Table of Contents
Glass is a versatile material, and it is now in use in various applications across multiple industries. Gone are the days when glass was always transparent and used in limited applications.
glass production has seen remarkable progress with technological advancements. Today, a wide variety of processed glass types are available in the market.
As per the latest market statistics, there are eight different types of processed glasses, each differing in parameters such as strength, safety, appearance, thermal tolerance, and more. Glass is now used across diverse segments, ranging from architecture and interior décor to furnishings and even delicate electronic devices.
The applications of each glass type are decided by its specific properties. In turn, the glass properties depend on the manufacturing process. Before diving into the different types of processed glass, let us first understand what processed glass is.
What is Processed Glass?
Processed glass means raw glass, which has undergone a mechanical treatment phase. The sole objective is to enhance its properties. Manufacturers process raw glass to improve its durability, aesthetics, safety, and functionality. Ultimately the process unlocks its extended potential in architecture, design, and beyond.
There are several commonly used glass processing techniques. These include:
- Heat treatment to improve durability
- Lacquering the surface to transform glass into a coloured variant
- Etching is applied to create textured or frosted surfaces.
Beyond these, numerous other techniques are found in Industrial practice. In this blog, we will discuss about the eight most commonly used types of processed glass in homes, and their unique features and benefits.
1. Tempered Glass (Toughened Glass)

Tempered glass is also known as toughened glass. It is manufactured with four times strength than standard glass. It is made by heating the glass to high temperatures and then cooling it quickly in a controlled way. This creates internal tension and surface compression, giving the glass a compressive stress of at least 10,000 psi. This is the reason behind the strength and resilience of tempered glass.
Tempered glass is commonly used in openings and other areas that require high strength and safety for its durability. Once the tempering process is complete, the glass cannot be cut, drilled, or incised, which adds to its safety credentials. This inherent toughness is why it is often referred to as safety glass.
The Benefits of Tempered Glass
- Strength and Durability: Tempered glass is remarkably durable and does not break easily. If it breaks, it shatters into tiny, blunt pieces, which are less risky to cause injury, and this safety feature has made it a safer alternative to standard glass.
- Increased Safety: Its ability to withstand pressure and impact provides greater safety, especially in high-risk areas of the home or commercial buildings.
- Heat Resistance: Tempered glass has excellent heat resistance, making it ideal for industrial equipment, such as furnaces, windows and other heat-sensitive applications.
- Versatility of Use: This glass is apt for an extensive range of uses in residential and industrial projects. Its strength, safety, and aesthetic appeal have made it a popular choice.
- Clarity and Visibility: The glass is transparent. That is why, tempered glass is often used in areas where clear visibility is a must, such as observation windows and partitions
Tempered Glass Uses in Home
- High-pressure & explosion-proof windows.
- Safety door windows & space partitions.
- Protective safety guards and building windows.
- Glass walls for elevators or stairways.
- Frameless shower doors and glass walls.
- Lighting fixtures, shower doors.
- Decorative panels for adding aesthetic appeal in home interior design.
- Display cases and cabinets in interior décor.
- Glass tabletops, glass doors.
2. Laminated Glass
Laminated glass is manufactured with two glass layers bonded together with one or more interlayers. It forms a permanent and durable bond. These interlayers hold the glass piece together even when broken. It results in a strong, uniform sheet that remains intact under impact. Laminated glass is available with various thicknesses. It can be manufactured using different combinations of glass types or coatings. The objective behind this variable manufacturing method is to enhance specific properties, such as low emissions, improved insulation and soundproofing.
Benefits Of Laminated Glasses
The construction of laminated glass results in its high tolerance power and durability, which are the reasons behind its varied benefits. Some of them are described below:
- Increased Security & Safety: The strength of laminated glass makes it almost impossible to break. Even if the glass is broken, the interlayers integrate the structure strength. It does not shatter even if broken, which reduces the risk of injury. It is Fire resistant too.
- Reduced Emissions: A laminated glass helps to reduce heat gain from the sun, which supports in maintaining a reduced temperature in a room. Its energy efficient for its interlayer, which acts as an active barrier to restrict heat transfer, UV Ray blockage, and cold outside air yet allows plenty of natural light.
- Reduced noise pollution: By Installing a quality laminated glass, you may reduce the effect of unwanted sound intrusion in home. It is helpful for decreasing noise pollution, and used as a preferred glass for home windows.
- Easy Maintenance: A laminated glass is easy to clean with soapy water and a soft piece of cloth or paper towel. It does not require intermittent repairing cost.
