Table of Contents
Quick Summary
- Any construction process begins with the first step of site analysis.
- Site analysis is the study and evaluation of the physical, environmental, cultural, and regulatory characteristics of a site chosen for a construction project.
- A thorough site analysis will help you to design a building that are efficient, safe, and sustainable.
- Site location, dimensions, orientation, climate, wind direction, topography, soil condition, vegetation, natural features, and surrounding land use are the key factors that contribute to a site analysis.
- Convenience factors of site analysis include infrastructure availability, water supply, drainage, electricity, and connectivity.
- Studying hydrology, precipitation, slopes, and water table guides foundation design.
- Additionally, other factors that contribute to site analysis are legal constraints, pollution levels, hazard assessment, and social context.
A comprehensive site analysis ensures proper room placement, structural safety, energy efficiency, and long-term performance of the building.
Site Analysis or study of a site is the first essential step in an overall design and construction process. It is considered as a preliminary step of designing process that includes in its scope the study of geographic location, climate, topography and many more allied factors. A proper site analysis can let us understand the physical constraints of the site which can even help in formulating the complete designing intricacies in the concerned site in accordance to the proposed project. Thus, after the completion of a site visit, a detailed site analysis has to be executed to detect and comprehend the features of the site, which can help to create an all-inclusive and dynamic design output.
How to do Site Analysis?
Some of the points for site analysis mentioned in the book – Site Analysis – A Conceptual Approach to Sustainable Land Planning and Site Design by James A. LaGro Jr., which is a reliable source for consultation for the people working on site analysis. Concerned people involved in professional site analysis must pay attention toward the indicated points during the site visit as well as during the site analysis for organized approach on the said matter as suggested in the said book.
01. Site Location

One of the foremost points of a site analysis is detail deciphering the site location, and it is done to be completely aware about the context of the target site. So, collect the site location details that comprises of the address, the road on which it is located, major junctions, surroundings, major landmarks, etc. Along with all these details, have a look at the various options through which you can reach your site.
02. Site Dimensions

The other important factor to be taken in count is the geometric data of the site, i.e., its dimensions and area. This data will help the architects in defining the footprint of the spaces as per the program or your requirements. The geometry of the site also helps to decide the architectural size, shape, and form of the construction i.e. if it will be built in regular, semi-regular or irregular form.
03. Site Orientation
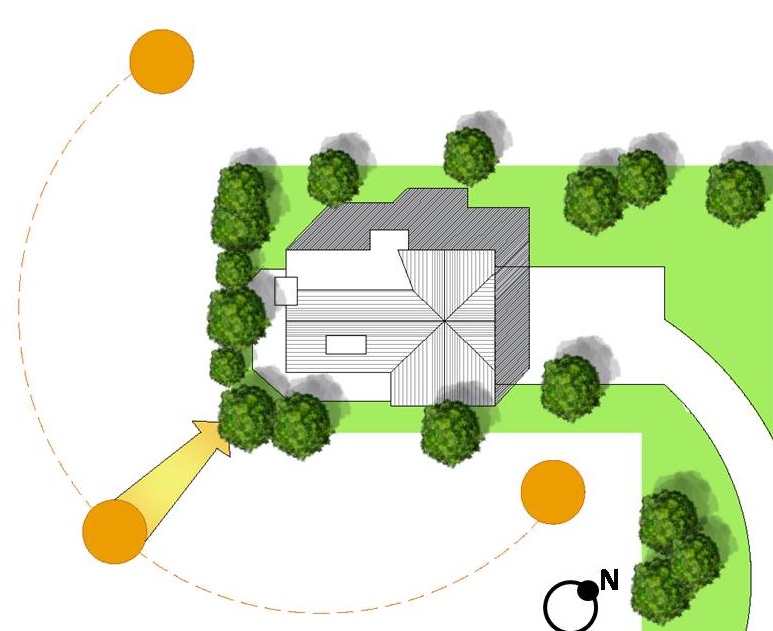
During the processing of a site analysis, a detail study of site orientation is very important. By combining the sun path and wind direction you will get some useful ideas regarding the best building design. The orientation of sun path will affect the building positioning and placement of the rooms and their interior spaces. It is basically the basic analytics that decide the size and location of the windows and doors for facilitating air, light and ventilation into the building
The plot orientation plays a major role to increase the energy efficiency of the building. To help you in knowing the importance of building orientation, we have shared a detailed blog with you:
04. Temperature Analysis
The average monthly temperature of the area round the year should be considered in the pattern of the design. In the warm climate, a design should be in such a way that it reduces the heat inside the building. In cold climate, the design should be in such a way that the sunlight on the building will impact maximum warmth inside the building. If we count in India, the country is divided into 5 climatic zones:
- Hot and dry
- Warm and humid
- Cold
- Moderate, and
- Temperate
Knowing the prevalent temperature at the site will help you choose the right building materials, insulation needs, façade design, and passive climate strategies.
05. Wind Direction Analysis
If someone wants to design a climate responsive building, it is important to consider wind and its flowing map through the interior spaces during various seasons. Generally, most of the site location will have some major direction from where the wind generally flows. But the wind direction does not remain consistent and predictable throughout the year as it varies from one place to another depending upon some local geographical factors.
06. Hydrology & Precipitation Analysis
The amount of annual rainfall that a site generally receives will give you an idea about the precipitation, which is expected throughout the year. It is also important to study the natural flow of water and existing storm water drainage including upper catchment contributory flow to the site.
During the site visit, a site analyzer also needs to identify water bodies like ponds, rivers, lakes, etc. and their location near the site. The size of the water body should be considered, because it may reduce the overall temperature of the area. Water table should also be considered while getting the site analysis done.
If your site is positioned near a water body, the water table may look shallow by its data interpretation. Shallow water table can affect the stability of the foundation and may create construction problems, particularly of foundations.
07. Site Topography

