Concrete is an important material for the construction industry. It is a mixture of cement, sand, aggregate, admixtures and water. Concrete mix is designed to accommodate a wide range of mechanical and durability properties to encounter the design requirements of a structure. Hence while working with concrete, there are many factors that are supposed to be checked in fresh condition as well as in the hardened condition. Such as in freshly mixed concrete, workability test is most important and in the hardened state, destructive tests like compressive strength test- cube test, tensile strength test and non- destructive tests like rebound hammer test, ultrasonic pulse velocity test etc. are important.
The compressive strength of concrete is the most common performance attribute which is used by the engineer when designing the structures. The compressive strength of concrete ensures that the delivered concrete mix will meet the requirements of the specific strength as designed by the engineer according to the work specifications and requirements. The results of compressive strength test of concrete give the idea regarding quality control, acceptance of concrete mix, structures strength estimation, the durability of concrete, healthy life of the structure etc.
What is Compressive Strength of Concrete?
Compression force is the physical force which applied in the inward direction on an object and causing it to become compacted. Compressive strength indicates the resistance power of the material or structure under the condition of compression. Compressive strength shows that how much the material or structure can resist the failure in the form of cracks and fissure. Any building element first needs to be strong enough to bear a load of similar units compress it, i.e. bricks over bricks and so on. Hence it is compressive strength which is very important. We have already discussed the test to check compressive strength of brick. Here we discuss the test to check compressive strength of concrete.
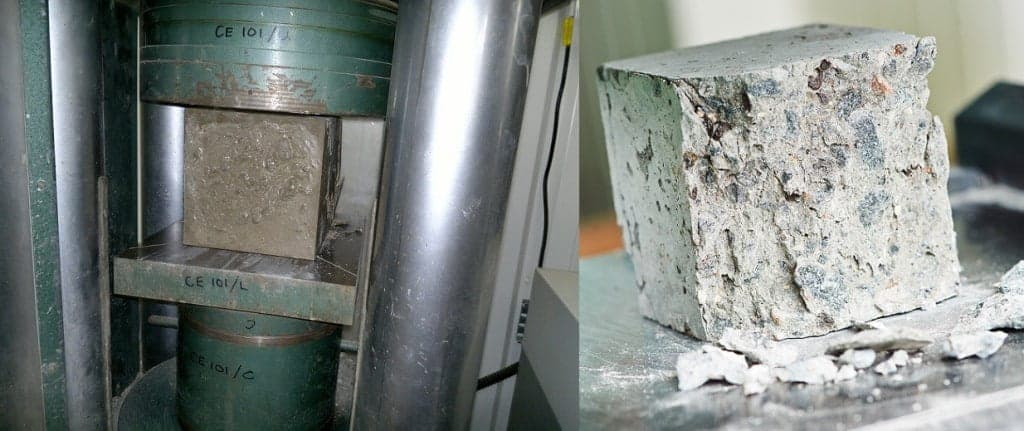
The compressive strength of concrete is measured by breaking concrete specimens in a compression testing machine or a universal testing machine. The compressive strength of concrete is calculated from the failure load divided by the cross-sectional area of specimens which is resisting the load. The compressive strength of concrete is measured in units of psi (pound-force per square inch) or MPa (megapascals), N/mm2 etc. The compression test is carried out on specimens like cube mould, cylindrical mould and prism mould.
In India, cube mould is most commonly used for the compression test and cylindrical mould is widely used in countries like America and England. Selection of concrete cube mould size for the test depend on the size of aggregate to be used in the concrete mix. Mostly 150 mm * 150 mm * 150 mm size of concrete cube mould is used for the cube test. Cylindrical mould is available in size of 150 mm internal diameter and 300 mm height.
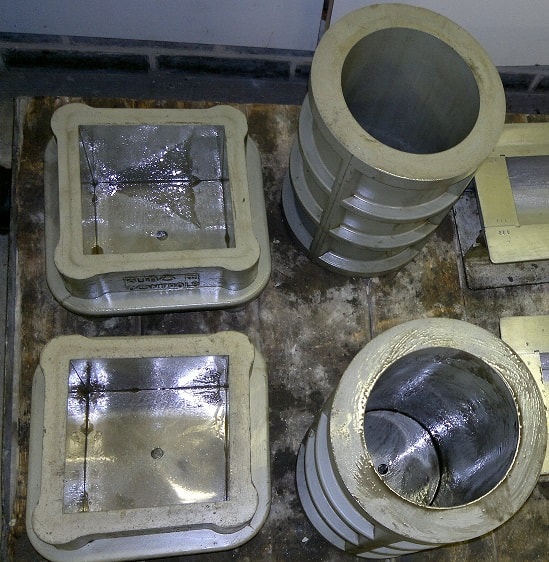

Cube Mould and Cylindrical Mould
Here, the cube test has been described to measure the compressive strength of concrete.
