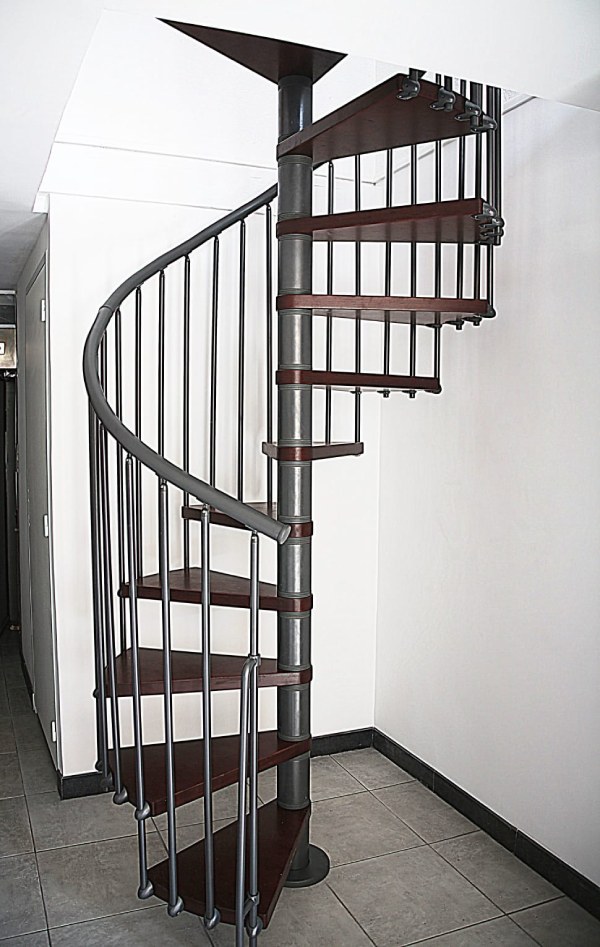
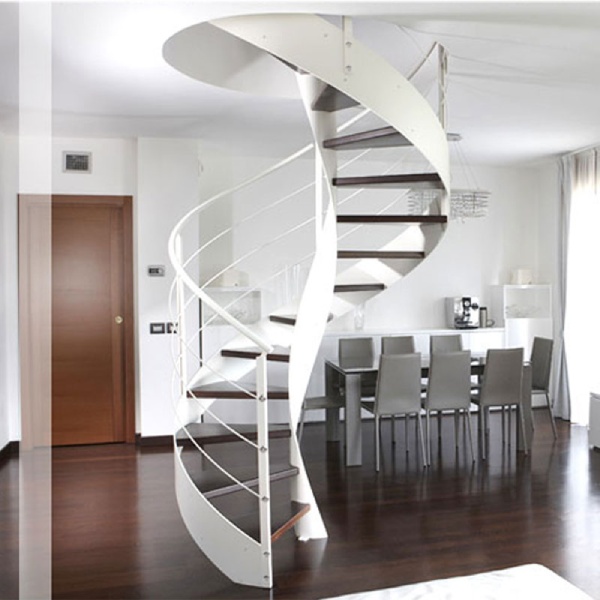








Case 2: Types of metal stairs based on on-going trends
It is essential to know about all the new trends especially in the design industry and many clients like to have trendy things in their homes. So, let us have a look at the modern and trendy designs of metal stairs.
