Concrete is one of the most versatile construction materials throughout the world. However, since the early 1800s, it is known that concrete is weak in tension. Weak tensile strength combined with the brittle behaviour of concrete results in the tensile failure without warning.
This is not desirable for any construction material. Thus, concrete requires some form of tensile strength to complement its brittle behaviour.
Historically, Steel has proved to be an ideal material as a Steel Reinforcement to complement concrete because the thermal expansion of both materials is the same. In other words, when cooled or heated both concrete and steel they expand or contract equally.
Steel also bonds well with concrete. In a composite material, the bond between two materials is necessary so that it functions as a single material. The bond between the two materials is due to the chemistry of the two materials, which produces a chemical bond between them. Besides, as the water from concrete evaporates, it shrinks and grips the steel bars also making a mechanical bond.
According to ‘Madan Mehta’, ‘Walter Scarborough’ and ‘Diane Armpriest’ (Authors of Building Construction), the mechanical bond is enhanced by using reinforcing bars or rebars that have surface deformations. Because a mechanical bond is a function of the area of contact between the two materials, the surface deformations increase such area over and above increasing friction between the two, thereby increasing the bond.
To know the various types of Steel Reinforcement, first, let us understand what is Steel Reinforcement?
Steel Reinforcement
Steel Reinforcement is in the form of rebar or wire of steel, which is utilized in concrete members to resist primarily tensile forces caused by externally applied loads or volume changes.
In Concrete steel is embedded in such a manner that the two materials act together in resisting forces. The reinforcing steel-rods, bars, or mesh-absorbs the tensile, shear, and sometimes the compressive stresses in a concrete structure. Plain concrete does not easily withstand tensile and shear stresses caused by wind, earthquakes, vibrations and other forces and is therefore unsuitable in most structural applications.
The most common types of Reinforcement are Plain & Deformed Reinforcing bars, Prestressing Steel and wire reinforcement made of steel.
Steel Reinforcement Types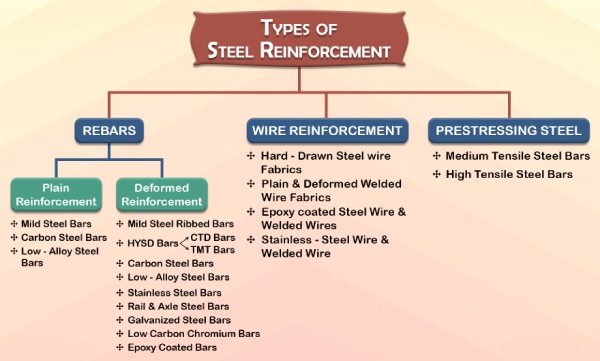
Steel Reinforcement Types & Classification
(a) Rebar
Rebar is a round bar or a finished product rolled to close tolerances and called reinforcing bar.
The types of steel bars used in construction are Plain & deformed reinforcement bars, ribbed bars, HYSD Bars, Carbon Steel Bars, Low alloy steel bars, Stainless steel bars, Rail & Axle steel bars, Galvanized steel bars, Low-carbon chromium bars and Epoxy coated bars etc.
01. Plain Reinforcement

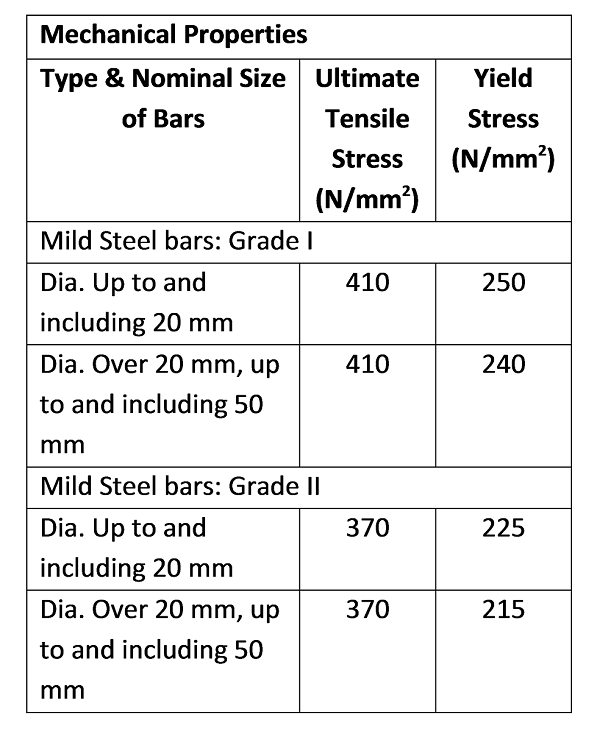
1.1 Mild Steel Bars
- The steel in use till these days for construction purposes was Plain mild steel bars. As per IS 432 (PART – I), It is designated as Fe-250 (Where 250 = 0.2 % Proof Stress or Yield Stress in N/mm2).