Laminated Glasses Uses in Home
Laminated glass is used in various ways in home construction, interior decoration, and areas where vision control or safety is essential. Some common applications include:
- Windows
- Doors
- Sunspaces
- Roofs
- Skylights
- Glass railings
- Curtain walls
- Decorative facades and partitions.
3. Frosted Glass
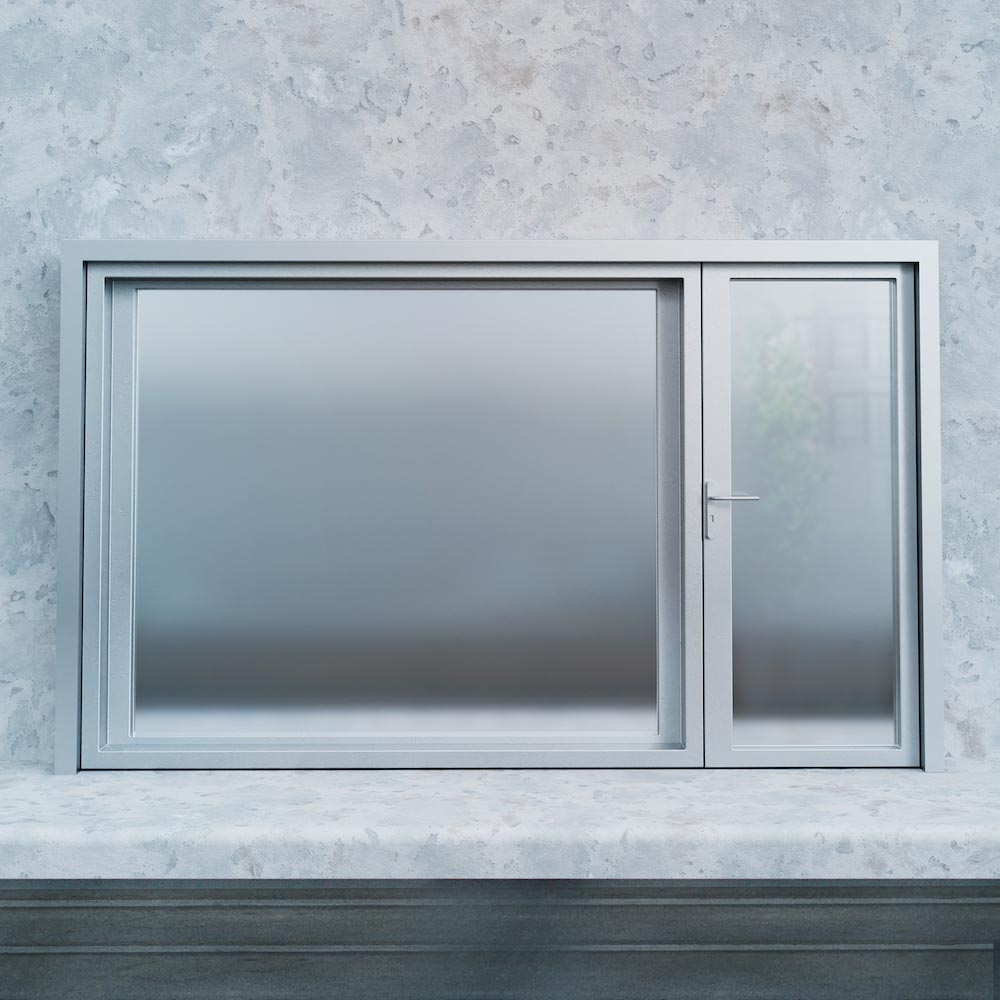

Frosted Glass is made of a translucent glass sheet that turns opaque after sandblasting or acid etching. The glass looks translucent because light gets scattered during transmission. The frosted impact can also be achieved by applying a vinyl film (used as a stencil) or through canned frosted glass sprays.
Benefits of Frosted Glass
- Aesthetic Appeal: One of the major reasons people select frosted glass for their personal spaces is its versatility and compatibility with various décor styles. With its elegant, opaque surface, frosted glass can enhance the beauty of any room, whether minimalistic or retro-themed.
- Natural Light Enhancement: Frosted Glass allows natural light to pass through while diffusing it evenly. When used in windows, it lets in sunlight and reduces the need for curtains. This not only improves room illumination but also lowers energy consumption by reducing the requirement of artificial light.
- Safety and Security: Frosted glass is often tempered or laminated, which means it doesn’t shatter into sharp, precarious shards like regular glass. This unique feature makes frosted glass a safer option for homes with children and pets.
- Increased Privacy: The opaque surface of frosted glass obstructs visibility, making it ideal for areas where privacy is essential.
