Table of Contents
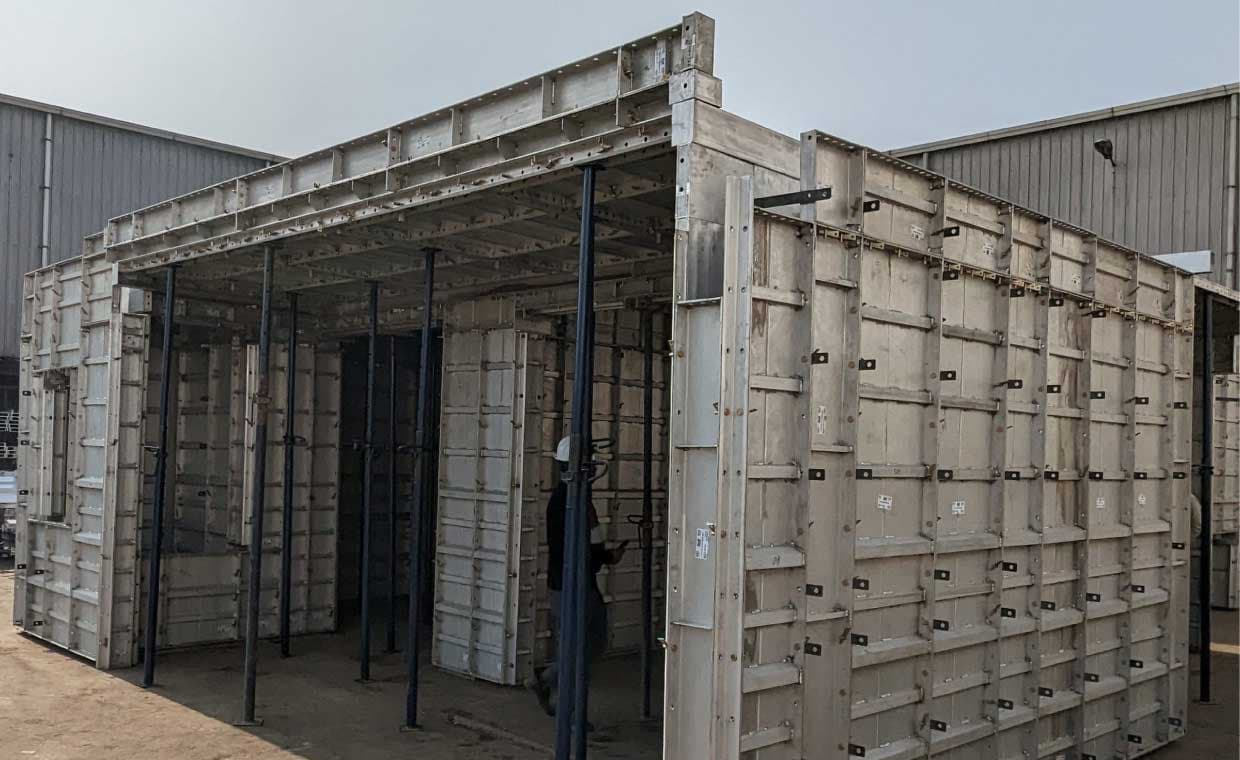
Mivan formwork, also known as aluminium formwork, is the advanced formwork system popularly used in construction. European building company developed this formwork system. In 1990, the Mivan construction business in Malaysia began producing these formwork systems. The Mivan technology widely used around the world, including European, Gulf, Asian countries and other regions. Using room-size forms, workers may quickly and efficiently build walls and slabs out of a single pour of concrete, speeding up the process of building many homes in a short amount of time.
This Mivan formwork is lightweight, and modular formwork system that can be easily assembled and disassembled on-site. It reduces construction time and costs, as it can be easily adjusted to fit the specific requirements of each project. Let’s understand Mivan formwork in detail.
Advantages of Mivan Formwork

There are several advantages to using Mivan formwork in construction projects:
1. Weight:
Mivan formwork is relatively lightweight so it is easy to handle.