- Nowadays, it is used only for small projects in underdeveloped and developing countries.
- According to ‘S. K. Duggal’ (Author of Building Materials), mild steel reinforcement has proved to be a better choice for impact and suddenly applied loads.
- A few other types of plain Rebars are Carbon steel plain bars and Low-Alloy steel plain bars conforms to the ASTMA615/A615M and ASTM A706/A706M respectively.
02. Deformed Reinforcement
Deformed reinforcements are steel rebar or steel wire having deformation on the surface. The purpose of the deformations commonly referred to as ribs are to enhance the bond and friction between the concrete and the bar or wire.
The types of deformed steel bars used as reinforcement are Mild Steel Ribbed bars, HYSD bars, Carbon Steel bars, Low-Alloy Steel bars, Stainless Steel bars, Rail & Axle Steel bars, Galvanized steel bars, Low carbon chromium bars, Epoxy coated bars etc.

2.1 Mild Steel Ribbed Bars
- For preventing ‘slip’ and improving the mechanical bonding between steel rebar and cement concrete, mild steel ribbed bars were developed and introduced around 1960.
- These are the hot rolled mild steel bars, but during rolling steel rods, ribs are produced on them. These ribs increase the bonding strength of the bars.
- Mild steel ribbed bars are not recommended by the Indian Standard Code or even American Society of Testing & Materials (ASTM).
- At the time of the introduction of mild steel ribbed bars, there was no specific patterns of ribs described. Rolling mills in different countries followed different patterns of rib.
2.2 High Yield Strength Deformed Bars (HYSD Bars) Conforming to IS 1786: 2008
- High Yield Strength Deformed Steel Bars were introduced in India in 1967. They completely replaced mild steel bars except in a few situations.
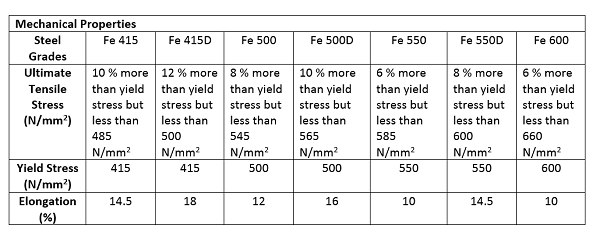
- As per IS 1786 High Yield Strength Deformed Steel Bars are used as reinforcement in concrete in the following rebar steel grades:
(i) Fe 415, Fe 415D
(ii) Fe 500, Fe 500D
(iii) Fe 550, Fe 550D
(iv) Fe 600
(Figure after Fe indicate as 0.2% proof Stress or Yield Stress in N/mm2& D indicates that it is more Ductile)
- High Yield Strength Deformed Rebar has lugs, ribs or deformation on the surface which inhibit longitudinal movement of the bars relative to the surrounding concrete. Thus, the deformed surface ensures a better bond between reinforcement and concrete.
- These bars results in a considerable increase in yield, tensile and bond strength when twisted hot or cold.
- Generally, the higher strength in steel can be obtained by increasing carbon content, Microalloying, Cold twisting or thermomechanical Treatment. In India, the TMT Process and Cold Twisting are used in the production of High Yield Strength Deformed Steel Bars.
