Table of Contents
Quick Summary
- Corrosion Monitoring Techniques are preventive methods in construction structure maintenance.
- Corrosion weakens reinforced concrete structures. It reduces safety and serviceability over time.
- Regular Monitoring helps in identifying corrosion risks early and avoid costly failures in bridges, buildings, dams, and chimneys.
- Visual inspection checks visible rusting, cracks, and spalling for quick assessment.
- Half-cell potential measures the corrosion probability of reinforcement using reference electrodes.
- Concrete resistivity test evaluates the rate of corrosion based on electrical resistance.
- Linear polarization resistance gives an instant corrosion rate for better structural evaluation.
- Vibrating wire and strain gauges track stresses, strain, and crack formation.
- Cover thickness detection process checks and validates adequate protection for rebars.
- Ultrasonic pulse velocity, radiography, and infrared thermography locate flaws and weak zones in a structure.
- Modern instruments combine multiple methods for accurate monitoring and safer structures.
Corrosion in reinforced concrete structures is a significant problem nowadays. It renders the structure lifeless, less resilient, and weaker in terms of serviceability and safety standards. Corrosion itself is an electrochemical attack process on steel. As a result, corrosion wastes a lot of resources and money in the modern construction industry, highlighting the importance of derouging and passivation. Hence, periodic corrosion monitoring is crucial for any reinforced concrete structure. To prevent the loss of money, resources and any significant incidents caused by corrosion in reinforced concrete structures, Gharpedia provides comprehensive information about Corrosion Monitoring Methods in this blog.
What is Corrosion Monitoring in Reinforced Concrete Structures?
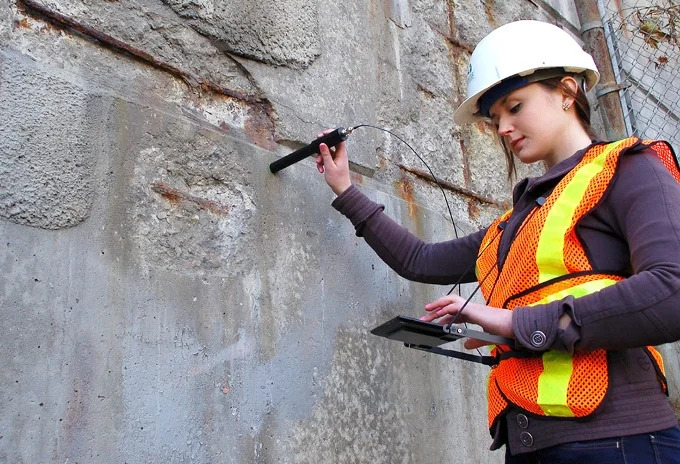

Courtesy - midtech