2. Versatility:
Mivan formwork can be used for various applications, including walls, slabs, columns, beams, and staircases. It can be easily adapted to fit the specific requirements of each project because of its easily removable parts.
3. Durability:
Mivan formwork is made from high-quality aluminium, which is known for its durability and ability to withstand harsh weather conditions.
4. Speed of Construction:
Mivan formwork can be easily assembled and disassembled on-site, which helps to reduce construction time and costs.
5. Cost-effective:
Mivan formwork is a cost-effective formwork solution as it can be easily adjusted to fit the specific requirements of each project and can be reused on multiple projects.
6. Quality of Finish:
Mivan formwork produces a high-quality finish, as it allows for precise concrete placement and produces smooth and even surfaces.
7. Safety:
Mivan formwork is a safe solution, as it is lightweight and easy to handle, reducing the risk of accidents on site.
Disadvantages of Mivan Formwork

Some potential disadvantages of using Mivan formwork include the following:
1. Cost:
Mivan formwork can be more expensive than other types of formwork, such as wood or steel, due to the cost of the materials and the specialized equipment required for its use. Also, cost-effectiveness depends on the regular upkeep of the layout and the elevation.
2. Complexity:
Mivan formwork requires a high level of precision and specialized equipment, making it more complex and time-consuming. Due to the box-type structure, shrinkage cracks can appear.
3. Limited to Certain Types of Buildings:
The Mivan formwork is mostly used in high-rise buildings and large projects. It is not suitable for smaller or more complex structures.
4. Required Skilled Labour:
Mivan formwork requires skilled labour for proper installation, which is difficult to find and increases labour cost.
Components of Mivan Formwork
The main components of Mivan formwork systems typically include the following:
1. Aluminium Panels
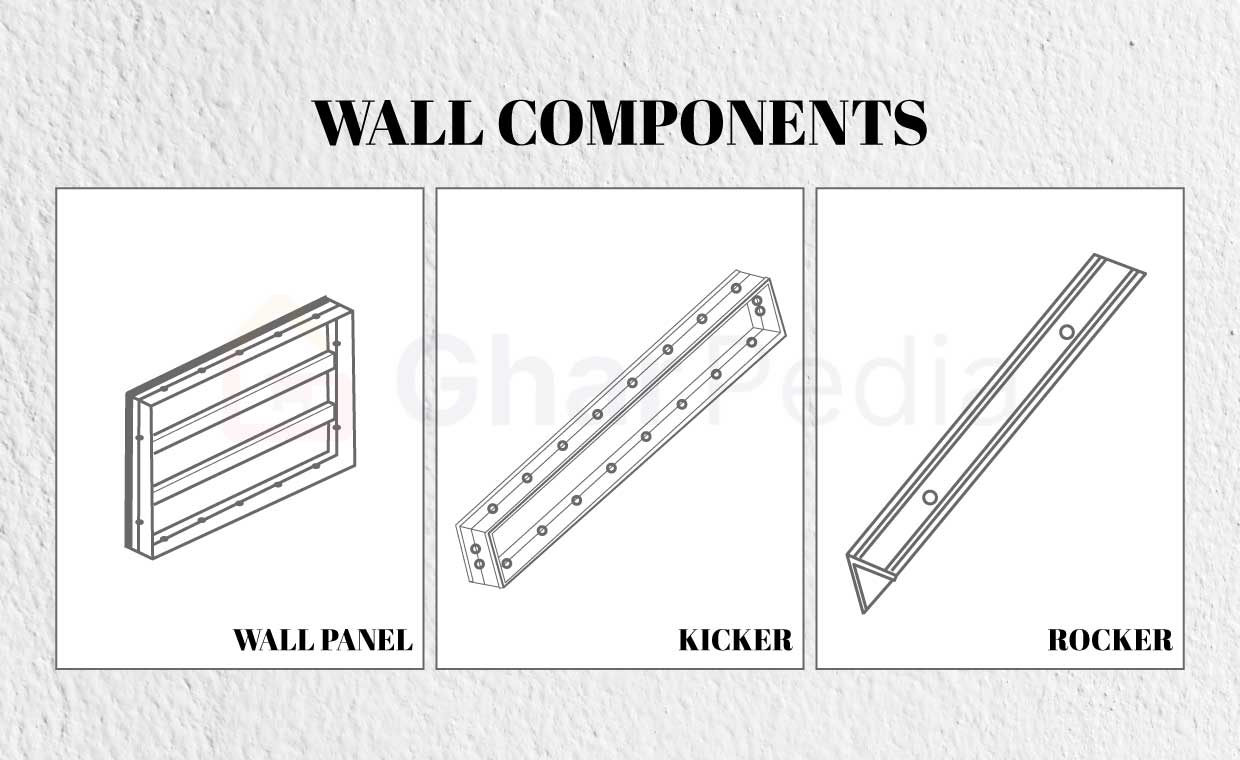
Aluminium panels are the main structural components of the formwork and are used to create the desired shape and size of the concrete structure. There are four subcategories of this:
- Rocker: A rocker is an L-shaped panel with stub pin holes that hold up the walls.
