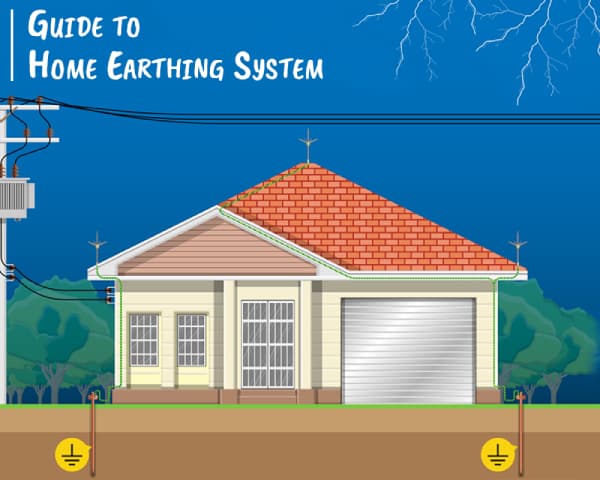
Earthing is a component of an electrical circuit that is of utmost importance. It can be either a neutral earthing or an equipment earthing. Making proper house earthing is a MUST of safety; therefore it is vital to know about its utility, and also about the impending risks if earthing is not done rightly. Knowing the nitty-gritty of earthing will promote your safety. With proper earthing installed, you may stay safe while using your electrical gadgets.
Earth has a conductive surface, so it is used as a safe charge conductor and neutralizer for universal standard of all-electric systems, and it is in use from the very beginning of the electrical distribution system installation. Electricity is essential in our life, but it also has certain dangerous risks imbedded in its distribution system that may have perilous effects on the users of these electrical systems if anything goes beyond the rule and safety protocols. Earthing is one such safety protocols in an electrical system/circuit.
If any fault occurs in an electrical wiring system, the fault it mostly leads to impact damage or it may cause failure of the equipment. During these fault phase, a potential difference occurs between the metal parts of the electrical system. If anyone by chance gets in direct touch with these parts, there is a high chance that they will be exposed to an electric shock which, can be fatal.
Considering such these risks and to make an electrical circuit safe for its users, the system of creating an earthing was introduced and the convention is still on.
Let us look at a few things about house earthing in the electric supply system.
House Earthing or Grounding
Earthing and grounding are two different words, but are used for conveying the same meaning. In an electric wiring system, the earth or ground is a conductor that provides a low barrier path for the earth to prevent hazardous voltages affecting the devices.
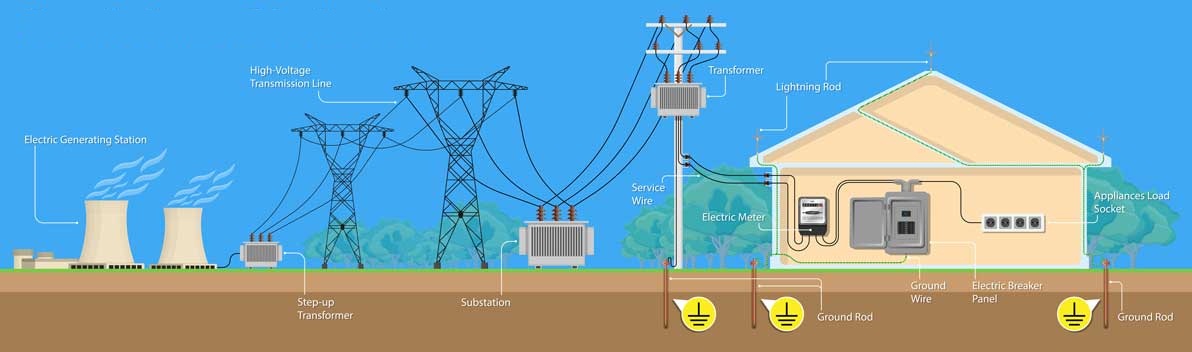
The word earthing is mostly used in Europe, Britain, and in the most commonwealth countries’ standards, i.e. IS (Indian Standard), IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), etc.
The word grounding is used in North American Standards, i.e. ANSI (American National Standards Institute), NEC (Nippon Electric Company), IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), UL (Underwriters Laboratories), etc.
What is Earthing or Grounding?