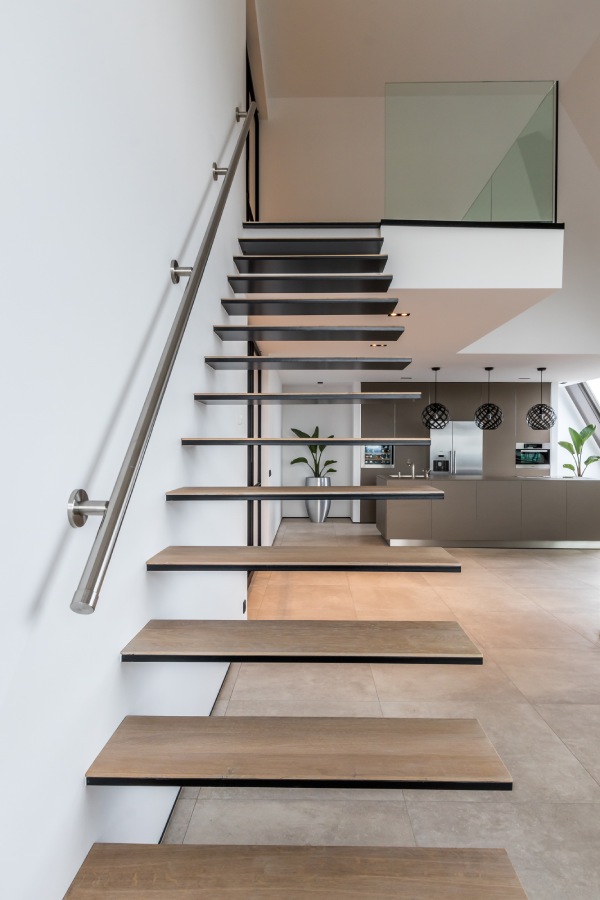
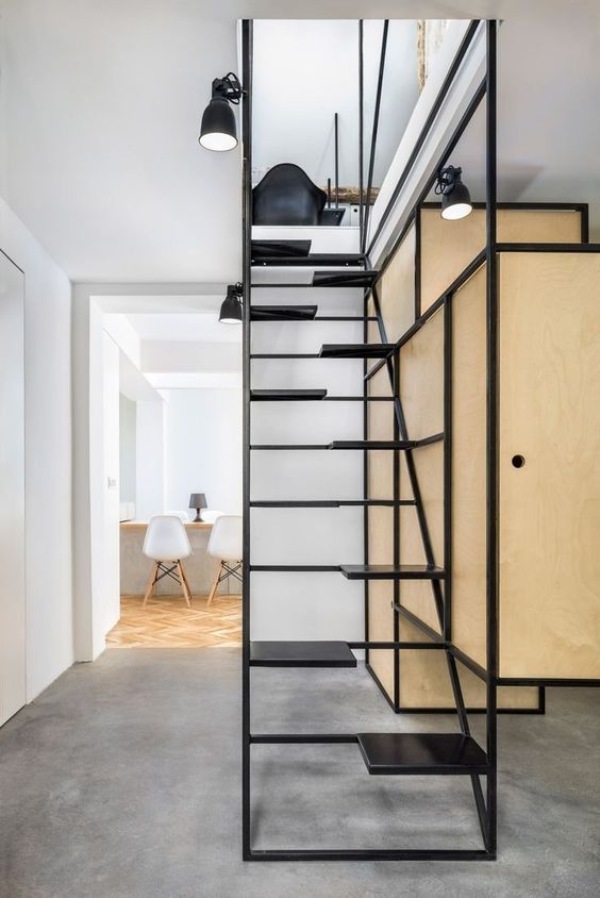
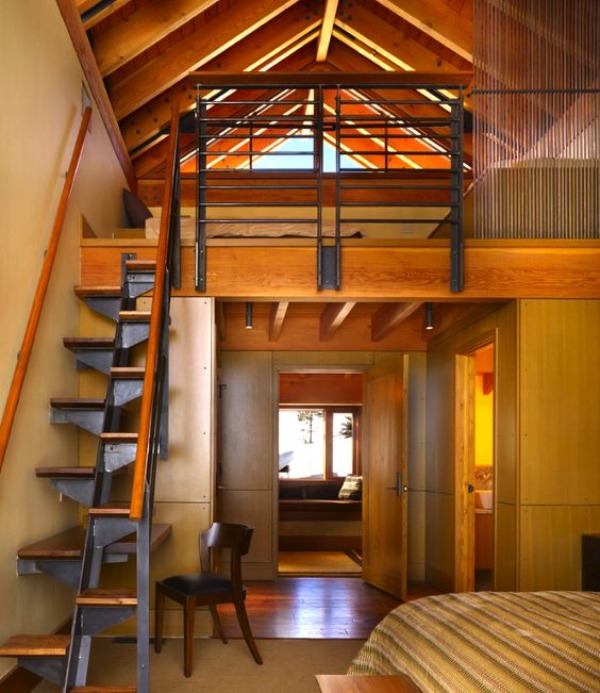
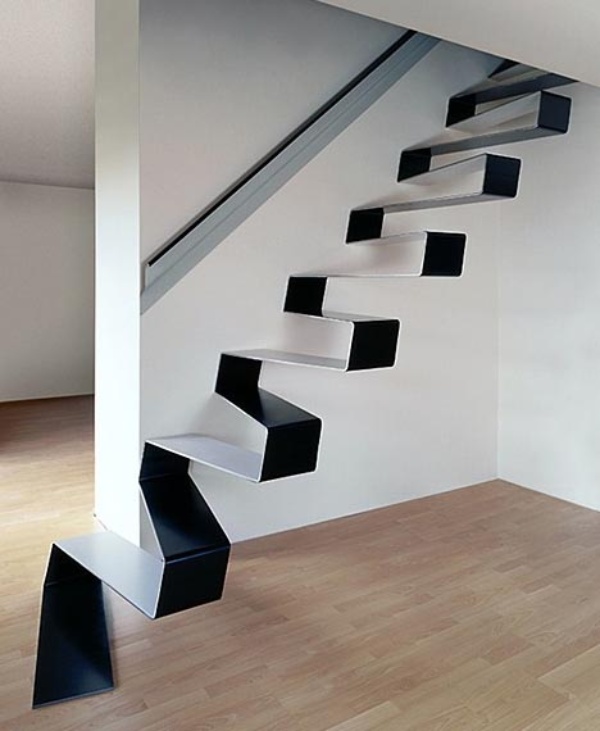
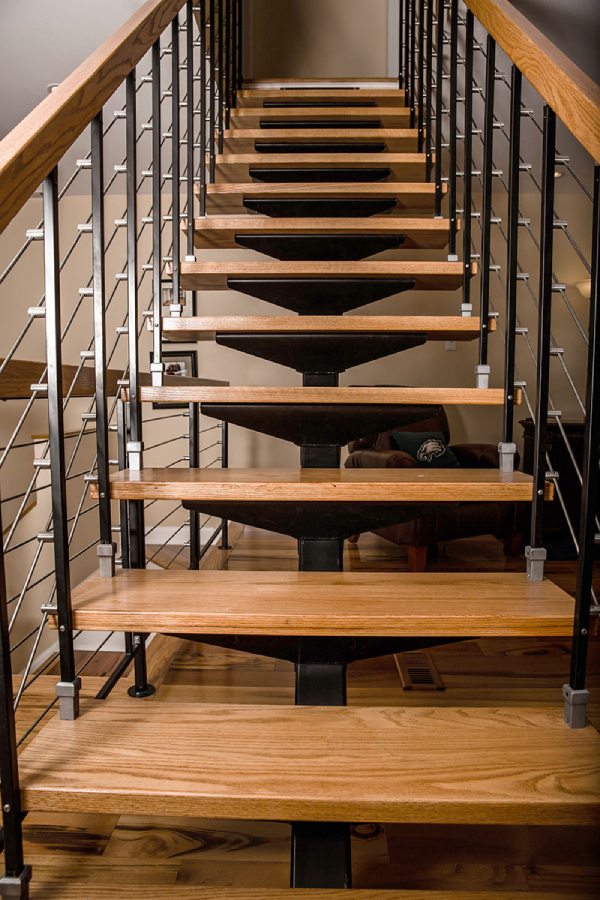








Non-metal Materials Used in Construction of Metal Stairs
So far, we have gone through the basic introduction to metal stairs, various types of metals used for the construction of metal stairs, major components of the stairs, and multiple types of metal stairs based on different criteria.
However, let us keep in mind that even some non-metal materials can be incorporated in metal stairs to increase its attractiveness and elegance. Now, let us get familiar with the various non-metal materials and how they enhance the attractiveness and beauty of metal stairs.
For the construction of stairs in different shapes and styles, the non-metal materials in the fabrication of metal stairs are:
01. Glass
02. Wood
03. Stone
Let’s have a closer look at these non-metal materials.
01. Glass
We can use glass in the railing, treads, and risers of a metal stair for an elegant look.