The process of assessing and foreseeing steel corrosion damage to reinforced concrete structures and providing the necessary facilities is known as Corrosion Monitoring. Corrosion Monitoring Methods can be used to measure the corrosion of steel in concrete structures. It simply refers to corrosion detection techniques used in the field and laboratories. It is crucial to conduct routine, periodic corrosion surveys and keep a record of the corrosion data in order to monitor the status of key structures like bridges, dams, chimneys, etc., starting from the building stage. As a result, there is now much room for research in this field.
Know the causes of corrosion of reinforcement steel in concrete-
Why is Corrosion Monitoring Important?
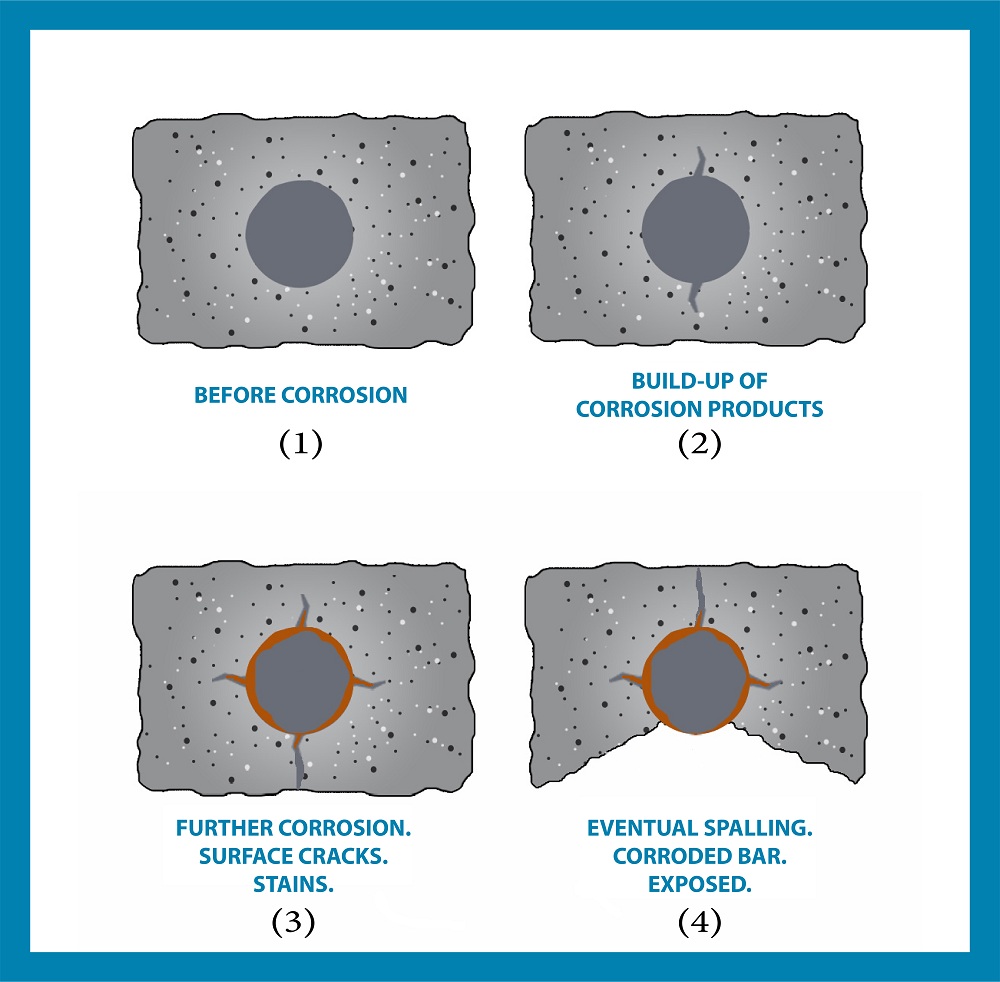
Concrete constructions have two sides, just like a coin. Unfortunately, accidents have risen along with the use of concrete construction. Here’s an illustration:
On a smaller scale, it frequently appears in headlines that many old buildings are being evacuated, people are being relocated, or the entire slab and beam fail and fall, killing many lives. In addition, there have been numerous significant accidents, detailed below:
The Gokhale Bridge at Andheri collapsed due to corrosion in the cables, as per a report by the Commissioner of Railway Safety (CRS).
The Bhopal Gas tragedy is also an example of corrosion failure.
Genoa, Italy Bridge Collapse “Italian engineering experts studied heavy suspicions that corrosion to the bridge’s steel cables contributed to the collapse, saying that it reduced the bridge’s overall strength by almost 20%.”
There are many reasons for building failure due to the corrosion of steel bars. Thus, if we predict the corrosion damage or identify the risk of steel corrosion in the concrete structure, we can increase the structure’s life and even prevent any major failure.
Corrosion Monitoring Methods

Courtesy - giatecscientific
As we know, corrosion is an electrochemical process, and we can find damage from corrosion by many electrical and chemical processes. Here are some non-destructive corrosion monitoring methods.
1. Non-Destructive Corrosion Monitoring Techniques