Standard Guidelines for Compressive Strength Test of Concrete
- IS: 516-1959
- ASTM C39/ C39M
- BS EN 12390: 2000
Test Apparatus and Material Required for Cube Test
(A) Apparatus for Cube Test:
- Compression Testing Machine or Universal Testing Machine
- Test Specimens: Concrete cube mould of size 150 mm * 150 mm * 150 mm. 100 mm size cubes may also be used as an alternative.
- Vibrating Machine
- Weighing Machine
- Gauging Trowel
- Measuring Cylinder
- Curing Tank
- Tray
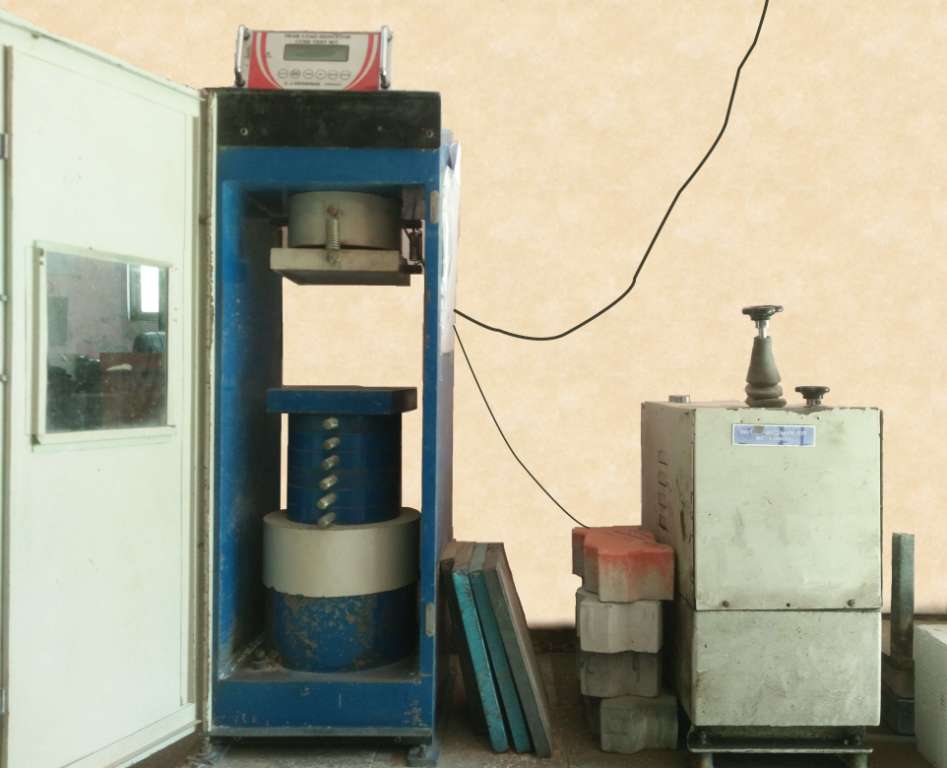

Compression Testing Machine
(B) Material Required:
- Cement, sand, aggregate and water.
Test Procedure for Compressive Strength of Concrete
01. Mixing of Material for Cube Test
The material can be in mixed in two different methods, either by hand mixing or in a laboratory batch mixer, without loss of water or other ingredients. If you want to know more about the mixing of concrete then refer different methods for mixing concrete.
Hand Mixing:
- The concrete batch is mixed on a watertight and non-absorbent platform with a shovel, trowel or another similarly suitable implement.
- First, cement and fine aggregate are mixed in a dry condition until the mixture is thoroughly blended and get a uniform colour.
- Then, coarse aggregate is added in the dry mix of cement and fine aggregate and mixed until the coarse aggregate is uniformly distributed throughout the batch.
- After that, water is added and the entire batch is mixed until the concrete appears to be homogeneous and get the desired consistency.
02. Preparation of Test Specimen for Concrete Cube Test
- Firstly, clean the concrete cube mould and apply the oil or another lubricant on the inner surfaces of the cube mould.
- Immediately after the concrete mixing, concrete is placed in the concrete cube mould in the three layers of around 50 mm thickness.
- For removing the entrained air and avoiding honeycombing and segregation, concrete should be stroked 35 times per layer for 150 mm cubes and 25 stokes for 100 mm using a tamping steel rod and then compacted by vibration using a vibrating table.
- After that finish the top surface of the cube mould in the mould by smoothening the surface with the blade of a trowel.