The topography of the site plays an important role in site analysis. The factor of topography depends on the slope of the land, i.e., whether it is a flat and plain, or an uneven surface. If a site shows a sloping surface, it becomes more challenging from the design point of view but it is always desirable to design a building along the contour of the plot. It helps in reducing the need of unnecessary cutting and filling with the soil to impose balance in the surface. The exact slope denomination of a sloping site can be obtained from the detailed contour map. Along with the slope, it is also important to check the stability of the slope. Furthermore, it is important to verify whether the slopes are strong enough to permit construction on it, and also the extent of the construction it can withstand.
For knowing more about importance of the site topography in a site analysis, please have a glance at our article named:
08. Condition and Types of Soil
Various types of soils are available to deal and analyze. Some of the common variations are sandy soil, clayey soil, laterite, marshy, rocky soil, etc. All these types of soils have different properties that affect the building, its foundation, and structural design. After determining the soil type, you need to calculate the safe load bearing capacity and then decide the appropriate structural system. Foundation will be designed accordingly.
Feature blog box – Best Soil Types for Strong Building Foundations
09. Vegetation & Natural Features
The natural vegetation that grows on the site is always much relevant for the site analysis. Any competent designer should design in harmony with nature to enhance sustainability and microclimate. Learn about the kind of vegetation present on site, its location, types, size, diameter or spread of the branches, the spread of leaves and the speed of growth as well as the spread of roots.
10. Manmade Features
Apart from all the natural features at site, it is very important to note the manmade features positioned at site during the site analysis. This manmade feature includes the details of adjoining buildings, fences, patios, shelters, plazas, etc. The existing historical features, if any, also should be documented. This knowledge will influence site planning and zoning decisions.
11. Surrounding Land Uses & Buildings
If the land located around the site is unused or barren or incompatible to use, it may create an issue in the design. Also, the setbacks and heights of the adjacent buildings are very important because it will affect the flow of air and sunlight ultimately in the new construction.
12. Infrastructure Facilities and Services

Major things which need to be considered are the water supply, waste disposal and drainage, electricity supply, etc. The location and levels of manhole, fire hydrants and any other fixtures positioned on site should also be kept in account. These factors are important while designing and planning for a new construction. Apart from these factors, the sizes of lines should also be noted.
13. Locally Available Resources
Locally available materials around the site should be studied during the site analysis as it will create the bulk cost efficiency and carrying convenience. It will impact organic sustainability by reducing logistics cost and related energy facilities.
14. Views from Site
During the site analysis, you should note the views you get to accumulate from all directions. This all-rounder view can help you in designing your building with proper form, solid-void composition, an apt construction technique, etc. For example, if you want to obstruct the views outside your site, you can go for a heighted compound wall or avoid cut outs in the wall of that side. On the contrary, if you want to remain connected with the view, maximize the number of cut-outs in the target wall, etc.
Additional Factors to Consider in Site Analysis
- Understand the legal and regulatory constraints of your site. Every site is governed by specific rules, zoning regulations, FSI/FAR limits, height restrictions, and local by-laws.
- Evaluate the pollution levels of your site, as this will influence room placement, façade design and material selection.
- Conduct a shadow analysis to determine sun exposure patterns throughout the year and to ensure better daylight planning.
- Explore the geography and potential hazard threats such as flooding, landslides, seismic activity, and soil liquefaction zones.
- Study cultural and social context of your site for a better house plan. This ensures that the building fits naturally and does not appear out of place.
Summing Up
Proper site analysis guides the designer to design the building by ensuring that the building will make the best uses of the resources available on the site like light, ventilation, views, etc. We hope this guide will help you in doing a site analysis in an appropriate, professional, and flawless way.
Apart from all these tips on a site analysis, if you are interested in knowing more about architectural designs, please have a glance at our most viewed articles.
Site Analysis FAQs
01. What is the main aim of a site analysis?
The main aim of a site analysis is to understand the physical and environmental characteristics of a site and make informed design decisions.
02. What are the most important factors in site analysis?
The most important factors in a site analysis include site orientation, soil condition, climate, and topography.
03. Who performs site analysis?
A site analysis is performed by professionals such as architects, civil engineers, planners, surveyors, and environmental consultants.
04. Why is soil testing important?
Soil testing is very important because the foundation design for the entire construction depends on the results of the soil test.
05. List the documents required for site analysis.
Site plan, contour map, climate data, soil test reports, local authority guidelines, and satellite imagery.
References
James A. LaGro Jr. (2008) Site Analysis – A Conceptual Approach to Sustainable Land Planning and Site Design. [Online] New Jersey, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Available from: https://www.google.co.in/books/edition/Site_Analysis/F0PNMKek-1AC?hl=en&gbpv=1
