Non-destructive corrosion monitoring methods are tested with little or no harm to the specimen or concrete structure. Many electrical methods are used through A.C. (alternating current) and D.C. (direct current) current methods. Some are explained below: Let’s have a detailed look-
01. Basic Corrosion Measurement Technique: Visual Inspection

If a structure starts to corrode quickly, followed by rusting of the steel, cracking and spalling, then the condition of the structure is monitored by visual inspection. Solutions are offered for corrosion circumstances with mild, medium, high or severe corrosion.
To check on the soundness of the concrete, a sonic inspection is also done using hammers.
02. Half-Cell Potential Method (HCP)
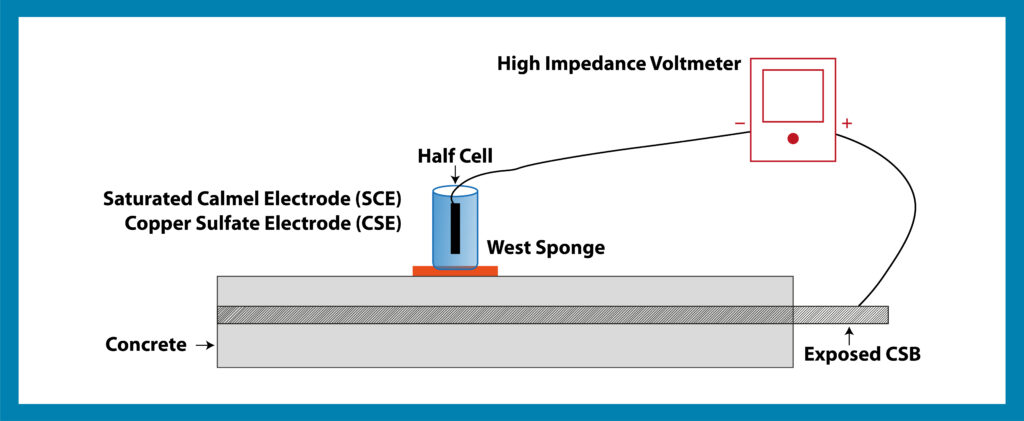
A half-cell potential method is also known as an open circuit potential method or a rest potential method. The principle involved in this corrosion monitoring method is to measure the corrosion potential of reinforcement with respect to a standard reference electrode, i.e., the saturated calomel electrode (SCE) or copper sulphate electrode (CSE), etc., done as per ASTM C 876, which shows the detailed procedure of the test. The following table shows the results in the probability of reinforcement corrosion, as per the ASTM C 876 [6] standard:
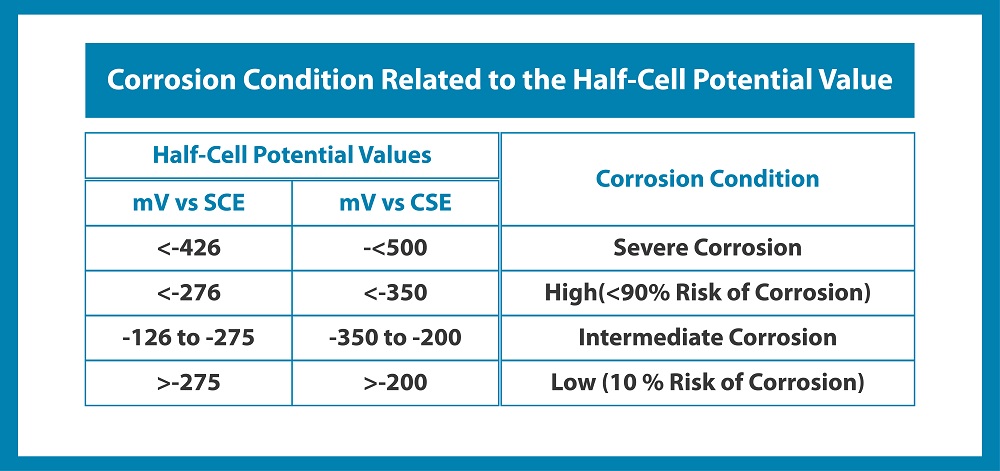
03. Concrete Resistivity Method
Courtesy - researchgate
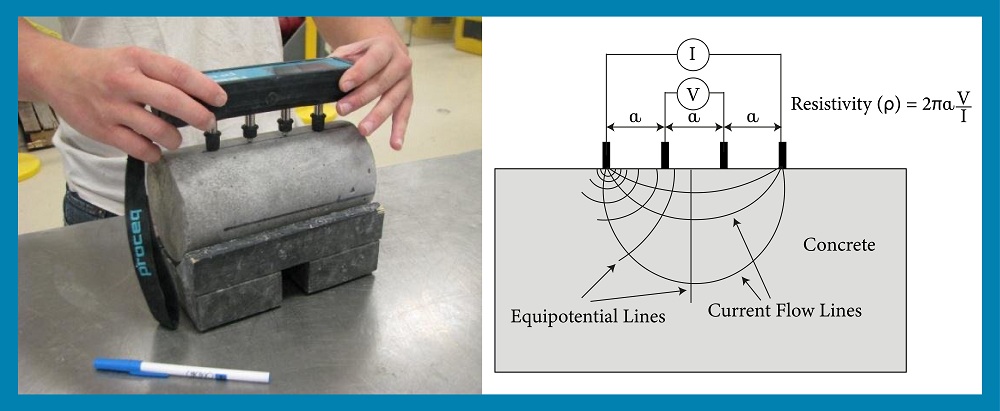
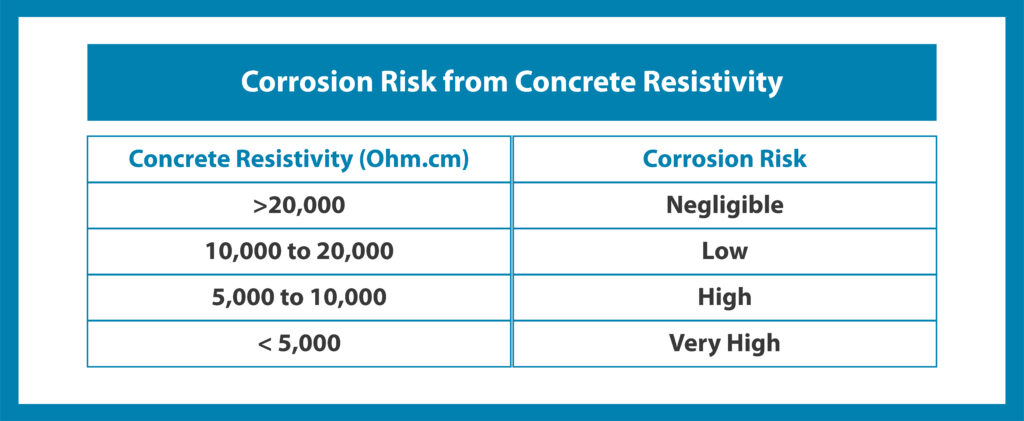
In the concrete resistivity test, the results are based on the resistance offered by the concrete medium. The electrical resistivity of the concrete is the most important factor in determining the intensity of the initiated corrosion process. If electrical resistivity is high, the corrosion process will be slow, and vice-versa.
According to the illustration, the Wenner four-probe method is typically used to measure the concrete resistivity. The current (I) is applied at the outer probes, the voltage drop (V) is measured in the inner probe, and V/I gives resistance R. Now, concrete resistivity can be calculated using the below formula.