Concrete Cube
03. Curing of Cube Test Specimens
- The test specimens are to be stored in a vibration-free place and in the moist air of at least 90% relative humidity. The temperature of 27°C ± 2°C is to be maintained for 24 hours ± 1 hour from the time of addition of water to the dry ingredients
- After this, the specimens are marked with a grade of concrete, date and organization name etc. and then the cube moulds are removed. The cubes are submerged in the clean fresh water until taken out for testing.
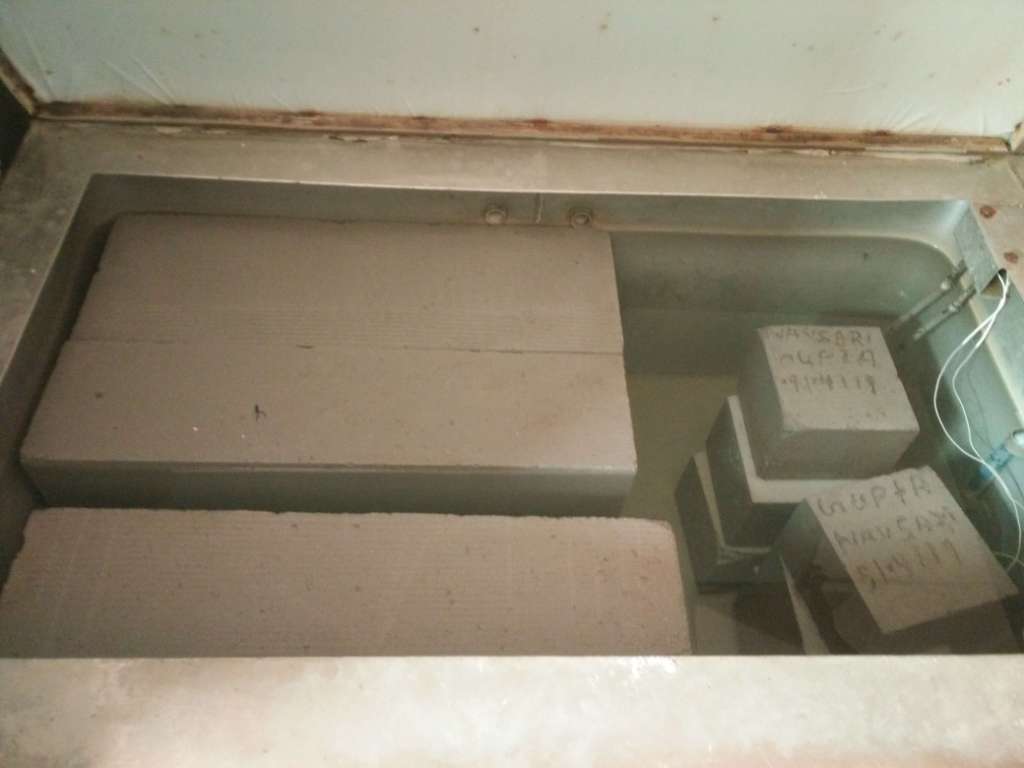

Curing of Concrete Cube
Age of Specimens at Test:
- Compressive strength test is conducted at standard ages of test specimens. Commonly it is tested at 3, 7 and 28 days.
Number of Specimens at a Time of Cube Testing:
- It is preferable at least three specimens from different batches are made for testing at each selected age. As that an example, 3 cubes specimen are tested after 3 days, 3 cubes specimen are tested after 7 days and another 3 cubes specimen are tested after 28 days i.e. in that case you will have to cast nine cubes while concreting.
04. Procedure for Testing the Cube Specimens
- Remove the specimens from the water just before the testing and wiped off the surface water and grit from the specimens. Don’t let dry it, cube test is conducted in wet condition of specimens.
- Take the dimensions and weight of the cube specimens.
- Clean and remove any loose sand or other material from the bearing surface of the testing machine.
- Now, place the cube specimen in the compression testing machine or universal testing machine.
- Cube specimen is placed in the machine in such a manner that the load can be applied to opposite sides of the cubes as cast.
- The cube specimen should be aligned centrally on the base plate of the machine.
- Rotate the movable portion of the machine gently by the hand; hence the plate touches the top surface of the cube specimen and load can be applied uniformly and without any shock.
- Apply the load gradually and continuously at the rate of 140 kg/cm2/minute until the cube specimen fails.
- Note down the load at which the cube specimen has failed and note any unusual features in the type of failure.
- Read and note the reading on dial gauge in right unit.