Frosted Glass Uses at Home
Frosted glass is most commonly used in areas where privacy is paramount, yet natural light is still desired. Common applications include:
- Shower enclosures
- Windows
- Partitions in bathrooms,
- Skylights
- Glass railings
- Kitchen cabinet panels.
4. Tinted Glass

Tinted glass is a type of processed glass treated with additives or coatings. The process is implemented to lessen the transmission of light and heat through it. The tint is artificial. It is achieved during the manufacturing process by adding metal oxides or by applying a film or surface coating afterwards. Tinted glass is available in various shades, with popular options being grey, bronze, blue, and green.
The Benefits of Tinted Glass
- Heat Reduction: Tinted glass contributes in reducing the amount of solar heat entering your home. It keeps indoor spaces cooler and reduces the need for air conditioning.
- UV Protection: It blocks harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, which can result in skin damage. Alo, it fades furniture, curtains, flooring, and artwork.
- Enhanced Privacy: Tinted glass is not a see-through type of glass. It is merely impossible to look through it. It provides privacy without blocking natural light.
- Glare Control: It minimises glare on screens and reflective surfaces, making it ideal for media rooms, offices, and living areas that receive direct sunlight.
- Energy Efficiency: Tinted glass contributes to better insulation by limiting heat gain and loss. It results in energy savings and reduces utility bills.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The glass is made with different color shades. Tinted glass adds a slim contemporary look to windows, doors, facades, and partitions.
- Safety and Strength: When combined with tempered or laminated glass, tinted glass can also improve strength and safety, improving the structural integrity of installations.
Tinted Glass Uses at Home
- Windows
- Main Entrance, balcony doors
- Shower enclosure and bathroom partitions
- Glass facades and glazing panels
- Skylights
- Room dividers
- Wardrobe and cabinet doors.
5. Mirror Glass

Mirror glass is manufactured with a reflective coating to one side of the glass. It enables a feature to reflect light and produce clear reflections like a traditional mirror. It’s commonly used in bedrooms, hallways, and dressing areas to create the illusion of a larger space. The glass also helps to enhance brightness by reflecting ambient light.
The Benefits of Mirror Glass Use in Home
- Expansive Impression of Space: Thanks to its reflective quality, mirror glass creates the illusion of a larger, more open space, making rooms feel more spacious and visually appealing.
- Energy Efficiency: It reflects light, both natural and artificial, which helps brighten the surrounding space. It reduces the requirement of additional light, especially in small or dimly lit areas, and contributes in lowering energy consumption.
- Elegant Aesthetic Appeal: Mirror glass adds a touch of elegance and sophistication to interiors. It can be seamlessly incorporated into a home’s interior for both decorative and functional purposes.
- Versatile Design Element: Mirror glass is popular for its versatility and adaptability. It pairs effortlessly with both modern and retro-style décor, with various colour schemes and textures.
Mirror Glass Use in Home
- Wardrobe doors
- Bathroom mirrors
- Wall panels
- Dressing areas
6. Insulated Glass Unit (Double/Triple Glazed)
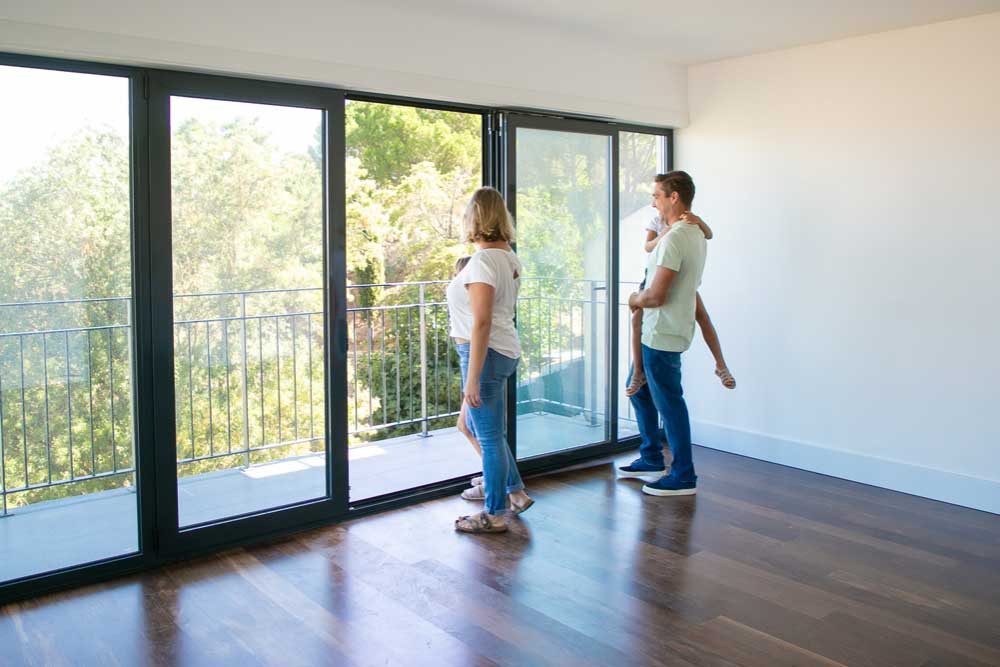

Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) are constructed with two or more glass panes, separated by a gas layer or vacuum. This layered design reduces heat transfer, noise, and condensation.