The term earthing and grounding means connecting the electrical system and equipment to the ground by using a suitable conductor. In other words, earthing is a process customarily used to increase the safety of electrical appliances and to prevent electrical shocks.
According to ‘Phil Hughes and Ed Ferrett’[357] (Author of the Book, Introduction to Health and Safety in Construction), the electricity Supply Company has one of its conductors solidly connected to the earth and every circuit supplied by the company must have one of its conductors connected to ground. This means that if there is a fault such as a breakage in the circuit, the current will return directly to earth and maintain the safety of the supply circuit. This process is known as earthing.
Purpose of Earthing in an Electrical Installation
Earthing is used for multiple purposes. Some of these utilities are,
01. To save human life from the danger of electrical shock, i.e., to provide an alternative path for the current to flow so that it will not impose any life risk on the user.
02. To provide a stable platform for the operation and safety of sensitive electronic equipment, i.e., to maintain the voltage at any part of an electrical system at a known value to prevent the risk of the supply of high voltage on the appliances or equipment, leading to its damage.
03. To protect buildings, machinery, and appliances under faulty conditions.
04. To provide a safe path to dissipate lightning and short circuit currents.
From a technical point of view, earthing has become a mainstream practice in the electrical industry for creating an electrical circuit due to some excellent advantages.
Benefits of Earthing System
01. The earthing system helps to detect all the defects that occur in the phase. Therefore, it protects the user against electric shock and prevents the circuit from damage.
02. If there is any insulation fault, the system of earthing helps eliminate the risk of fire or explosion in the circuit.
03. Earthing in an electrical system can resist damage to electrical appliances and devices by preventing excessive current flowing through the circuit.
What happens if Earthing is not Done Properly?

If items are not correctly grounded with an earthing system, the supplied electric current can become unbalanced. This is responsible for a short circuit in the electrical system. An improper grounding can create higher risk/damage in the electric system. As a result, various electrical equipment may get damaged, and the risk of fire and short circuit increases.
In such a situation, you can save yourself and your family members from becoming victim to short circuits. Follow these
Before knowing the various methods of earthing, let us see the components of the earthing system.
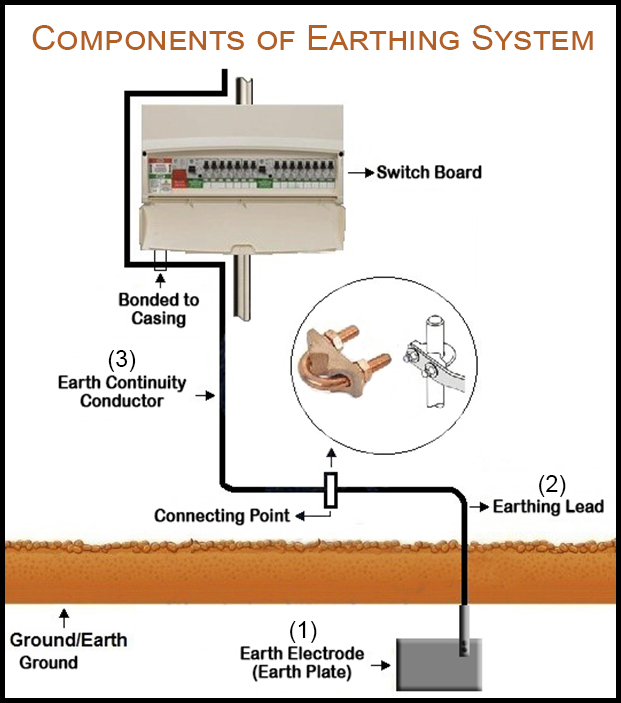
Components of Earthing System
An electrical earthing system consists of the following basic components:
01. Earthing Electrode:
A metallic plate, pipe or a ground rod is used as electrodes for domestic wiring.
02. Earthing Lead:
Earthing lead is the connector between the consumer earthing point and the exposed metallic part.
03. Earthing Conductors:
Earthing conductor is a type of conductor, which connects the consumer earthing point with other parts of the installation that needs earthing.
Different Types of Earthing Systems for Home
Earthing for home is achieved by connecting the electrical appliances or components to earth by using a good conductor called ‘Earth Electrode’. This ensures a very low resistance path from devices to the earth. The various methods of earthing are as follows:
01. Plate Earthing
02. Pipe Earthing
03. Rod Earthing
Apart from the multiple methods of earthing mentioned above, the two methods are mostly used in house earthing. i.e. Plate Earthing and Pipe Earthing.