From the above grade of steel bars, the D after figure indicated Ductile Bars. Ductile bars are usually used when buildings are constructed for better seismic performance and Earthquake resistant.
They are generally preferred and used in Zone IV & V, i.e. zone likely to have an earthquake. Higher the ductility, deformations without collapse/ failure.
2.2.1 Cold Twisted Deformed Bars (CTD Bars)

- The process of cold working involves stretching and twisting of mild steel beyond yield plateau to obtain cold twisted deformed bars.
- Drawbacks of Cold Twisted Deformed Bars are that there are surface stress and visible cracks due to cold twisting which leads to higher corrosion rate and durability problems. Therefore, most of the European countries gave up the use of Cold Twisted Deformed Bars within a few years of its making.
- However, in India CTD Bars were commonly used up to 1992. Cold Twisted Deformed Bars (CTD Bars) were sold in India under the brand name “TOR STEEL”.
2.2.2 Thermo Mechanically Twisted Bars (TMT Bars)
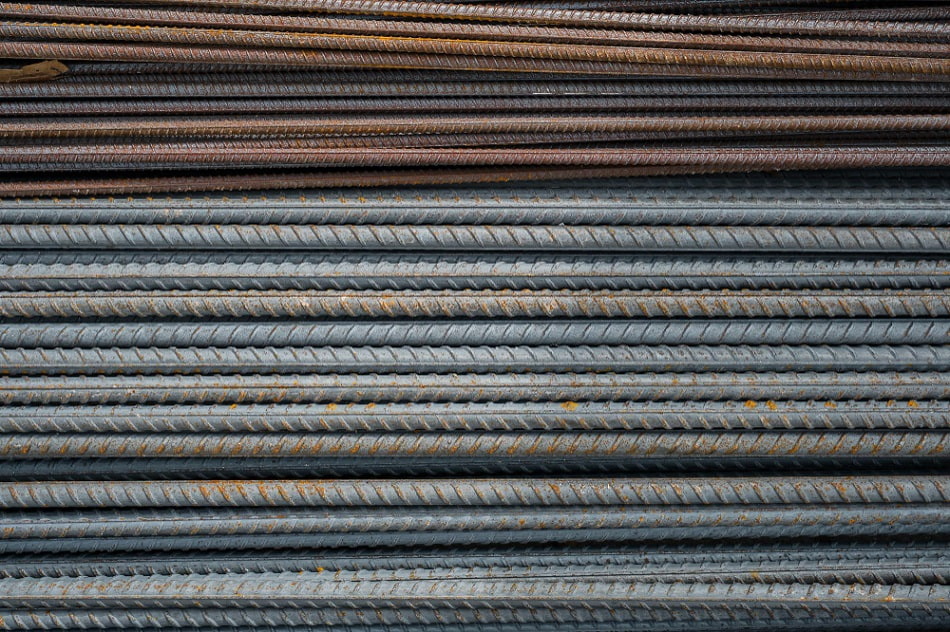

- The other method uses is a thermo – mechanical Treatment (TMT) Process in which red hot rebars are quenched through a series of water jets causing a hardened outer layer surrounding a softer core.
- Thus Resulting rebars have higher yield strength than mild steel and is characterized with definite Yield Point, Superior ductility, Weldability and bendability.
- Thermo – Mechanically Treated Bars (TMT Bars) are produced in various grades by Steel Authority of India Ltd. (SAIL) and TATA Steel. The trade names of these bars are known as SAIL – TMT and TISCON – TMT respectively.
- Thermo – Mechanically Treated Bars (TMT Bars) are nowadays a fundamental requirement for construction in India.
- TMT Bars have improved properties such as yield strength, ductility, toughness and corrosion resistance.
- TMT Bars have high resistance to seismic loads due to its higher ductility. These make them as most suitable for use in earthquake- prone areas.
- With the improved properties, TMT Bars are economical and safe for use. Hence it is widely used as a reinforcement for the construction of roads, Buildings, Bridges etc. TMT Bars are recommended for use in high – rise buildings because of saving in steel due to higher Strength.