Resistivity of Concrete (ρ) = 2πaR
Where,
a = Inner electrode distance in the cm
R = Measured resistance in ohm. (R=V/I)
V = Voltage drop
I = Current
The following table shows the corrosion risk from concrete resistivity:
04. Linear Polarization Resistance Method (LPR)
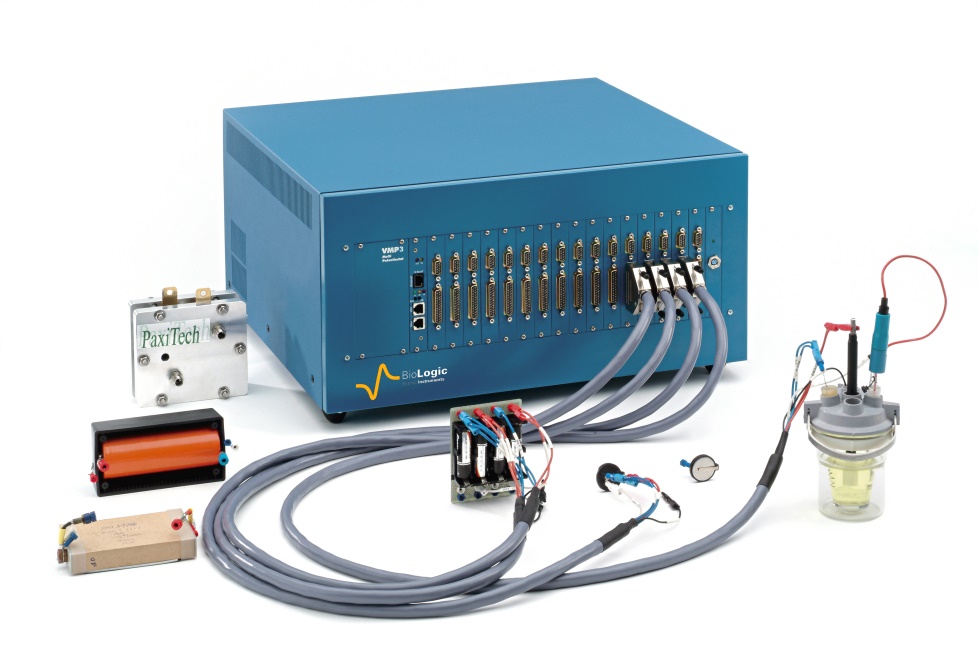

Courtesy - stinstruments
The linear polarization resistance (LPR) technique has become one of the most popular and well-established corrosion measurement techniques. It determines the instantaneous corrosion rate of reinforcing steel in concrete. The technique is rapid and non-intrusive. This method provides more detailed information than a simple potential survey and enables a more detailed assessment of the structural condition. It is also a major tool in deciding upon the optimum remedial strategy to be adopted.
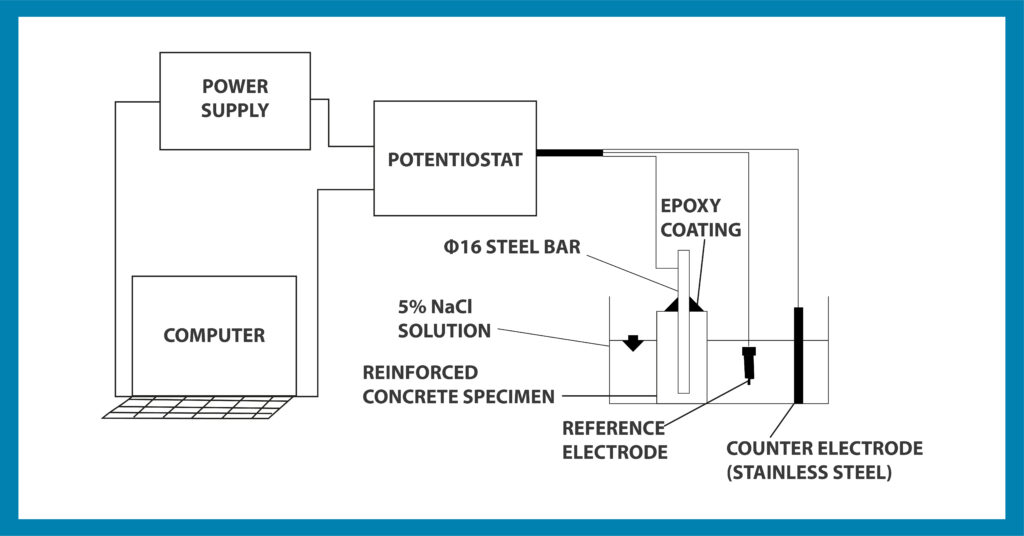
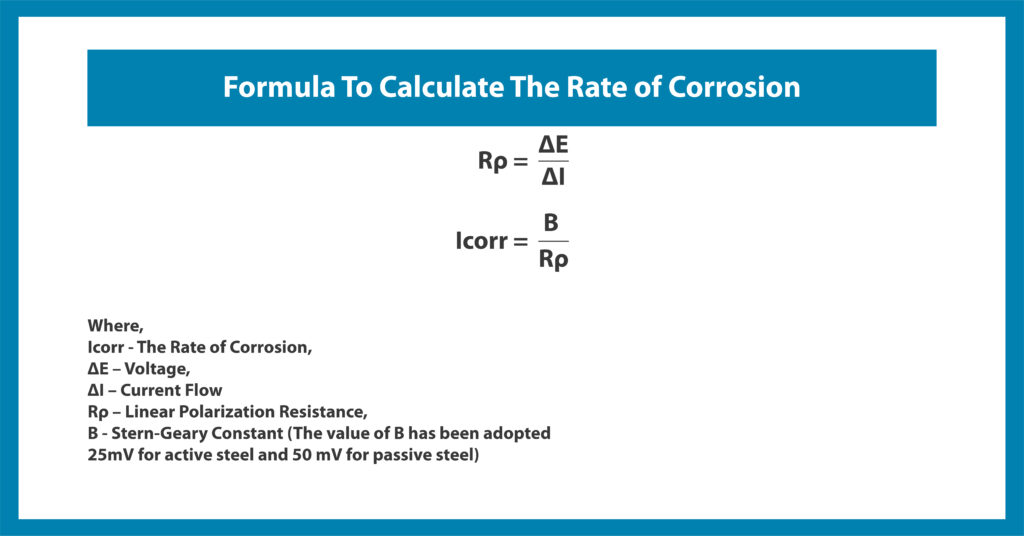
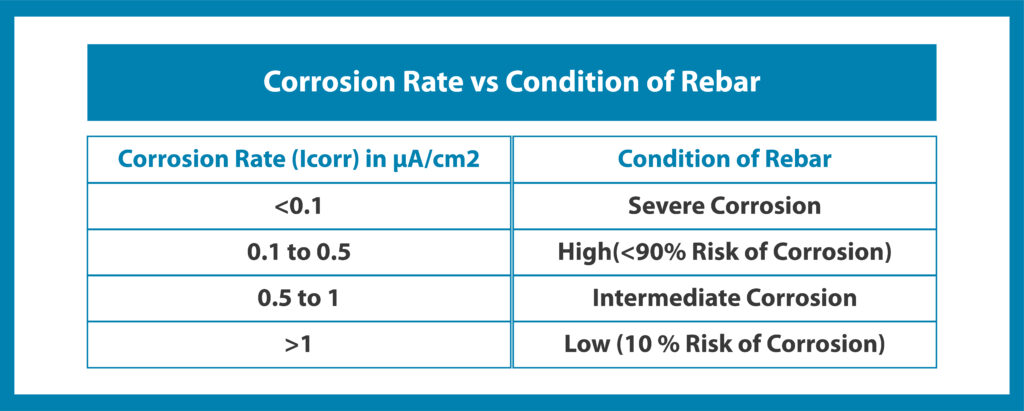