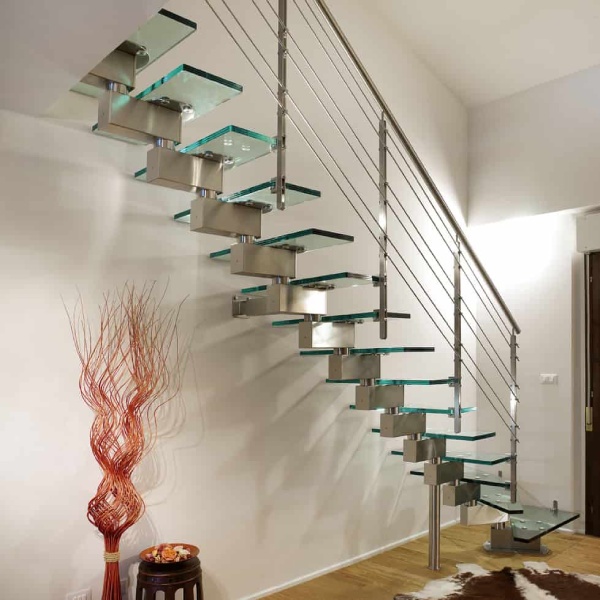
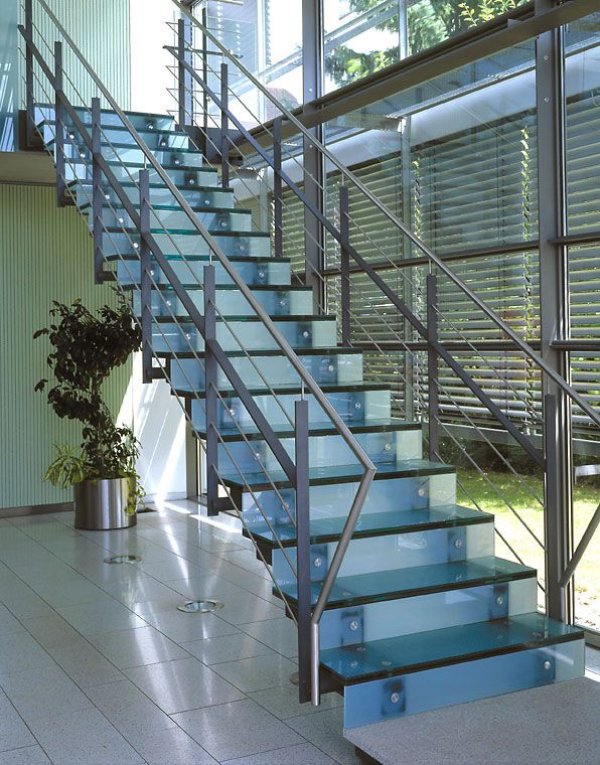



02. Wood
Wood can be used as a step and railing for an attractive look.
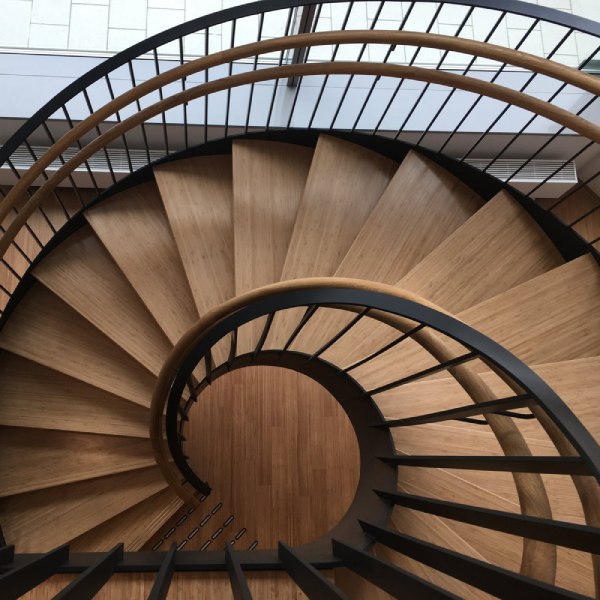
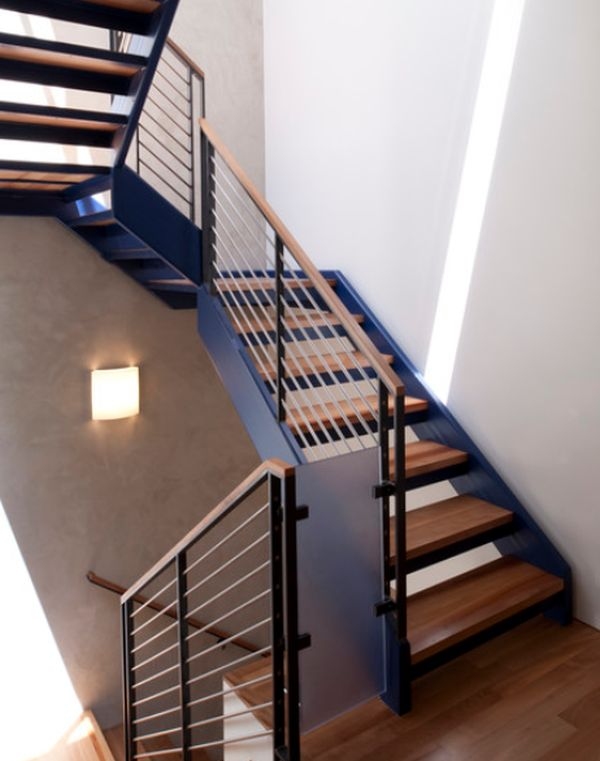
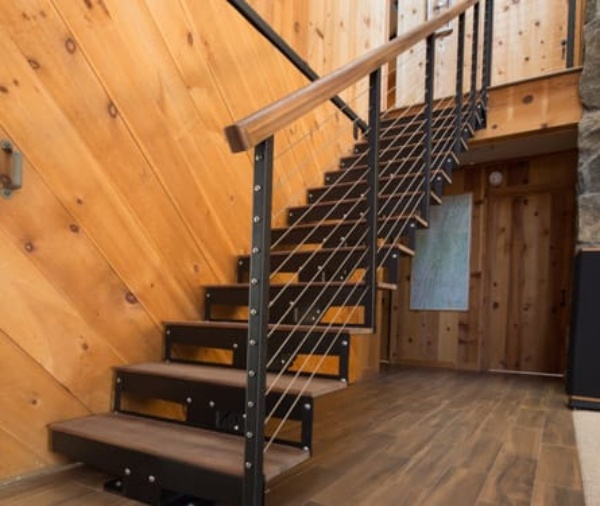



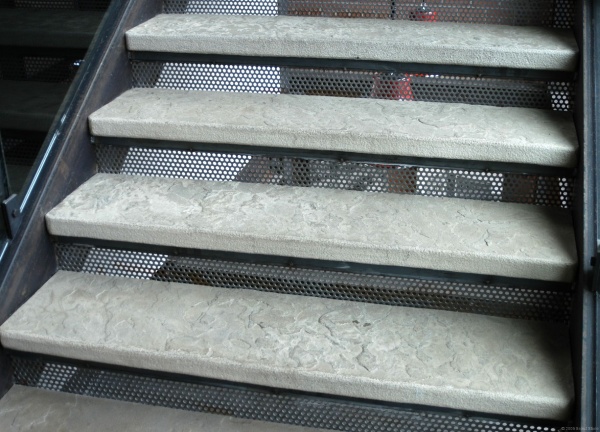
03. Stone
We can utilize stone as a step to make the metal star trendy and attractive.


Let us get into the pros and cons of metal stairs to decide whether or not we should opt for them in our house.
Advantages of a Metal Stair
01. Metal stairs are very easy to maintain.
02. Metal stairs can be customized in different shapes, styles, and designs that make the space look more versatile.
03. Metal stairs won’t require a lot of structural reorganization, thus, it can be installed easily on the site.
04. Metal stairs are sturdy enough that it can withstand any environment.
05. They are more durable than wood (mostly when the stairs are situated in direct contact with the environment, i.e. outdoors).
06. Metal stairs are pest and insect resistant.
07. Metals like steel, aluminum etc. can even be recycled, which would indirectly reduce the adverse effects on the environment.
Disadvantages of a Metal Stair
01. There is a chance of metal stairs rusting if a rust-free metal is not used for the fabrication or if good quality paint is not applied.
02. Metal stairs are less attractive compared to wooden stairs, as the latter are more eye-catching.
