Constructing a house is one of the most crucial issues concerning any individual. It brings thousands of questions, doubts, and thoughts in mind regarding what to choose and what not and how to go about planning the construction. There are infinite beliefs, rules, regulations and principles, which need your prior attention. This article will give you an idea about general primary principles of building planning that one should consider while planning a house or a building.
Principles of Building Planning
Firstly, let’s understand what does principle of planning mean?
“The concept of positioning all the elements and units of a building in a systematic and practical manner to have the maximum and best utilization of the available space, area and facilities is termed as Principles of Building Planning.”
There are several principles that affect the planning of a building. This article will give you a brief knowledge of all those principles.
Effect of Climatic Condition
Before planning a building or starting any construction, architects and planner must ensure the climatic condition of the particular location. Usually, local climate plays important role in the construction. Mainly, temperature (i.e. cold and hot), humidity, rain, snow, wind, and sunlight are the climatic factors that affect the building. All these notable factors play an important role in choosing the position of rooms, doors, windows, ventilation, balconies, and all other units of a building.
Apart from this, materials and techniques used for the construction highly depend upon the weather. Illustrating with it an example, in a country like India; majority regions experience a rainy season for the span of the 3-4 months, while the rest is winter and summer. This favours the houses which are built with brick, cement, concrete and also having a roof with terrace. Whereas, if we talk about the cold countries; there is snowfall for many months. Hence a roof without a terrace is preferred and at most wood is used as construction materials. Understanding this, we can sum up that the building’s major features depend upon the climatic condition of the location.
Are you looking for information on different types of roofs, which is suitable for various weather conditions? Here’s our article that will give you the details.
Now, after considering the climatic effects on principles of building planning, let us go through the other major principles of the same.
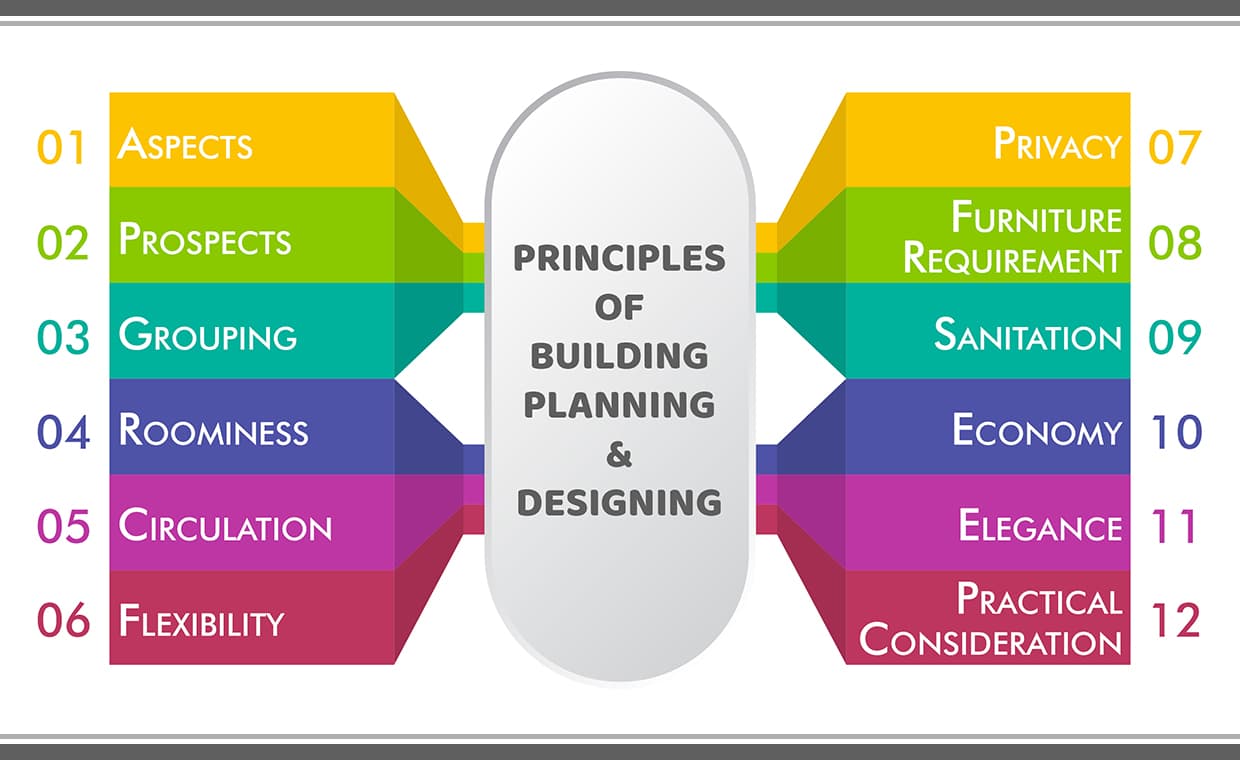
01. Aspects
02. Prospects
03. Grouping
04. Roominess
05. Circulation
06. Flexibility
07. Privacy
08. Furniture Requirement
09. Sanitation
10. Economy
11. Elegance
12. Practical Consideration
The above was short map. It’s time to learn each of them individually.
