The Building has two main components, one is constructed above the ground level is known as super-structure while another is constructed below the ground level is called sub-structure. Foundation system falls into the category of sub-structure. The foundation is the part of a building that transfers the load of the structure to the ground. The foundation transfers the load of structure in such a manner so that the soil below the footing never undergoes excessive settlement. To resist the excessive settlement, the footing should be designed considering the factors like type of building, type of soil, the minimum depth of foundation, site topography, etc. The groundwater level, underground water courses, old drains, pits, wells, the old foundation, etc, and presence of excessive sulphates or other injurious compounds in the groundwater and soil should also be considered at the time of footing design.
The minimum depth of foundation is the most important factor which affects the stability of footings. Hence the foundation should be located at a minimum depth, that the footing gets maximum stability and it can easily transfer the load of the structure to the ground.
Here we discuss the minimum depth of foundation based on the type of soil. If you want to know more about types of footings and important criteria to choose the right foundation then read various types of footings for your house and 10 important criteria to choose the right foundation for your house.
What is the Minimum Depth of Foundation?
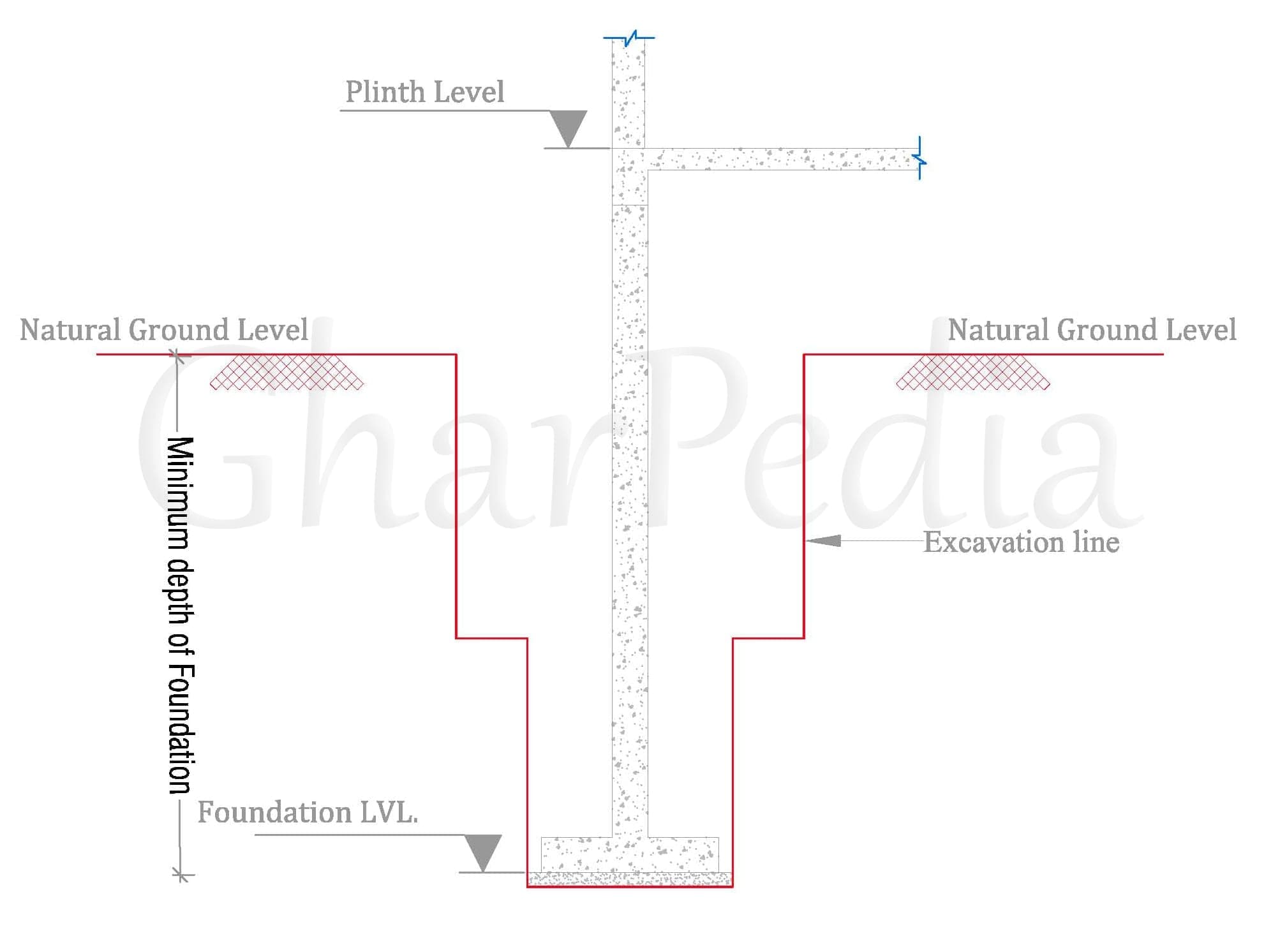
The minimum depth of foundation is a minimum vertical distance between the base of the footing and the natural ground surface.
