Table of Contents
Solar energy is an abundant and renewable source of power that harnesses the radiant light and heat from the Sun through various technologies to generate electricity, heat water, power and various applications. It is considered an essential source of renewable energy.
What Is the Definition of Solar Energy?

Solar energy is derived from the sun’s radiation and is one of the most abundant renewable energy sources available. Electromagnetic radiation from the Sun includes visible light, UV rays, and infrared radiation. Solar energy is one of the most popular energy sources in the 21st century, and the world’s richest solar energy resources are found in the United States.
When sunlight hits the solar panels, the photons in the sunlight excite the electrons in the semiconductor material, generating a flow of electricity, which can power appliances, lighting, and other electrical devices in residential, commercial, or industrial settings. Batteries can store extra energy for later consumption or to feed back to the grid.
Due to its lack of dangerous gases or pollutants during operation, solar energy is considered a clean and sustainable source of energy. It gives an alternative to petroleum-based products like natural gas, coal, and petroleum, which are limited resources and produce greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, causing climate change.
Also Read: Complete Guide to Solar Panel Installation
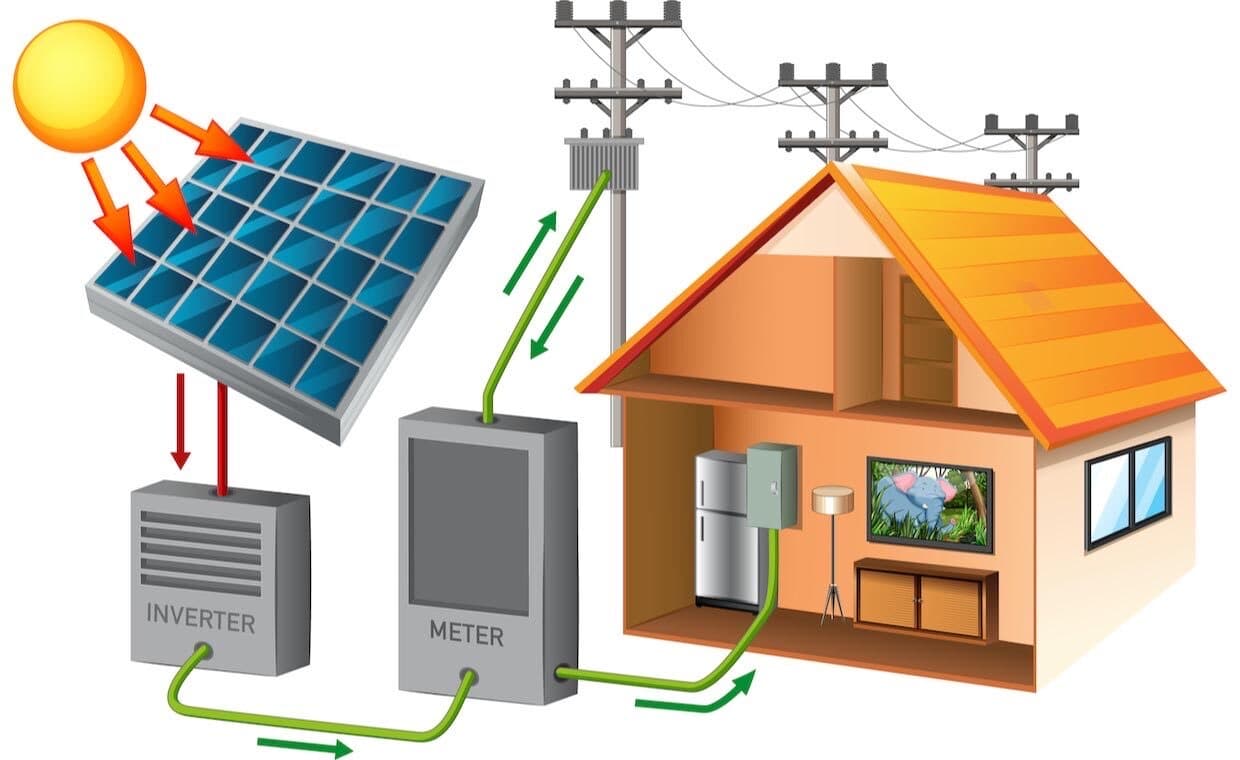
The Basic Fundamentals of Solar Energy

