Building foundation is the part of the building which is in direct touch with the ground and which transmits loads of the superstructure to the supporting soil. Two basic types of foundation are the:
- Shallow foundation
- Deep foundation
The pile foundation is classified into a deep foundation. But under reamed piles are not, as they are not driven deep.
Pile is a slender structural member made of steel, concrete, wood or of composite materials. Piles are classified on the basis of their function or the use and materials of its composition.
What is Under-Reamed Piles Foundation?
Under-Reamed Piles Foundation is an answer in area where black cotton soil could cause structural instability. Many times, during, soils undergo volumetric changes due to moisture variation underneath the ground surface. This expansion and shrinkage can cause distress which is very dangerous and critical as far as bearing of the foundation is concerned. The fact is that Under Reamed Piles are considered as most safe and economical foundation for such black cotton soils or expansive soils.
Based on the Function the Piles are Classified as:
- End Bearing Piles
- Friction Piles
- Compaction Piles
- Tension Piles
- Anchor Piles
- Fender Piles
- Batter Piles
- Sheet Piles
Based on the Materials and Composition of the Piles are classified as:
- Concrete Piles
- Timber Piles
- Steel Piles
- Composite Piles
- Sand piles
Concrete piles are further divided into the precast concrete pile, cast-in-situ concrete pile, prestressed concrete piles. The Under-Reamed Pile is the type of cast-in-situ concrete pile.
Here, we will discuss about the under-reamed piles.
Development History of Under-Reamed Pile
The problem of damage to a structure in expansive soil is worldwide. These soils are available in all continents. There is considerable damage to built properties due to it. The damage to structures is mainly due to shrinkage and swelling behavior of soil.
Under-Reamed Piles have been considerably experimented upon by Central Building Research Institute (CBRI), Roorkee, for use in black cotton soils and appears to provide an excellent solution to foundation problems in expansive soils.
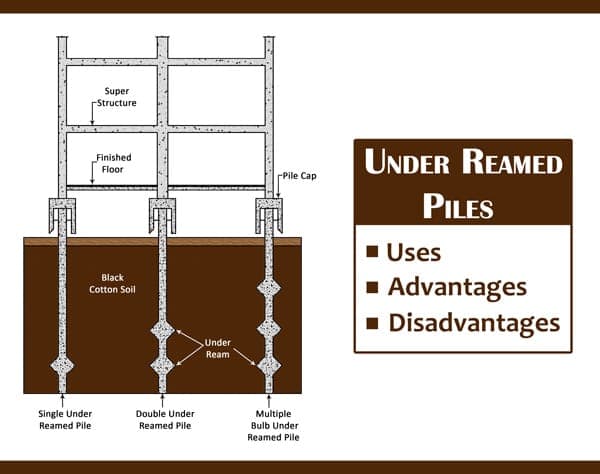
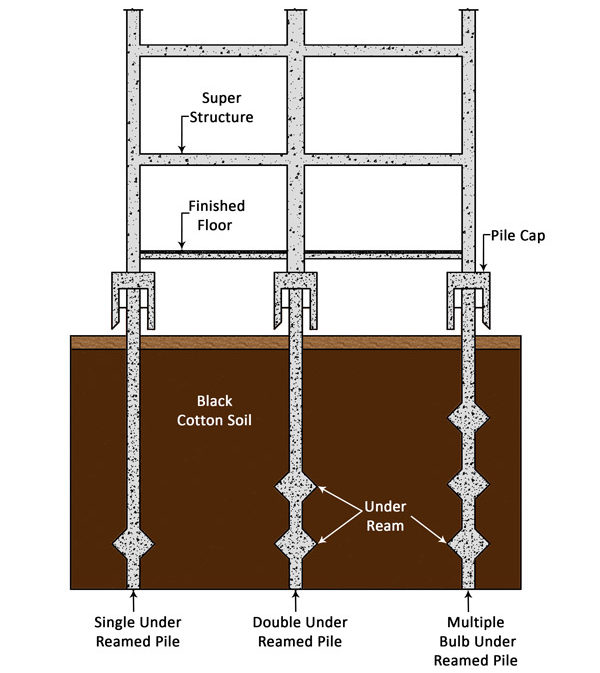
Definition of Under-Reamed Pile
A cast-in-situ concrete pile with an enlarged bulb at bottom made by either cutting or scooping out soil or by any other suitable process is called Under-Reamed Pile. Under-Reamed Piles are also called bored cast-in-situ concrete piles.
A pile formed in the ground for transmitting the load of structure to the soil by the resistance developed as its tip or along its surface or both is termed as bearing piles. If the piles supports primarily by resistance developed at pile point or base, it is referred to as an “End- Bearing Pile” and if the load as supported primarily by friction along its surface, the pile is termed as Friction Pile. When it is primarily meant for resisting uplift or pull, it is called an “Anchor Piles”.
According to ‘DR.B.C. Punmia, Ashok Kumar Jain, Arun Kumar Jain’ (Author of Soil Mechanics and Foundations), An Under-Reamed Pile is a cast-in-situ concrete pile, having one or more bulb in its lower portion. This bulb is called an under ream.
When only one bulb is provided at the bottom of the pile, it is known as single Under-Reamed Pile foundation. When two or more bulbs are provided at the bottom of the pile, it is known as multiple bulbs Under-Reamed Pile foundation.