Minimum Depth of Foundation in the Soil which changes its volume:
Soil changes its volume with changes in seasons. The change in volume of soil is caused by alternate wetting and drying due to the changes in seasons. The foundation should be located below the depth to where the soil does not change its volume. This depth usually does not exceed about 1m, except many parts of the world where the subsoil consists of clay (Expansive Soil or Black Cotton Soil) that shrink and swell significantly.
The clay or soil like black cotton soil may be stiff enough to sustain a load of 200 or 300 KPa (2.04 to 3.06 kg/cm2 or 0.2 to 0.3 N/mm2) without settlements thus it is possible to make temporary or light structures without damage. In case of heavy structures like single or double storied house, it is advisable to rest the foundation minimum 300mm below the depth to where the cracks cease.
In case of excavation in or around ditch, pond, watercourse, filled up ground or similar condition adjoining or adjacent to the subsoil, the foundation should be located down to a depth where the effect of such conditions ceases. Also, provide the retaining walls (lateral support or similar works) for shielding the effects of such adverse elements.
In case of the rock or such other weather resistant ground, the foundation should be extended to a depth of at least 50 cm below the natural ground level to prevent the slipping or other unwanted movements.
If the groundwater table is close to the foundation, then the soil below the foundation moves due to the seepage of water. Hence the foundation should also be located below the depth where the groundwater table does not affect the bottom of the footing. Ideally it should be located either in wet or dry zone but it should not be located in a zone which continuously becomes wet and dry as per seasonal variations.
Minimum Depth of Foundation in Weakened Soil:
The foundation should also be located below the depth where the soil is not weakened by holes of tree roots or cavities produced by burrowing animals or worms. The weakened soil can be found by excavating test pits for the foundation. Observe the holes and the cavities on the face of test pit and locate the foundation below the depth of it. The withdrawal of water from the ground by the root systems of large trees close to the house may also be the reason for the differential settlement. Hence remove the trees close to the house and then rest the foundation at the suitable depth. It is advisable that the tree which grows to large size should be placed 8m away from the foundations.
Minimum Depth of Foundation in Cold Regions:
In cold regions like the US, the foundation of outside column or walls should be located below the depth where the frost may cause a perceptible heave. In this region, the depth may be as great as 1.5m. Rest the outside walls or columns of heated buildings may require deeper foundation than the inside columns.
Minimum Depth of Foundation when Soil has Soluble Salt or Chemicals:
In some regions, the foundation concrete may deteriorate due to soluble salt, sulphate or other dangerous chemicals presents in the groundwater or soil. In the industrial area, the land can be contaminated by the dump of chemical waste which may also deteriorate the concrete of foundation. To protect the foundation in both cases, cast the foundation with the M20 grade or still higher grade of the concrete. Use special cements like high alumina cement, super sulphated cement or portland pozzolana cement for concrete. If possible, make the concrete impermeable. Also, apply the bituminous coating on the surface of foundation which will protect the concrete from the infiltration of water. Rest the foundation below the depth to where the effects of soluble salts or chemicals cease and if possible, replace all the excavated soil by filling the new yellow soil.