- Kickers: It forms a wall face at the panel’s top, serving as a ledge to hold the panel.
- Stub Pin: It connects the various building materials that make up a wall.
2. Aluminium Beams
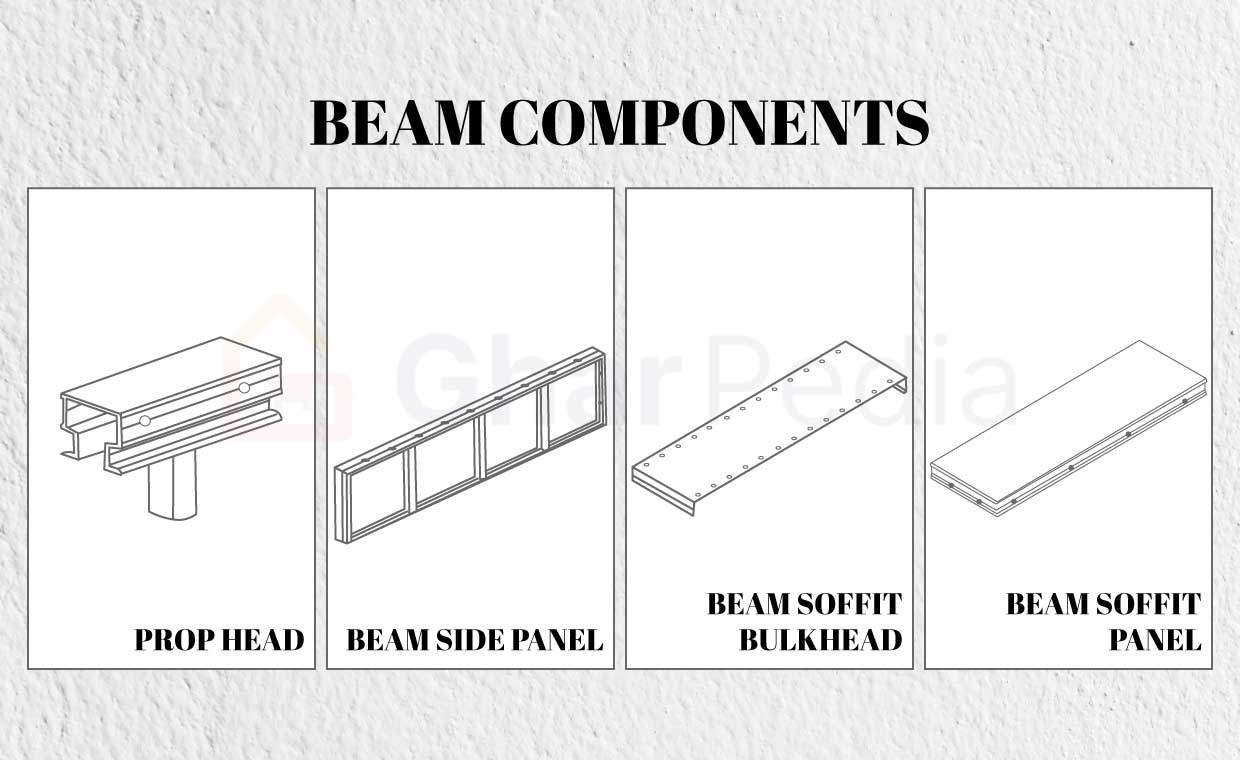
Aluminium beams are used to support the panels and create the framework of the formwork. It has several components:
- Beam Side Panel: Panels used to form beam sides are typically cut to a rectangular shape.