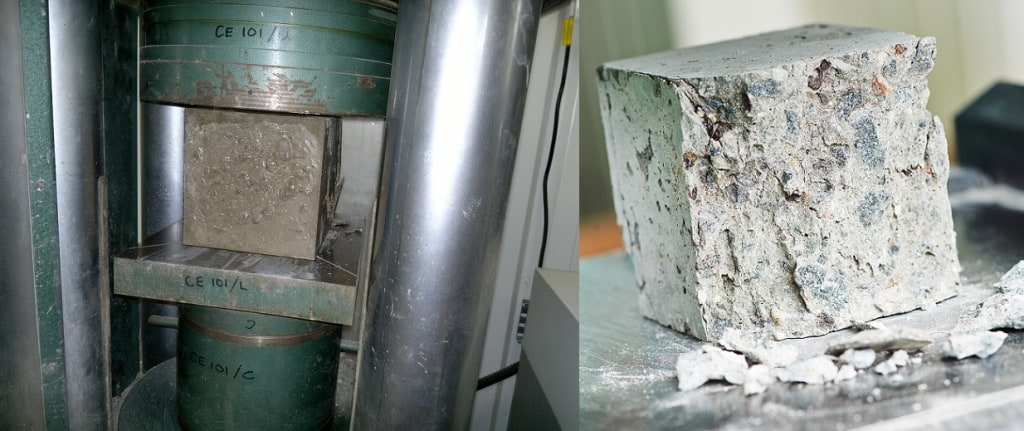

Concrete Cube Test and Its Failure
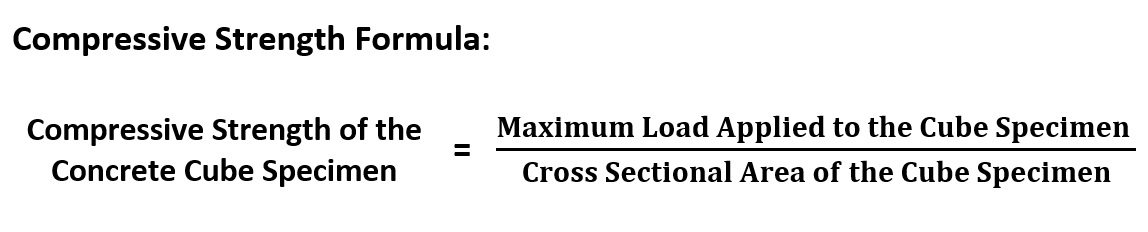
Result Calculation of Compressive Strength Test of Concrete
Points to be Taken Care of
(a) At the Time of Curing of Cube Specimens:
- The water in which the cube specimens are submerged should be renewed every seven days and should be maintained at a temperature of 27° ± 2°C.
- The cube specimens shall not be allowed to become dry at any time until they have been taken out and tested.
(b) At the Time of Testing of Cube Specimens:
- Cube specimen should be carefully aligned at the center of the steel plates and no packing should be used between the faces of the test specimen and the steel platen of the testing machine
- Minimum three specimens should be tested at each selected age (days) of testing. If there are any visible or noticeable defects in specimens then do not consider those cube specimens.
- Do not consider the specimens strength, that gives strength differing by more than 15 % from the average value of all the test specimen’s strength.
Recommended Result of Cube Test
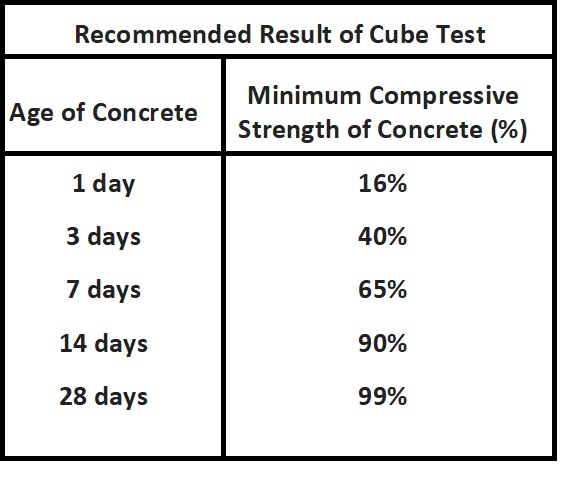
As an example, if the grade of concrete is M25 than the compressive strength of concrete after 3 days should be 10 N/mm2, after 7 days strength should be 17 N/mm2, after 14 days strength should be 23 N/mm2, after 28 days strength should be 25 N/mm2.
Cube test is the most common test conducted on hardened concrete, partly because it is an easy test to perform, and partly because most of the desirable characteristic properties of concrete are qualitatively related to compressive strength of concrete.
Also Read:
Tests to Check the Compressive Strength of Cement
In-Situ Concrete Pull Out Test for Compressive Strength
Hardened Concrete Core Test for Compressive Strength
Penetration Resistance Test for Concrete Compressive Strength