Minimum Depth of Foundation when there is Difference in Ground Level:
Following are the best-suited criteria for the minimum depth of foundation when there is the difference in level or ground is sloping.
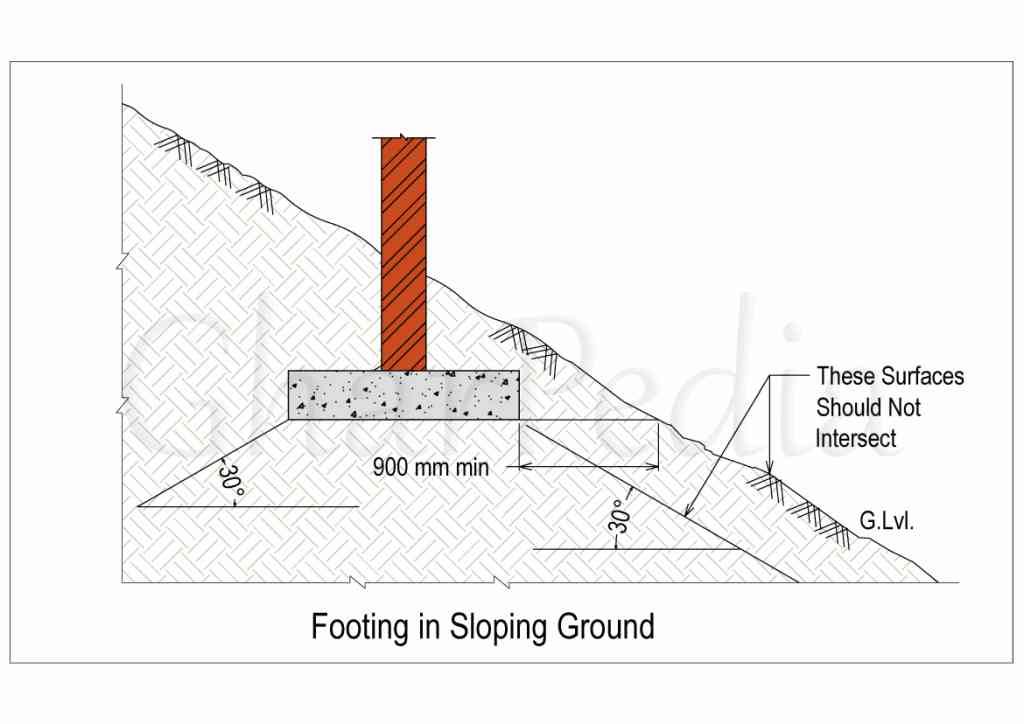
01. The minimum depth of footing in sloping ground with the rock, the horizontal distance shall be at least 600 mm or 2 feet from the lower edge of the footing. In case of sloping ground with normal soil, the horizontal distance shall be 900 mm or 3 feet from the lower edge of footing. The sloping surface shall not intersect a frustum of bearing material and the sides of footing should make an angle of 30 degrees with the horizontal axis.
Understand this criterion with the help of the following figure.