As per the setup shown in the figure, a potentiostat instrument connected to the computer measures the corrosion rate (Icorr). The formula below calculates the rate of corrosion, and the results are compared with those in the following table:
05. Vibrating Wire and Electrical Strain Gauges
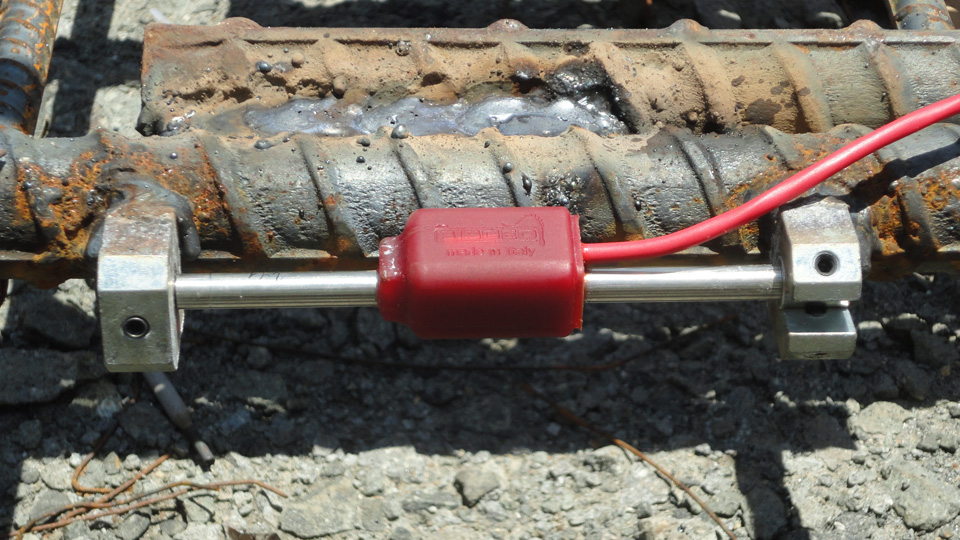

Courtesy - sisgeo
Along with the sensors, a vibrating wire and strain gauge are used to measure the stress and strain in the concrete structure. The results are directly displayed on the output device. It is also used successfully in structural health monitoring (SHM), which is done nowadays in old buildings, bridges and many other projects. In addition, it is used to detect the formation of internal cracks in concrete. Gharpedia has written a detailed article on how to avoid cracks in the concrete. To proceed, click on the below link:
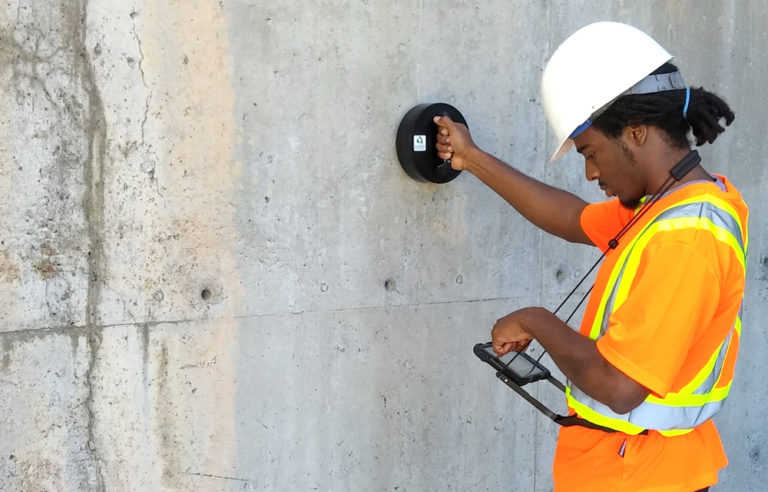
06. Cover Thickness Method
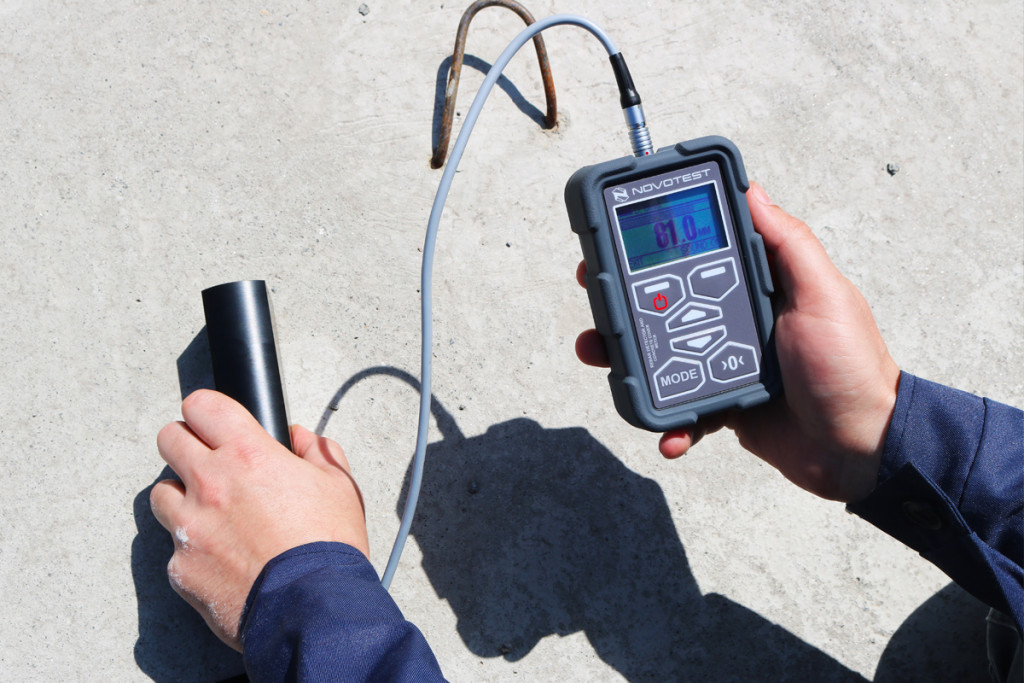

Courtesy - Novotest