2.2.2.1 Corrosion Resistant Rebar:
- The latest development of reinforcing bar are the thermo – mechanically treated high – strength corrosion resistant (TMT – HCR) rebars.
- The TMT – HCR rebars have superior resistance to aggressive weather conditions. The chemistry of TMT – HCR rebar is appropriately designed for substantially reducing atmospheric and marine corrosion.
- TMT – HCR Rebar finds wide applications in different spheres including coastal and marine environments which are susceptible to corrosion, bridges, dams, industrial structures and high-rise buildings.
2.3 Deformed and Plain Carbon Steel Bars
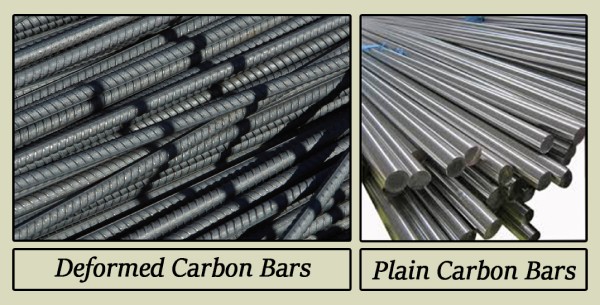
Deformed and Plain Carbon Steel Bars
- Carbon Steel Reinforcing bars conforming to the requirements of ASTM A615/A615M.
- Carbon Steel bars are the most commonly specified type of reinforcing bar and can be used in a wide variety of applications where there are no special performance requirements.
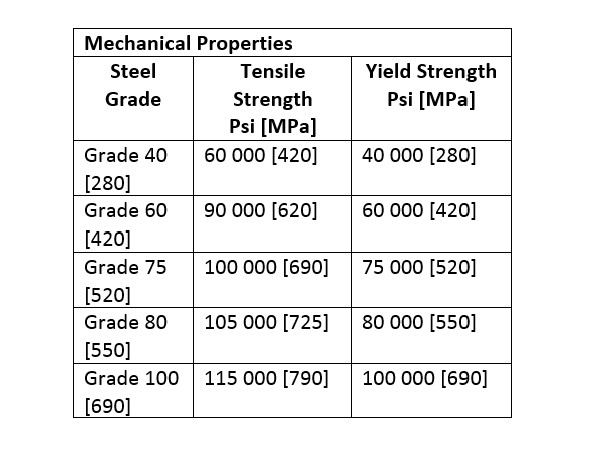
Bars are designed as per following rebar steel grades,
- 40 000 psi [280 MPa] or Grade 40 [280]
- 60 000 psi [420 MPa] or Grade 60 [420]
- 75 000 psi [520 MPa] or Grade 75 [520]
- 80 000 psi [550 MPa] or Grade 80 [550]
- 100 000 psi [690 MPa] or Grade 100 [690]
- It is rebar that is without anti- rust coating and has the lowest price compared to zinc coating and epoxy coating.
- Due to its price advantage, it is useful for building.
2.4 Low Alloy Steel Bars
- Low Alloy Steel Reinforcing bars conform to the requirements of ASTM A706/A706M.
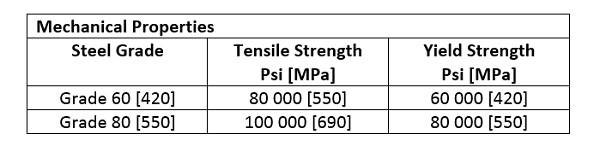
- These Bars are usually designated as Grade 60 [420] and Grade 80 [550] respectively.
- The bars shall be processed from properly identified heats of mold – Cast or Strand – Cast Steel.
- The Steel used in the production of these bars shall be made by the process of the electric – furnace, basic – oxygen or open – hearth.
- The low – alloy steel bars are specified in situations where enhanced weldability and ductility are needed.

2.5 Stainless Steel Bars
- Stainless Steel Bars have features of long – life cycles and long-term corrosion resistance property. Although it is the most expansive rebar, it has superior effectiveness of cost.
- The physical and mechanical properties of stainless-steel bars conform to ASTM A955/A955M-16 and are the same as those for carbon-steel bars conforming to ASTM A615.