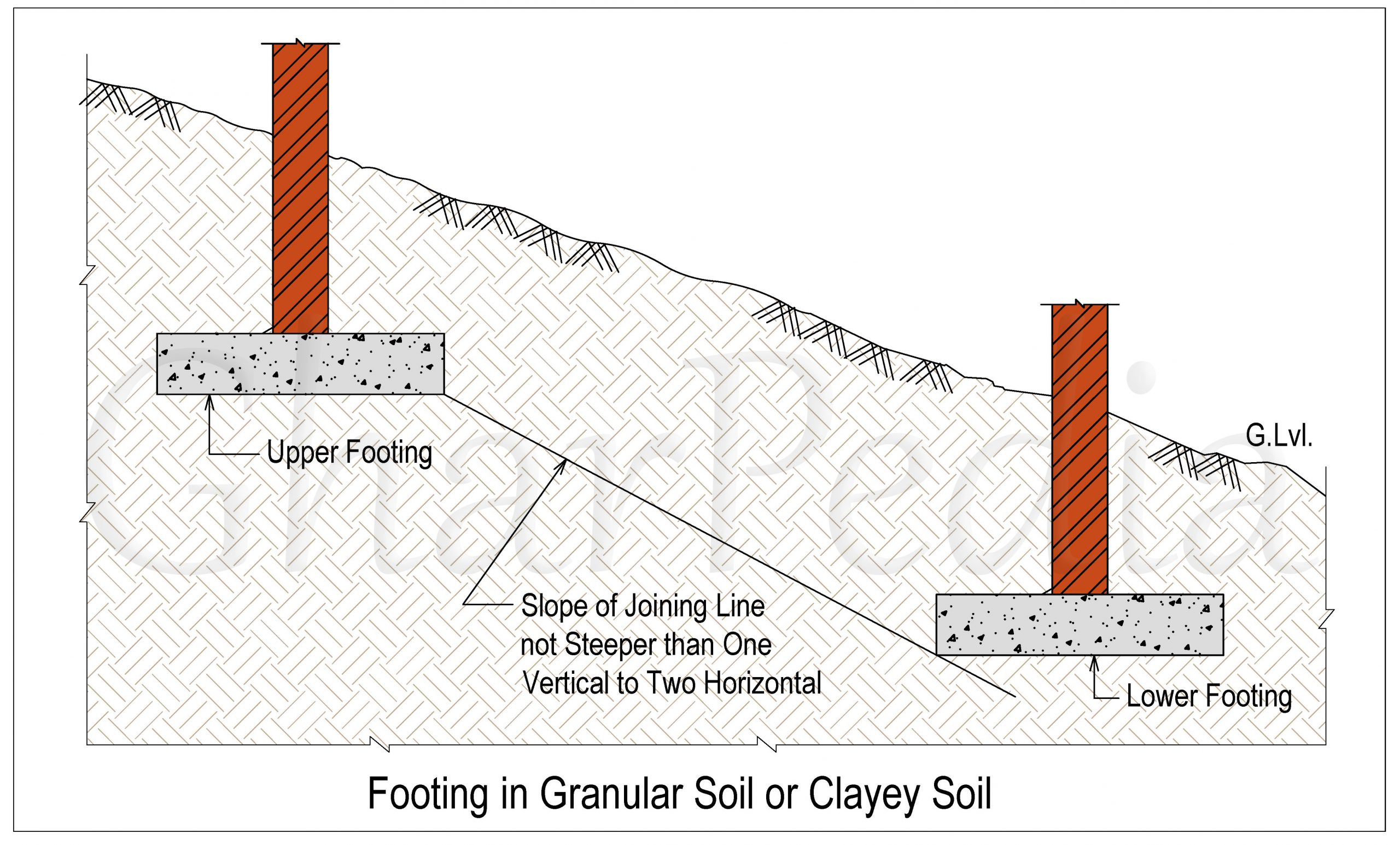
02. In case of footing in granular soil, a line drawn between the lower adjacent sides of adjacent footing shall not have a steeper slope than one vertical to two horizontal.
03. In case of footing in clayey soil, a line drawn between the lower adjacent side of the upper footing and the upper adjacent side of lower footing shall not have a slope steeper than one vertical to two horizontal.
Understand 2nd and 3rd criteria with the help of the following figure.
Aforementioned three criteria shall not apply where the provision of lateral support i.e. retaining wall are provided all around and when the factor of safety of foundation soil against shearing is not more than four.
Thus it is due to the minimum depth of foundation, the structure resists the lateral pressure or thrusts and it also prevents the tilting, sliding or turning. Hence the structure gets stability when the foundations are located based on the criteria of minimum depth which must never be located. Remember it is very difficult to retrofit the foundation, and impossible to take it deeper once laid. So never economise on foundation. It is always unwise to economize on structural engineer as well as foundations.
Must Read:
Signs of Foundation Problems in Your House
Know the Causes of your Foundation Cracks
Reasons for Building Collapse due to the Foundation Failures






