In this corrosion monitoring technique, a cover meter or a profometer is generally used for measuring concrete cover. It’s able to detect rebar size, direction and position. The location of longitudinal main bars and secondary tranverse reinforcing bars is established by moving the instrument along the surface of the concrete. The meter needle also indicates a maximum deflection when the axis of the instrument is parallel to and directly over the axis of a reinforcing bar or a group of bars.
Know the importance of concrete cover in reinforced concrete structures-
07. Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Method (USPV)
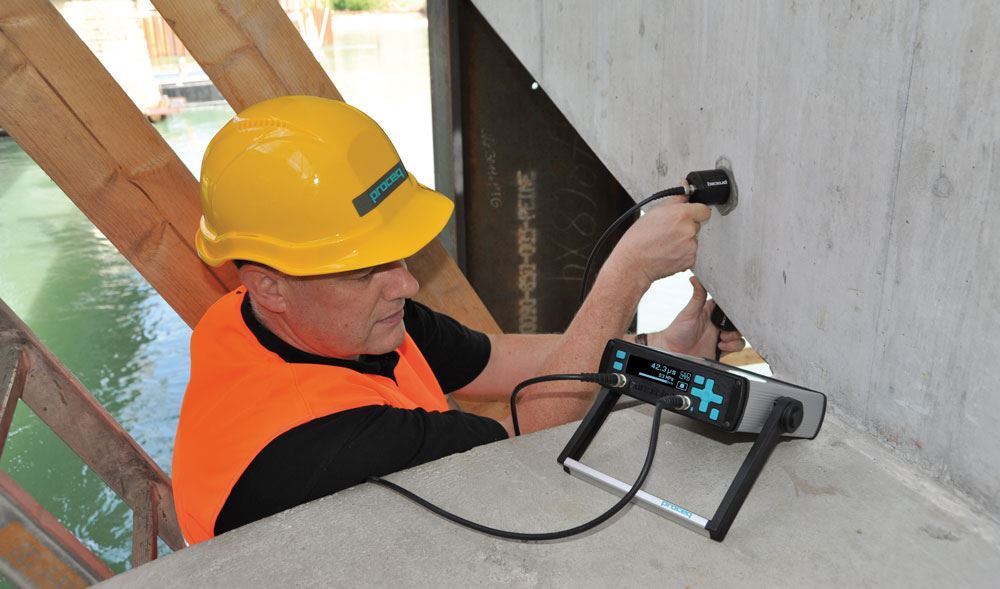

Courtesy - globallgilson
The Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity method (USPV) is a non-destructive corrosion measurement technique. It involves measuring the speed of sound through materials in order to predict material strength and detect the presence of internal flaws such as cracking, voids, honeycomb, decay and other damage. The main advantage of the ultrasonic test is its ability to find general changes in condition, such as areas of weak concrete in a generally sound structure.