- Beam-Prop-Head: It’s V form ensures that the beam will be properly supported.
- Soffit Beam Panel: It is typically positioned atop the prop head to provide stability for the soffit beam.
3. Deck Components
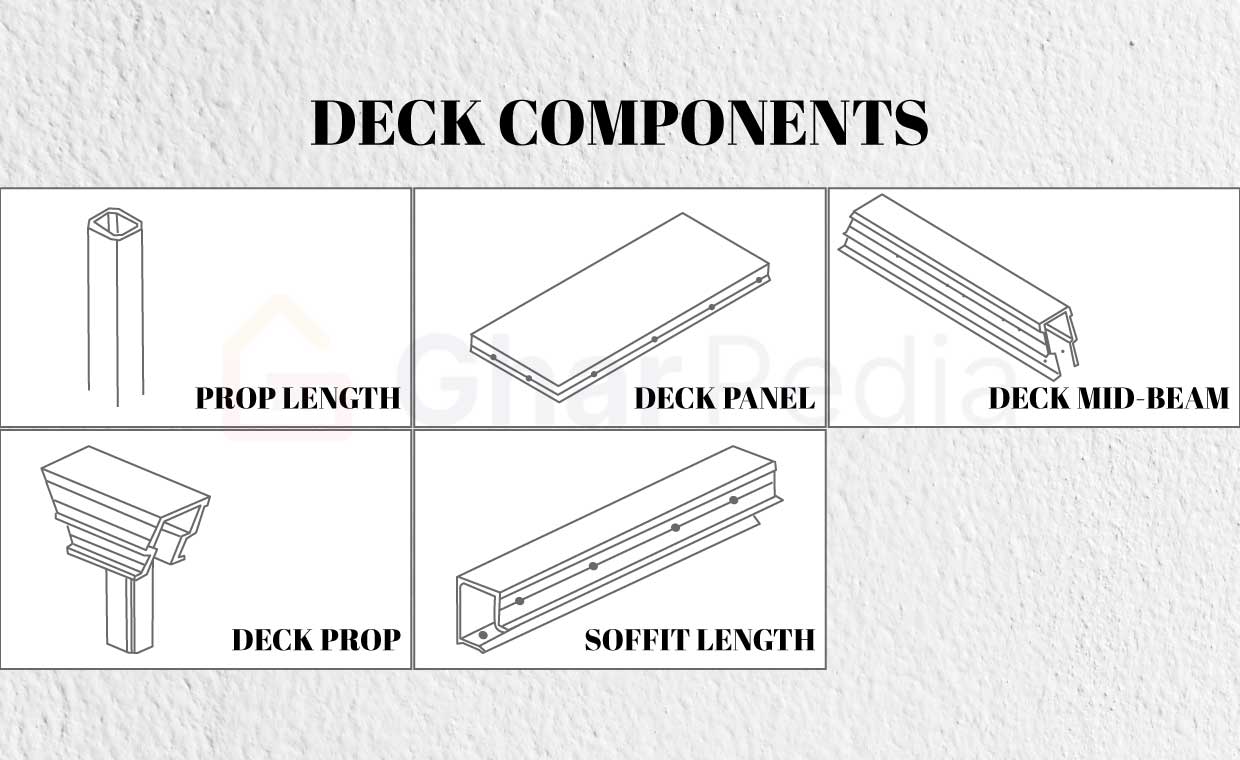
The slab is cast using a horizontal flat box called a deck panel. It consists of:
- Decking Panels: The slab is laid out on a horizontal level surface.