01. Plate Earthing
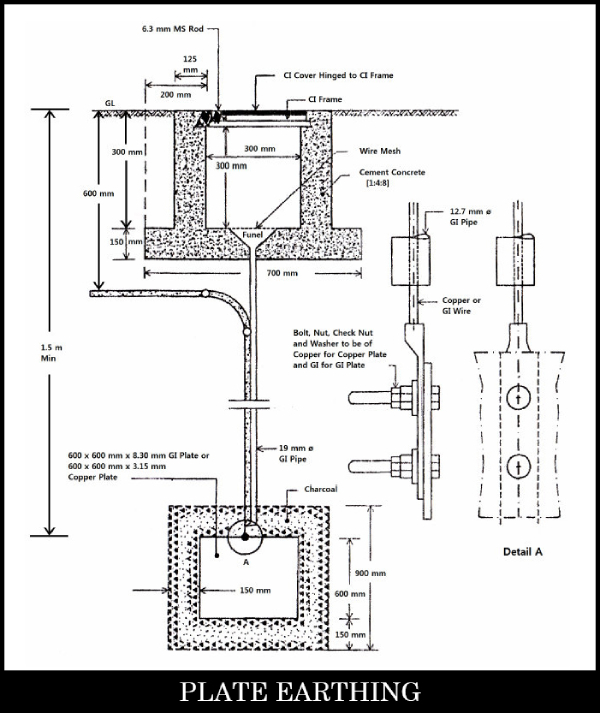
In Plate earthing, a copper plate (of dimension 600mm x 600mm x 3.15 mm) or a GI plate (of 600mm x 600mm x 6.3 mm) is used as an earth electrode. The GI plates are frequently used nowadays. The plate is kept with its face vertical, and embedded 3 meters into the ground.
Alternate layers of salt or coke surrounding the electrode for a minimum thickness of about 150 mm. The earthing wire is securely bolted to the earth plate with the help of bolt, and must be made of copper for copper electrode or ofGI if it is a GI electrode.
According to ‘U. A. Bakshi and V. U. Bakshi’[358] (Author of Book: Elements of Electrical Engineering), the earthing efficiency gets increased with the increment of the plate area and depth of embedding. If the resistivity of the soil is high, then it is necessary to implant the plate vertically at a greater depth into the ground.
This method has only one disadvantage. In this arrangement the discontinuity of the earthing wire from the earthing plate below the earth cannot be observed physically. This may cause confusion and may result in heavy loss under faulty conditions.
02. Pipe Earthing
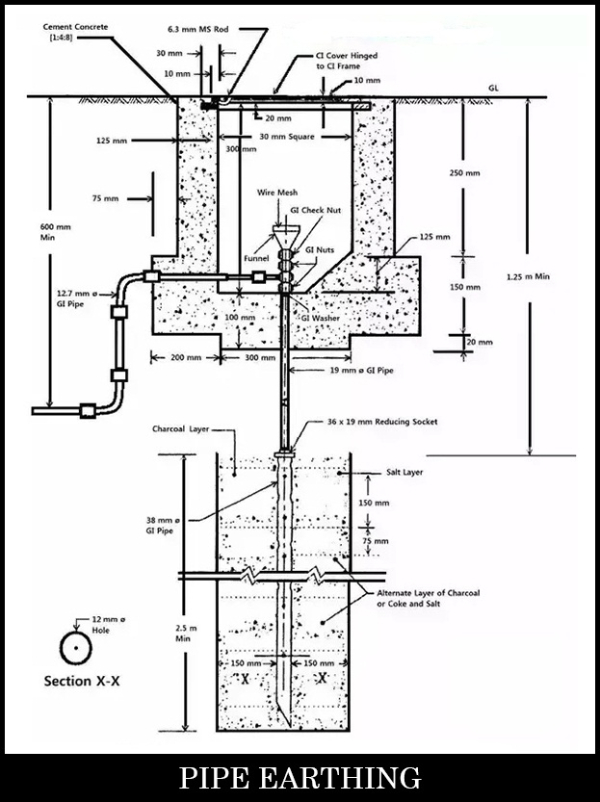
In this method of earthing, galvanized pipe of length 2.5mm and 38mm internal diameter is placed vertically (upright) in soil. The inclination should not be more than 30 degrees from the vertical.