2.6 Rail & Axle Steel Bars
According to A996/A996M – Standard Specification for Rail – Steel and Axle – Steel Deformed Bars for concrete reinforcement, these types of bars are designated with “R” for rail – steel and “A” for axle – steel.
Rail – Steel Bars are designated as the following rebar steel grades,
(a) 50 000 psi [350 MPa] or Grade 50 [350]
(b) 60 000 psi [420 MPa] or Grade 60 [420]
Axle – Steel Bars are designated as the following rebar steel grades,
(a) 40 000 psi [280 MPa] or Grade 40 [280]
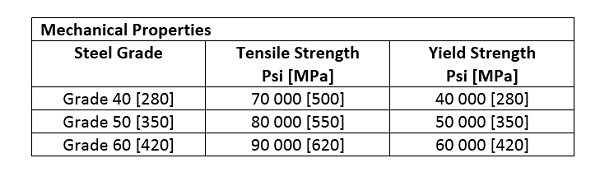
(b) 60 000 psi [420 MPa] or Grade 60 [420]

2.7 Galvanized Steel Bars
- Galvanized (Zinc – Coated) bars are obtained by dipping ASTM A615, ASTM A706 and ASTM 996 Bars in a molten bath of zinc in accordance with ASTM A767/A767M.
- It is normal black rebar with a layer of zinc coating, which can prevent the rebar from rusting and corrosion.
- According to the ‘Fahim Al – Neshawy’ (Scientist of Department of civil engineering in Aalto University, Finland), Owing to the property of zinc coating, it can be used in bridges.
2.8 Low – Carbon Chromium Bars
- Low-carbon chromium bars conforming to ASTM A1035/A1035M are permitted to be used only as spiral reinforcement or transverse reinforcement in columns.
- These limitations are imposed because the chromium steel used to manufacture reinforcing bars has low ductility and a relatively large minimum yield strength of 80,000 psi.
2.9 Epoxy Coated Bars

Deformed and Plain Epoxy-Coated Bars
- Epoxy-coated bars are manufactured in the following two ways.
- The first method, a protective epoxy coating is applied by the electrostatic spray method to ASTM A615, ASTM A706 and ASTM A996 in accordance with ASTM A775/A775M-07a. The bars are usually fabricated after the application of the epoxy coating.
- In the second method, ASTM A615, ASTM A706 and ASTM A996 bars are prefabricated and then coated with a protective fusion-bonded epoxy coating by electrostatic spray or other suitable methods in accordance with ASTM A934/A934M-07.
- According to the ‘DAVID P. GUSTAFSON’ (Technical Director of Concrete Reinforcing Steel Institute), Epoxy – Coated rebars are considered by many engineers to be one of the most effective and corrosion protection systems.
- Epoxy Coated bars were first used in bridge decks as early 1973 in Pennsylvania. Since then, the uses of Epoxy-coated bars have continually expanded.
- More states and government agencies are specifying coated bars in bridge decks and in other transportation structures.
- Epoxy – Coated bars are now used in parking garages, marine structures, water and wastewater treatment plants and other hydraulic structures.
(b) Wire Reinforcement
The various deformed wires that can be used as a steel reinforcement are hard-drawn steel wire fabrics, welded deformed wire fabrics, Epoxy coated steel wire and welded wire, Stainless steel wire and welded wire.
01. Hard – Drawn Steel Wire Fabrics Conforming to IS 1566: 1982
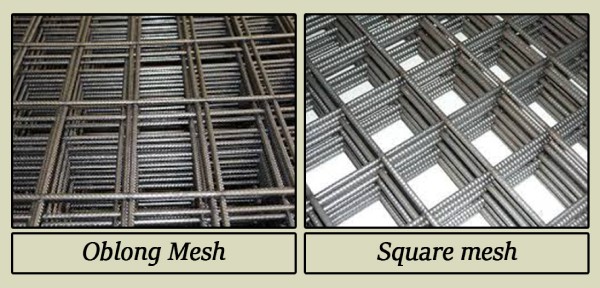
Hard-drawn Steel Wire Fabrics are made by a series of wires arranged at right angles to each other. According to IS 1566, There are two types of Hard-drawn Steel Wire Fabrics,
(i) Oblong Mesh
(ii) Square Mesh
- The wire shall be cold-drawn from mild steel made by a various process such as open hearth, electric duplex, acid Bessemer, basic oxygen or combination of them.