Know the factors affecting ultrasonic pulse velocity-
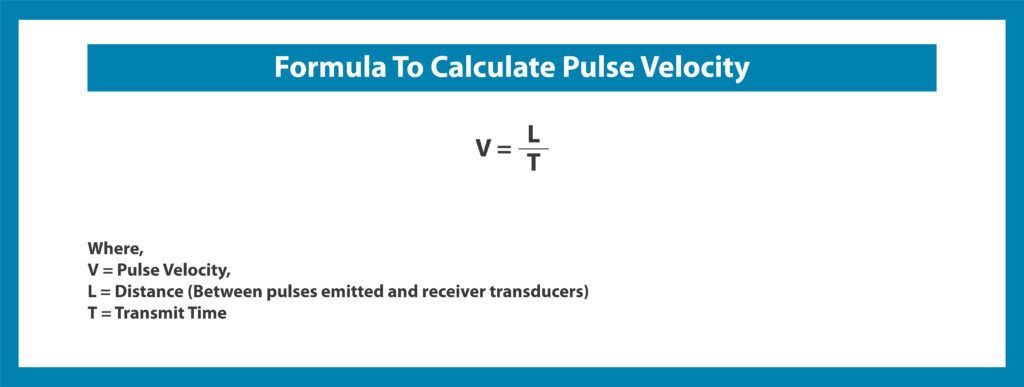
The following formula has been used to calculate pulse velocity:
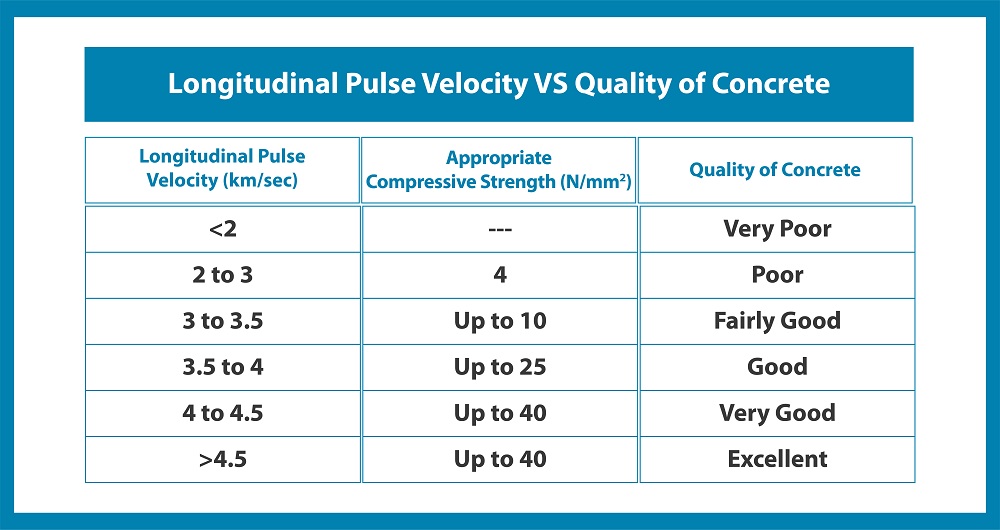
The following table shows the pulse velocity vs quality of concrete.
08. X-ray /Gamma Radiography Method
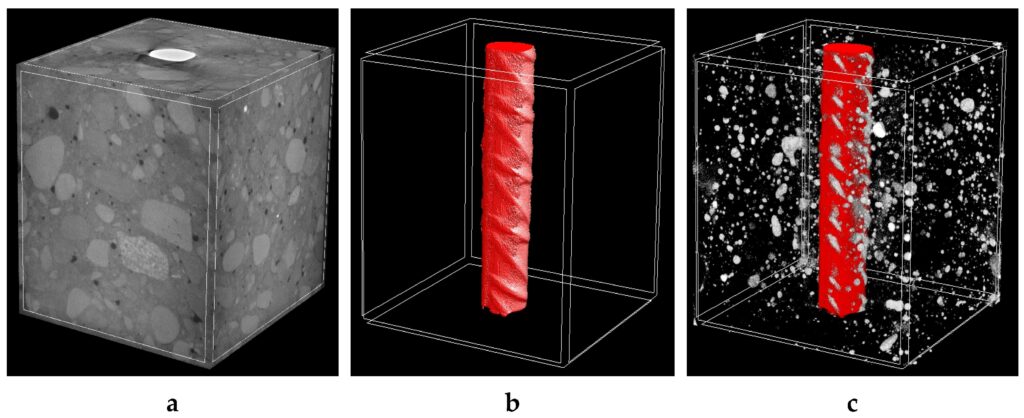
Courtesy - mdpi
Radiography methods use radioactive isotopes for concrete testing. It is a reliable method for detecting internal cracks and voids. Here, photo-images are generated to locate the defect area or spot in the concrete structure. However, it is also a costly method. The figure shows the x-rays of the concrete cube with reinforcement, along with defect spots, voids and cavities.