The pipe is kept surrounded by pieces of coke or charcoal and salt in the alternate layers of about 150 mm around the pipe, and it is done to decrease the resistance. The earthing wires are connected to the GI pipe above the ground level, and can be physically inspected from time to time. These connections can be checked for performing ground continuity tests. This is the premium advantage of Pipe Earthing method over the Plate Earthing method.
The only disadvantage of pipe earthing system is the complexity in deciding the right pipe length. In this system, the embedded pipe length has to be increased sufficiently if the soil specific resistivity is of a higher order value. This increases the obligation of doing excavation work and hence the process incur higher cost than other earthing option(s).
We use a lot of electrical cables and wires in our premise, but if someone asks us the difference between wires and cables, we often get confused. Don’t get confused, refer
Earthing Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the earthing system is an obvious way to ensure that the system functions at par for long. Maintenance of system means checking and execution of actions carried out to operate an electrical equipment or restore the arrangement to an acceptable and safe condition. The maintenance should be done according to the manufacturer’s suggestion, and the recommendation is mostly found explained in the manufacturers’ manuals, however, the maintenance of earthing arrangement largely depends on the factors like its use, the working environment, and the equipment type.
Maintenance management schemes can be based around several techniques designed to focus on the vulnerable parts that frequently tend to deteriorate and need to be maintained for ensuring prevention of health and mitigating safety risks. These techniques include:
01. Preventative Planned Maintenance
Preventative Planned Maintenanceusually involves replacing weak/faulty parts or setting the necessary adjustments at preset intervals.
02. Condition Based Maintenance
In Condition Based Maintenancecourse, critical parts are monitored and maintained as and when necessary to avoid massive hazards.
03. Breakdown Based Maintenance
Breakdown Based Maintenance is carried out when some faults or failures occurs. This is only acceptable if the failure is counted as an immediate hazard and normalcy can be corrected before the probability of risk gets increased. If, for example, a bearing overheating gets detected by a monitoring device, it is recommended officially to wait for the overheating problem to occur as long as the equipment can be stopped and relevant repairs can be carried out before the fault becomes dangerous to persons employed.
This type of maintenance is carried out only when faults or failures have occurred. This is only acceptable if the failure does not present an immediate hazard and can be corrected before the risk increases.
Service Life of Earthing System
According to the research paper “Prediction of service life of building materials and components” by ‘Erik Brandt’, a material’s service life is the period after installation, during which all essential properties meet the demand or may exceed minimum acceptable values when they are routinely maintained.
The earthing system should be designed at least with 50 years of service life expectancy in most environmental and soil conditions. Also, its service life depends on the type of material used in the earthing system.
Cost of Earthing
According to the Department of Housing and Urban Development, and Certain Independent Agencies – USA, the cost of a grounding system is challenging to measure. For a typical new home, the cost includes a material with grounding features and the labor to properly connect the grounding parts. The materials involve a cable with a conductor for grounding purposes and grounding terminals of wiring devices and connectors at electric panel boards.
In short, the earthing system’s cost depends on the cost of the various components of the earthing system, i.e., earthing electrode, wires, etc. Also, the cost of the various components varies with its manufacturing company.
Summing up the entire discuss in, a house earthing or grounding system is one of the most important aspects of any electrical installation. The main reason for adding earthing in electrical networks is safety. A well-designed earthing system for home is useful for the safety of the users; also, it helps in reducing electromagnetic disturbances, and maintaining the overall network of the supply system.
Various methods and standards are followed for providing earthing in electrical systems. If proper earthing is not done, electrical equipment and humans are likely to be harmed. Due to this, proper care must be taken while providing the earth grid in the electric supply system.
Before you leave this page, just check once what we have written in other exciting posts, which we know that you will surely like. Read here –
Tips to Avoid Accidents Due to Electrical Shock and Fire in Monsoon!
31 Tips to Prevent Electrical Hazards During Holidays
Image Courtesy: Image 1, Image 2, Image 3, Image 4, Image 5, Image 6
