03. Metal stairs are heavy and as a result, increases the dead load.
04. Unlike wooden stairs, components cannot be adjusted as per the size constraints at the site. The only way to fit a metal stair perfectly at the desired place on the site is by measuring the staircase components precisely before its fabrication.
05. If the metal is not readily available in the particular area, the transportation costs will increase.
Conclusion
While metal stairs can be one of the most elegant structures in your house, there are a lot of things one must consider before opting for one. To get the perfect metal stair, care must be taken while deciding the proper metal and the appropriate type of metal stair as per the theme of your house.
Image Courtesy: Image 1, Image 2, Image 3, Image 4, Image 5, Image 6, Image 7, Image 8, Image 9, Image 10, Image 11, Image 12, Image 13, Image 14, Image 16, Image 17, Image 18, Image 19, Image 20, Image 21, Image 22, Image 23, Image 24, Image 25, Image 26, Image 27, Image 29, Image 30, Image 31, Image 33, Image 34, Image 36, Image 37, Image 38, Image 40, Image 41, Image 42, Image 43, Image 44, Image 45, Image 47, Image 49, Image 50, Image 51, Image 52, Image 53, Image 54, Image 55, Image 56, Image 57, Image 58, Image 59, Image 60, Image 61, Image 62, Image 63, Image 64, Image 65, Image 67, Image 68, Image 69, Image 70, Image 71, Image 72, Image 73






