- Sunlight: The sun emits electromagnetic radiation, including visible light and ultraviolet (UV) rays. Sunlight is composed of small packets of energy called photons.
- Photovoltaic Effect: The photovoltaic effect is the process by which certain materials, typically semiconductors like silicon, can generate an electric current when exposed to sunlight. This effect occurs when photons from sunlight strike the surface of a solar cell, releasing electrons from their atoms and creating a flow of electricity.
- Solar Panels: Multiple solar cells are joined together to form an array of solar panels, commonly referred to as photovoltaic (PV) modules. These solar panels are made to absorb sunlight and produce power.
- Inverters: The electricity generated by solar panels is in the form of direct current (DC), which must be converted to alternating current (AC) to be usable in homes and buildings. Inverters perform this conversion, enabling the power to be used by most electrical devices and to be fed into the grid.
- Net Metering: When a solar system generates more electricity than is being consumed, the excess power is returned to the electrical grid. The system owner earns credits or monetary compensation on their electricity bill for their surplus energy.
- Grid Connection: Solar energy systems can either be connected to the electric grid or operate independently as standalone systems. Grid-connected systems allow homeowners to draw electricity from the grid when their solar panels are not producing enough electricity, such as during the night or on cloudy days. David (2015) discusses the components and cost considerations of a home solar PV system.
- Off-grid Systems: Off-grid solar systems, also known as standalone systems, operate independently of the electric grid. They typically include solar panels, a battery bank for energy storage, and inverters to convert DC to AC. These systems are commonly used in areas with limited grid access or by individuals seeking complete energy independence.
Understanding these fundamentals is essential for making informed decisions about adopting solar panels for a home setup. It empowers individuals to effectively implement solar energy solutions in their homes.
Also Read: Home Solar Installation: A Complete Guide
Uses Of Solar Energy in Daily Life

Installing a solar panel for home use is one of the most effective ways to harness solar energy in daily life, providing clean electricity for powering appliances, lighting, and other essential household needs. Let’s look at the uses of solar energy in daily life in detail.
1. Home Appliances

The energy produced can be used to operate heavy machines and household electronic devices such as TVs, fans, and laptops.
2. Heating

The thermal energy produced by the solar cells can be used in various ways, such as heating water, swimming pools, or even rooms.
3. Cooking

You can use a solar cooker as an alternative to traditional cooking methods. Cooking with a solar cooker is easier than you may think.
4. Garden Lighting

Installing solar lights can enhance the aesthetics of any garden or lawn at your home. They come in a variety of styles and can truly make your landscape stand out, especially at night.
5. Home Beautification

Some solar lights or lamps are used as decorative elements in the home. They can be placed in the living room, dining room, bedroom, or outdoors. Available in various colours and designs, these lights add a touch of elegance and luxury to the entire home.
6. Solar EV Charging

Electric vehicles (EVs) have become increasingly popular. However, setting up or locating a trustworthy system for charging remains the biggest obstacle to choosing EVs. Solar energy offers a cost-effective solution for this issue, whereas conventional energy sources can be difficult to access and inefficient to use.
7. Solar-Powered Pump

Water is pumped from the collection source to the tank using solar-powered pumps. Unlike electric pumps, which require a lot of power to perform the same task, solar-powered pumps save on energy costs.
8. Solar Ventilation and Cooling
Solar energy can be used for ventilation and cooling. Solar attic fans, for instance, help regulate temperatures by expelling hot air from the attic, reducing the load on air conditioning systems.
Solar Energy Benefits

Solar energy benefits include significant cost savings, reduced environmental impact, and increased energy independence for homeowners.
- Cost Savings: By using solar panels to generate your own power, you can significantly reduce your monthly electricity bills. Solar energy allows you to offset or even eliminate your reliance on grid electricity, resulting in long-term cost savings.
- Environmental Sustainability: Solar energy is a clean, renewable source of power. Using solar power in your home reduces greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and your carbon footprint. Buonocore et al. (2024) found that expanding solar photovoltaic energy offers significant health and climate benefits.
- Increased Property Value: Solar panels are an attractive feature for homebuyers and can increase the value of your property. Studies have shown that houses equipped with solar energy systems sell faster and at a higher price than similar homes without solar installations.
- Long-Term Durability: Solar panels are designed to be durable and have a long lifespan. Solar panels can last 25 years or more with proper installation and minimal maintenance.
- Opportunity to Learn: Installing solar panels in your home provides an educational opportunity for you and your family. It allows you to learn about renewable energy, energy conservation, and sustainable living.
For a deeper understanding of the advantages and challenges of solar energy, you can explore this comprehensive guide on the pros and cons of solar energy.
Limitations Of Solar Energy