09. Infrared Thermograph Method
The infrared thermograph method is based on the spectroscope principle; the electromagnetic wave is absorbed and reflected, and the image is formed, as shown in the figure.
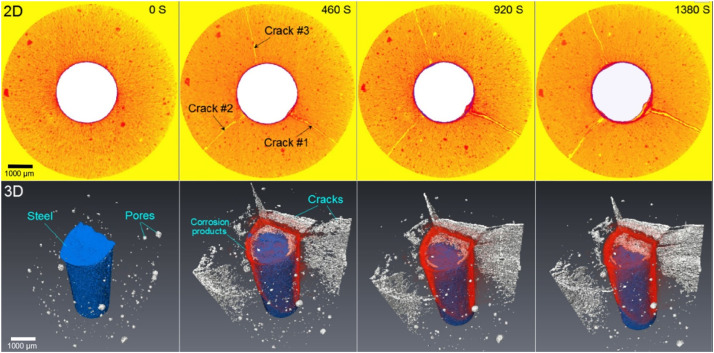
Courtesy - ars.els.cdn.com
The bridge section with the damaged zone is depicted in the picture below as an example of how the new infrared thermograph technology produces a favourable result.
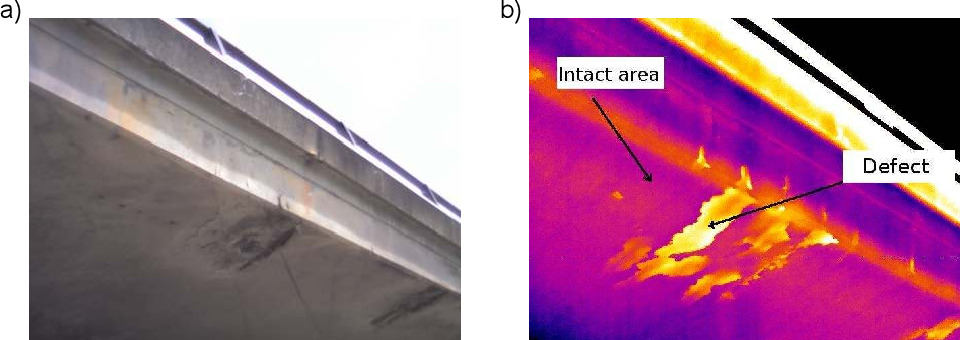
Courtesy - d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net
Gharpedia has also written a blog on non-destructive concrete tests for structure strength. Click on the below link to read-
Concrete Corrosion Control Methods
The following concrete corrosion control methods are used to prevent corrosion in reinforced concrete structures:
- Metallurgical Methods
- Corrosion Inhibitors
- Coating To Reinforcement
- Fusion Bond Epoxy Coating
- Galvanized Reinforcement
- Cathodic Protection
- Coating to Concrete
- Design and Detailing As Per Indian Standards
To learn how to repair corrosion-damaged concrete, follow the link below.
Summing Up
On a final note, as technology and engineering advancements are taking place at a rapid rate, many of these corrosion monitoring methods are now available in one instrument. Almost all parameters are measured, and you get the output directly on a laptop or tablet connected to the corrosion measuring device. A direct report is also prepared on the output device. With better and more efficient corrosion monitoring methods, one can save resources and prevent major accidents in construction technology.
In case you want to know more about the repair of concrete, click on the below link:
5 Right Steps for Repairing of Concrete
Image Courtesy: Image 2, Image 4, Image 8(a), Image 8(b), Image 10, Image 14, Image 15, Image 16, Image 19, Image 20, Image 21
FAQs on Corrosion Monitoring Techniques
1. What is Corrosion Monitoring in Reinforced Concrete Structures?
Corrosion monitoring is the process of detecting and assessing steel corrosion in concrete to prevent structural failures. It helps in predicting damage, planning repairs, and extending the life of structures like bridges, buildings, and dams.
2. Why is Corrosion Monitoring Important in Concrete Structures?
Monitoring corrosion is crucial because undetected corrosion weakens steel reinforcement, leading to cracks, spalling, and even collapse. Early detection through corrosion monitoringsaves repair costs and enhances safety.
3. What are the Main Corrosion Monitoring Methods Used in RCC?
Common methods include Half-Cell Potential (HCP), Concrete Resistivity,Linear Polarization Resistance (LPR),Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (USPV), and Infrared Thermography. These non-destructive techniques accurately evaluate corrosion without damaging the structure.
4. Which Corrosion Monitoring Technique is the Most Reliable?
The Linear Polarisation Resistance (LPR) method is considered one of the most accurate and reliable techniques. It provides real-time data on corrosion rate and steel condition, helping engineers decide on timely maintenance.
5. How can Corrosion in Reinforced Concrete be Prevented?
Corrosion can be reduced by using coated or galvanised reinforcement,cathodic protection, corrosion inhibitors, adequate concrete cover, and following IS code guidelinesduring design and construction.
Author Bio
Mihir Solanki –
References
Saraswathy Velu (2007) in Corrosion Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete Structures – A Review in January 2007 International Journal of Electrochemical Science 2(1), DOI:10.1016/S1452-3981(23)17049-0, License CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 [online] Available From: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/26495162_Corrosion_Monitoring_of_Reinforced_Concrete_Structures_-_A_Review



