Uses of Under-Reamed Piles
Under-Reamed Piles are widely used for different types of soils such as sandy soils, clayey soils and also expansive soils. Under-Reamed Piles are required to be taken down to a certain depth because of the following considerations:
- To avoid the undesirable effect of seasonal moisture changes in expansive soils such as black cotton soils.
- To reach hard strata.
- To obtain adequate capacity for downward, upward, lateral loads and moments.
- To take the foundations below the scour level.
- They have also been found useful for factory buildings and machine foundations.
- Under-Reamed Piles are also used under situations, where the vibration and noise caused during construction of piles, are to be avoided.
The Under Reamed Piles have also been extensively used by Sthapati Designers & Consultants Pvt. Ltd., for supporting the floors of large halls, airports etc., at ground / plinth level where there is huge earth filling. If the earth filling is not done in a professional way i.e. in the layer of 20 cm thick with compaction at optimum moisture content, it is likely to settle. Hence to take care of the same, the grade slab was provided on series of Under Reamed Pile spaced at 3 m center to center. Here the grade slab is designed as a flat slab supported on Under Reamed Piles where the pile cap acts as the pedestal of the columns as in flat slab and here no beams are provided for saving the cost. This has also worked and is performing very well since years. This has been done at terminal buildings for Surat and Amritsar International Airports along with many other public buildings.
More details about Under-Reamed Pile
According to ‘Indian Standard Code’ (1980) Under-Reamed Piles are generally designed in such a way that, they can support the load from the structure and transmit to the soil without causing any soil failure and settlements.
- In deep deposits of expansive soils, the minimum length of piles, irrespective of any other consideration shall be 3.5 m below the ground level.
- If the expansive soil deposits are of shallow depth and overlying non-expansive soil strata or hard strata, Piles of smaller length can also be provided.
- The diameter of Under-Reamed Piles varies from 20 cm to 50 cm.
- Minimum length of Under-Reamed Pile is 3.5 m.
- The diameter of under reamed bulbs may vary from 2 to 3 times the diameter of the pile depending upon the feasibility of construction and design requirements.
- The centre to centre spacing for Under-Reamed Piles should not be less than the 2 times diameter of the pile.
- The vertical spacing between two bulbs varies from 1.25 to 1.50 times the diameter of the bulb.
- The load carrying capacity of Under-Reamed Piles can be increased by making more bulbs at base.
- The ultimate bearing capacity of Under-Reamed Piles can be calculated from soil’s properties. If soil properties are not available directly from laboratory and field tests, they may be directly obtained from in situ penetration tests.
Under-Reamed Piles may be constructed by selecting a suitable technique at a given site. The advantages and disadvantages of the Under-Reamed Piles are as follow:
Advantages of Under-Reamed Piles
- It decreases the vertical settlement and also differential settlement.
- It is used when soil tends to swell and shrink due to moisture variation or expansive nature of the soil.
- Provision of under-reams or bulbs has the advantage of increasing the bearing and uplift capacities.
- When the number of bulbs are increased from one to two, the load carrying capacity of the Under-Reamed Pile is increased.
- The provision of bulbs is of special advantage in Under-Reamed Piles to resist uplift and they can be used as anchors.
- The cost advantages of Under-Reamed Piles are due to the reduced pile shaft diameter, resulting in less concrete needed to replace the excavated material.
Disadvantages of Under-Reamed Piles
- At a depth, where nature of soil varies with a climatic condition, Under-Reamed Piles are not suitable for waterlogged soil, as they take load by friction.
- These piles need strict quality control and regular supervision during the construction.
- Most of the times, Under Reamed Piles are driven manually with hand operated machine. Hence maintaining plumb of pile is very essential, because if they are not in plumb whole load transfer mechanism would change.
Two types of situation may be visualized. In the first, the soil strength is constant or increases with depth as in residual soil. Second, soft deposits occur below the strong top layers.
We would like to share with our readers very interesting aspects of the same. Our mentor Shri Mahadev Desai stated that the Under Reamed Pile is used invariably for compound wall and small low-rise structures extensively in Gujarat, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh etc. He said that at many places the contractors were either ignorant or not competent and hence though they did piles but the bulb i.e. under reaming was not done. However, to his surprise, these structures are safe and sound even today and nothing happened to them. Since years, it is suggested that, it really needed a detailed research as far as bulb is concerned, at least for small structures.
Summing up, all soil shrinks on drying till the shrinkage limit is reached. They also swell if water is available to them when they are dry. In addition, there are special soil called expansive soils in which this problem is very prominent. Because of expansive nature soils, they do noticeable damages to buildings.
Under-Reamed Piles are bored cast-in-situ concrete piles having one or more number of bulbs formed by enlarging the piles stem. The piles are best suited in soils where considerable ground movements occur due to seasonal variation, filled up grounds or in soft soil level.
Therefore, according to the ‘P.C. Varghese’ (Author of Foundation Engineering Geotechnical Aspects), If the soil is slightly expansive (made of ordinary illite or kaolinite clays and not expansive clays), ordinary simple structural footings can be used for the construction of a light weight building. However, In very highly expansive soils, Under-Reamed Piles are the only acceptable solutions.
Must Read:
Foundation System: All the Basic Things You Need to Know
10 Important Criteria to Choose the Right Foundation for Your House
6 Major Reasons for Failure of Pile Foundation!

