- Deck Prop: The slab is supported by the deck prop, which is the same as the beam deck prop, and the deck panel is the one that takes the load.
- Soffit Length: The length of the soffit is typically used for the necessary support for the deck panel as per the room’s perimeter.
4. Connectors
Connectors are used to fasten the panels and beams together to create a stable, self-supporting structure.
5. Fixing Systems
Fixing Systems are used to secure the formwork to the foundation or supporting structure and may include screws, bolts, or other types of fasteners.
6. Accessories
Mivan formwork systems may also include various accessories, such as panel edge profiles, formwork ties, and corner brackets, to help create a secure and stable formwork structure.
Process of Implementation of Mivan Formwork
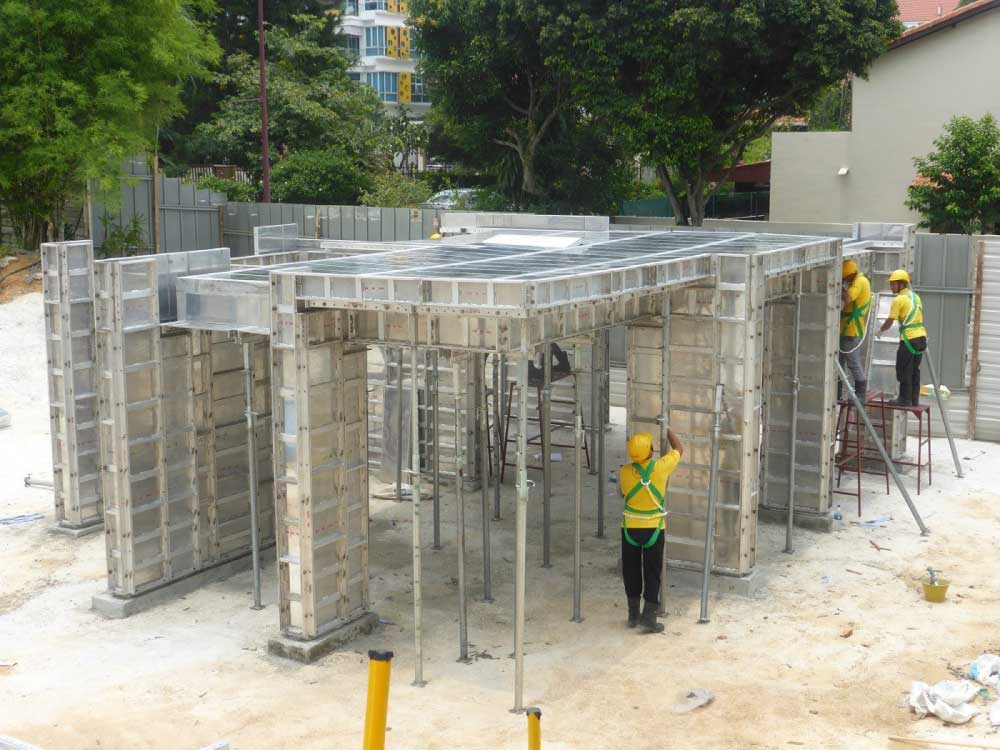

The process of implementing Mivan formwork, or aluminium formwork typically involves the following steps:
1. Planning and Design
The formwork design and layout must be carefully planned in advance to ensure that it meets the requirements of the project. This may involve creating detailed drawings and working with the project team to determine the size, shape, and configuration of the formwork.
2. Material Procurement
The necessary materials and equipment must be procured, including the aluminium panels, beams, connectors, and fixing systems.