- Upfront Cost: The initial investment required to install a solar energy system can be significant. Costs include the panels, installation, permits, and additional equipment such as inverters and batteries, if needed.
- Weather Dependence: Solar energy production depends on sunlight, meaning that solar panels generate less electricity on cloudy days or at night.
- Space Requirement: Solar panels require a certain amount of space for installation. Limited roof space or shading from nearby trees or buildings can impact the efficiency and output of the system.
- Maintenance and Lifespan: Although solar panels are generally low-maintenance, they still require periodic cleaning and inspections to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Permitting and Regulations: Obtaining permits and adhering to local regulations can add complexity and delay the installation process of a solar energy system.
Also Read: 5 Pros and Cons of Solar Power System: How Reliable Is It Really?
Maintenance Of Solar Energy System

Maintaining a solar energy system involves several tasks to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Here are the key maintenance steps:
- Regular Cleaning:
Dust, debris, bird droppings, and pollen can accumulate on solar panels, reducing their efficiency. Cleaning them every 6–12 months with water and a soft brush is recommended. Avoid using abrasive cleaners or detergents. - Inspection of Inverters:
Inverters are critical for converting DC to AC electricity. Regularly inspect them for error codes or operational issues. Most inverters last 10–15 years and may require replacement during the lifespan of the solar panels. - Monitoring System Performance:
Use monitoring apps or systems to track energy production. A significant drop in output could indicate a problem with the panels, inverter, or wiring. - Inspecting Wiring and Connections:
Check for any visible damage, loose connections, or corrosion in the wiring. Animals like squirrels can sometimes chew through cables. - Checking Mounting Structures:
Ensure that the brackets and mounts securing the solar panels are in good condition, especially after severe weather conditions. - Professional Maintenance:
Schedule professional maintenance every 2–5 years. Experts can assess panel performance, test electrical connections, and perform more thorough cleaning.
In addition to these tips, if you’re interested in learning more about maintaining solar panels at home, be sure to check out our detailed blog.
How to Maintain Your Solar Panels at Home?
Conclusion
In conclusion, installing a solar panel for home use is a smart and forward-thinking investment that brings a wide range of solar energy benefits. From cost savings and increased property value to environmental conservation, solar energy empowers homeowners to take control of their energy usage. A well-designed home solar system not only ensures long-term financial savings and energy independence but also plays vital role in building a cleaner, greener future. Embracing solar power today means investing in a more sustainable tomorrow.
FAQs Related to Solar Panel
01. What Happens to Solar Panels During a Power Outage?
Grid-connected solar systems automatically shut down during power outages to prevent electricity from feeding into the grid and endangering repair workers. However, hybrid or off-grid systems with battery storage can provide backup power during outages.
02. Can Solar Panels Work in Cold Climates or Snowy Regions?
Yes, solar panels are efficient in cold temperatures, as they generate more electricity when operating in cooler conditions. Snow can be an issue if it covers panels, but it often melts quickly due to the panel’s dark surface absorbing heat.
03. Do Solar Panels Work on Cloudy or Rainy Days?
Solar panels still generate electricity during cloudy or rainy days, but their efficiency is reduced. The amount of energy produced depends on the intensity of light penetrating the clouds.
04. How Can I Recycle or Dispose of Old Solar Panels?
Solar panels can be recycled, with components like glass, silicon, and metal frames repurposed. Contact local recycling centers or manufacturers who often offer take-back programs.
05. Is It Possible to Expand a Solar System Later?
Yes, most solar systems are scalable. You can add more panels or increase battery capacity, but ensure the inverter and mounting system can handle the expansion.
Also Read: How Successful are the Residential Rooftop Solar Panels in India?






