- According to IS 432 (PART II): 1982, the diameter of hard-drawn wire is 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm, 8 mm and 10 mm.
- Mesh sizes, Weight and size of wires for square and oblong welded wire fabric shall be as agreed to between the purchaser and manufacturer.
- The Specification of Steel Wire also available in ASTM A496/A496M-07.
02. Welded Deformed Wire Fabrics
- Welded Deformed wire is fabricated from a series of wires arranged at right angles to each other and welded at all intersection. It is much stronger than mild steel and available in different width rolls under ASTM A497/A497M-07.
- Also, Plain Welded wire fabrics are available which conforms to ASTM A496/A496M-07.
- Welded Wire fabrics are used for floor slabs on well-compacted ground, road and runway pavements, culverts and small canal linings.
Other types of wire which used as reinforcement are,
- Epoxy Coated Steel Wire and Welded Wires, which conforms to the ASTM A884/ A884M-06.
- Stainless-Steel Wire and Welded Wires, which conforms to the ASTM A1022/ A1022M-07.
(c) Prestressing Steel
- Prestressing Steel generally consists of wires, bars, strands or bundles of such elements.
- The Steel is stressed under high-tensile forces either before the concrete is cast (Pretensioned) or after the concrete is cast and has hardened (Posttensioned).
01. Medium Tensile Steel Bars
- The steel reinforcement having an ultimate tensile strength more than 540 N/mm2 is categorized as Medium tensile steel Bars.
- These types of rebars are used when concrete reinforcement requires strength more than that of Mild steel Bars.
02. High Tensile Steel Bars
- The steel reinforcement having an ultimate tensile strength in a higher range (1000 – 2200 N/mm2) is categorized as High Tensile Steel Bars.
These types of rebars are generally used in prestressed concrete construction.Structural Steel shapes are made out of the kind of steel, which is found out a precise cross-section, at the same time it follows definite standards for mechanical properties. It comes in various shapes like I-beam, Z shape, HSS shape, L shape structural channel, T shaped, Rail profile, Bar, Rod, Plate, Open joist of web steel etc.
Also Read:
What is the Difference Between Mild Steel and Stainless Steel?
Pros & Cons of Steel Reinforcement Bars
Conclusion
Summing up, Reinforced concrete is a composite material in which reinforcing bars or other types of steel reinforcement have been integrated to improve the properties of concrete.
Steel reinforcements are provided in Reinforced cement concrete (RCC) structure to resist tensile stresses. It has been utilized as an economical construction material in buildings, bridges and many other types of structures throughout the world. Steel Reinforcement is also an essential contributor towards cracks control of the concrete structure.
In addition to being readily available, reinforced concrete has been universally accepted because of its properties. Reinforced concrete structure are very durable and can also have a long life under severe climate or environmental conditions provided proper protection of the steel reinforcement is done.
Nowadays, Thermo – Mechanically Treated Bars (TMT Bars) are widely used steel reinforcement type in the construction of a houses. Galvanized reinforcing bars, epoxy-coated bars and wires, Stainless steel bars and wires are used in parking structures, bridges and other structures in highly corrosive environments where corrosion resistance of Steel Reinforcement is the main concern. However, they are costlier than TMT Bars.
Therefore, Reinforcement steel in reinforced concrete provides compatibility to the structures, the steel bars are robust in nature that they have the ability to withstand to rigors, the wear and tear during the construction activities. Reinforced steel is easily available and leftover after the service life of a structure can be recycled again and used for new construction (If not corroded).
Also Read:
8 Tips for You to Buy Steel Bars!
The Ultimate Guide to Steel Rebars Size and their Types
Image Courtesy: Image 6