The Benefits of IGU Glass
- Energy Efficiency: IGUs reduce heat transfer, helping your home to remain cool in summer and warm in winter. This leads to lower energy bills.
- Noise Reduction: The air or gas layer between the panes acts as a sound barrier, making interiors quieter and more peaceful.
- Condensation Control: IGUs minimise condensation build-up on the glass surface, preventing moisture damage and mould growth.
- Enhanced Indoor Comfort: IGU glasses help maintain a consistent indoor temperature, which creates better comfort inside.
- UV Protection: IGUs can block a significant amount of harmful UV rays. As a result, they protect furniture, flooring, and artwork from discolouration issues.
- Enhanced Security: Thicker, multi-pane glass is harder to break than single-pane glass, adding an extra layer of safety.
- Eco-Friendly Option: IGUs reduce energy consumption, IGUs promote sustainability in the home and lower the carbon footprint.
IGU Glass uses In Home
- Windows
- Sliding and French Doors
- Skylights
- Glass Facades
- Conservatories or Sunrooms
- Soundproof Rooms.
7. Patterned Glass (Textured Glass)
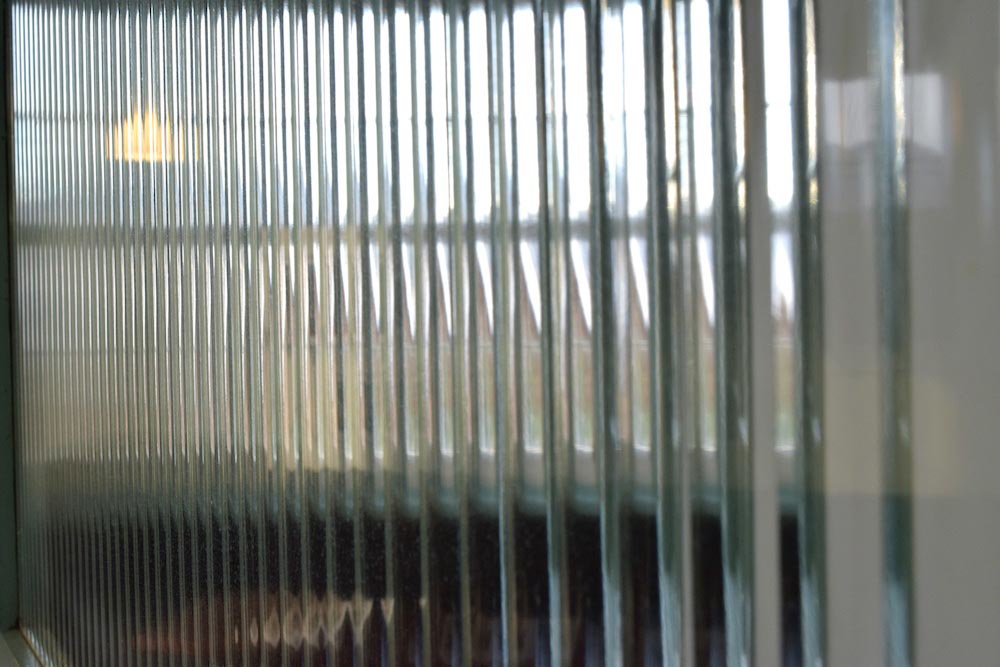

Patterned glass is also called textured glass. It is made with decorative designs embossed on its surface. The glass is light-friendly but restricts visibility through it. Patterned glass protects privacy while also looking stylish.
The Benefits of Patterned Glass
- Restricts Visibility, Not Light: Patterned glass restricts direct visibility. However, it allows natural light to filter through.
- Decorative Appeal: The glass is available in various textures and designs. After installation, it adds a stylish and artistic touch to glass-installed spots.
- Versatile Use: This glass variety is suitable for both modern and traditional interiors.