3. Pre-assembly
The formwork panels and beams may be pre-assembled in a factory or on-site to reduce construction time. Like the precast concrete, the steel mesh is created at the factory to fit the dimensions of the building precisely. When the steel mesh is finished, it is transported to the construction site and installed. This is put up to support the building’s framework and hold the concrete in place until it reaches 50% of its final strength. The steel mesh is prefabricated in a factory, and the aluminium formwork is erected on the spot.
4. Setting up the Formwork
The formwork is then set up on the construction site, following the plans and drawings that were created in the planning and design phase. This may involve attaching the panels and beams to the foundation or supporting structure using the fixing systems. Room-sized walls and framed floor slabs are constructed alongside wall-reinforcing steel. Aluminium metal slabs are lightweight, easy to work with, and precisely manufactured. These are joined using a pin and spearhead technique and can be destroyed immediately once the concrete structure is set. The shuttering plates or forms are set in place once the steel mesh has been set up. These shutters also come with precut holes for doors and windows.
5. Concrete Pouring
Once the formwork is secured in place, the concrete can be poured and allowed to cure. After the cast has been removed, a hard-concrete building with steel rebar reinforcing the walls will be constructed in its place. Because these aluminium frames can be used repeatedly, we can keep construction site waste to a minimum.
6. Stripping and Cleaning
After the concrete has cured, the formwork can be stripped or removed, and the surface can be cleaned and finished as needed.
7. Reuse or Disposal
When the concrete has reached the desired strength and rigidity, the formwork can be deshuttered. The formwork panels and beams may be reused on future projects if they are in good condition or disposed of if they are no longer usable.
Future Scope of Mivan Formwork
Some potential areas of future development for Mivan formwork include:
1. Improved Efficiency
There may be opportunities to develop new technologies or techniques that make it easier and faster to set up and dismantle Mivan formwork, which could reduce labour costs and increase productivity.
2. Increased Versatility
Mivan formwork can create a wide range of structures, but there may be opportunities to develop new attachments or components that allow it to be used in even more applications.
3. Enhanced Safety
As with any construction method, safety is a major concern. There may be opportunities to develop new safety features or procedures for using Mivan formwork to reduce the risk of accidents on construction sites.
4. Greater Sustainability
Mivan formwork is already known for its durability and reusability, but there may be ways to further improve the system’s environmental footprint, such as using more sustainable materials or design changes that reduce waste.
5. Expanded Markets
Mivan formwork is already used in many countries worldwide, but there may be opportunities to expand into new markets or regions where the system has yet to be widely adopted.
Conclusion
A kind of aluminium formwork, Mivan formwork is used worldwide and has proved to be an economical to the traditional method of construction which is labour-intensive and time-consuming. Overall, Mivan formwork is a popular choice for many construction projects due to its many advantages and the potential for cost savings. So, the decision is yours on how you would like your house to be built.
Also Read: Aluminium in Construction: A Lightweight Revolution
FAQs
1. How Thick is Mivan Formwork?
A typical Mivan formwork panel is around 4mm thick and it is made up of high-strength aluminium alloy with a 4mm thick skin plate.
2. How Many Times We Can Use Mivan Shuttering?
You can use Mivan formwork 250 to 300 times.
3. Is Mivan Formwork better than RCC?
Despite initial higher costs, Mivan’s formwork efficiency, adaptability, and environmental benefits make it better alternative to RCC, emphasizing the evolving landscape of construction.
Author Bio
Nafisa Nazneen Choudhury – Nafisa Nazneen Choudhury is a Civil Engineer (completed B.E. from Assam Engineering College) and is currently pursuing M.Tech in Structural Engineering at National Institute of Technology, Silchar. She is a Technical Content Writer, having over 3 years of experience and has wrote many articles related to Civil Engineering. She is also a Book Author (Authored – “Dream Tales of NNC: Revenge By Murder”) and her book can be found on Amazon. She is also a Guest Author at Gharpedia. Moreover, she is a certified member at Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE) and National Society of Professional Engineers (NSPE). She writes her blogs at her website – nnc2017.wordpress.com. She can be reached on LinkedIn.






