- Diffuses Glare: It reduces the harshness of sunlight. Also, it can restrict unwanted glare in bright rooms without blocking natural light.
- Easy Maintenance: The textured surface can camouflage smudges and fingerprints better than clear glass. This feature makes it more user-friendly than clear glass.
- Customisation Options: This type of glass is available in multiple patterns, thicknesses, and finishes to match any design need or decor style.
The uses of Patterned Glass
- Bathroom windows
- Cabinet doors
- Wardrobes and sliding doors
- Skylights and ceiling Panels
- Staircase railings and balustrades
- Entry doors and side panels
- Room partitions
8. Low-E Glass (Low Emissivity Glass)

Low-E glass contains a special coating that reflects and reverses heat. It keeps a home cooler in summer and warmer in winter. This glass variety can block UV rays but allows natural light in. It reduces energy bills. Low-E glass is see-through, efficient, and easy to maintain by DIY initiatives.
The Benefits of Low-E Glass (Low Emissivity Glass)
- Energy Efficiency: Low-E glass can reflect heat back to its source. It helps maintain indoor spaces cool in summer and warm in winter. As a result, it reduces the need for artificial heating or cooling systems in the home, resulting in lower energy bills.
- Restricts Harmful UV Rays: The glass filters out the major portion of ultraviolet rays. As a result, protecting furniture, curtains, flooring, and artwork from fading over time.
- Allows Natural Light In: Despite its coating, Low-E glass remains clear. It lets in natural daylight, keeping interiors bright without increasing heat.
- Reduces Condensation: Its insulating properties help maintain a consistent surface temperature, which can reduce condensation on windows in cooler climates.
- Environmentally Friendly: Use of less energy helps lower your carbon footprint, making Low-E glass a sustainable choice for eco-conscious homes.
The Uses of Low-E Glass (Low Emissivity Glass)
- Windows
- Sliding Doors and French Doors
- Skylights
- Glass Facades and Large Glazing Panels
- Conservatories and Sunrooms
- Green Homes and Smart Buildings
Final Thoughts
Processed glass is a modern invention that accentuates both beauty and functionality in contemporary homes. From tough tempered glass to colourful tinted glass to energy-saving Low-E glass, each glass type has its unique benefits.
These glasses can serve various purposes, such as brightening rooms, offering privacy, or keeping home interiors naturally conditioned. However, you need to know the best features of these glasses to reap the optimum benefits from your selection and installation.
No matter if you are constructing a new home, building an addition, or upgrading your existing one, the proper glass installation can make a significant difference. It’s more than just a construction hardware. It is a part of a chosen lifestyle.
It’s time to use the best-processed glass that suits your needs, and then can you enjoy the best ROI from your investment.
Also Read: Raw Materials Used in Glass Manufacturing Process
FAQs on 8 Types of Processed Glass for Your Home
1. What Are the Prime Uses of Processed Glass?
Processed glasses are widely used in constructing secure doors and covering facade areas. In fact, its multifaceted use potential makes it a multipurpose building material. Tempered glass is a popular choice among builders. It is one of the most efficient types of glass, boasting high heat insulation properties. These premium features make it ideal for sun-exposed windows, doors, patios, and balconies.
2. What Is the Best Glass for Home Windows
For windows in a home, tempered glass is the best option. Tempered glass offers resilience and energy efficiency. You can reduce your energy bills, and these glasses will also not succumb to breakage even when put under pressure.
3. Which Is the Strongest Glass for Homes?
Laminated glass (also called safety glass) is an excellent choice for safeguarding your home with strong and resilient glass protection. Laminated glass is manufactured by fusing two panes around a layer of polyvinyl butyral. The entire process is executed with high heat and intense pressure.
4. Which Glass Is Better for Blocking Sunlight?
Laminated glass blocks more than 99% of UV rays because plastic interlayers between single panes of glass absorb UV radiation.
5. How Do You Identify the Type of Glass?
Try looking closely at the edge of the glass. Tempered glass will display a smooth, slightly rounded edge without sharp corners. Untampered glass will show a sharp, unfinished edge. You may also observe tiny nicks or divots in the glass edge. Tempered glass undergoes intense heating and rapid cooling processing, resulting in a durable surface.
References
P. Barboux, A. Laghzizil, Y. Bessoles, H. Deroulhac, G. Trouvé (2004) in Paradoxical crystalline morphology of frosted glass https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2004.08.011 in Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, Volumes 345–346, 15 October 2004, Pages 137-141 [Online] Available from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0022309304005356






