01. What is an ASPECT in building planning?
A building is a complete constitute of different rooms and blocks in it. All the rooms are located according to the standard use of components considering the proper access of natural resources, i.e., sunlight and wind.
According to the research paper “Planning, Designing and Estimation of High Ceiling Residential Building (G+1)” presented by ‘J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman’&’ P.Soundarya’, ASPECT is defined as a significant arrangement of doors and windows in abuilding, which are enough and efficient to provide sunlight, hygiene, wind, and eco-friendly environment. There must be sufficient light and ventilation in each room and across the house.
The aspect of building can be achieved by arranging the rooms, kitchen, veranda, and many other components in proper directions. The ways to cover the direction with advisable aspect is given below:
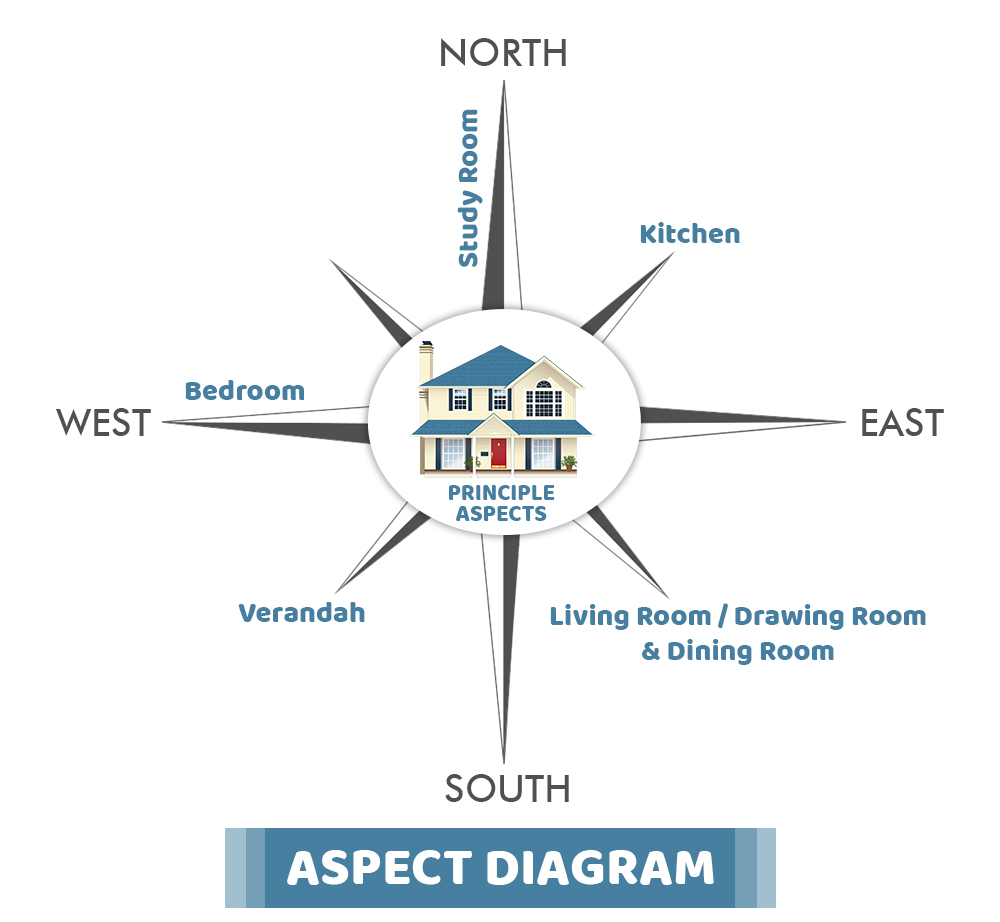
The above diagram indicates the appropriate directions which should be preferred for the positioning of various rooms in a house.
After understanding aspect, it becomes necessary to have good circulation of sunlight in a house. The following link features the importance and ways to improve sunlight naturally.
02. What are the PROSPECT principles in building planning?
In these modern times, all the buildings and constructions are aimed to achieve an aesthetically appealing look from both exteriors and interior considerations. The appearance of a house or a building is defined as PROSPECT.
The standards are raised to accomplish the building’s pleasant look by locating doors and windows at an accurate location to view nature’s beauty and avoid unwanted attributes from getting entry into the house.
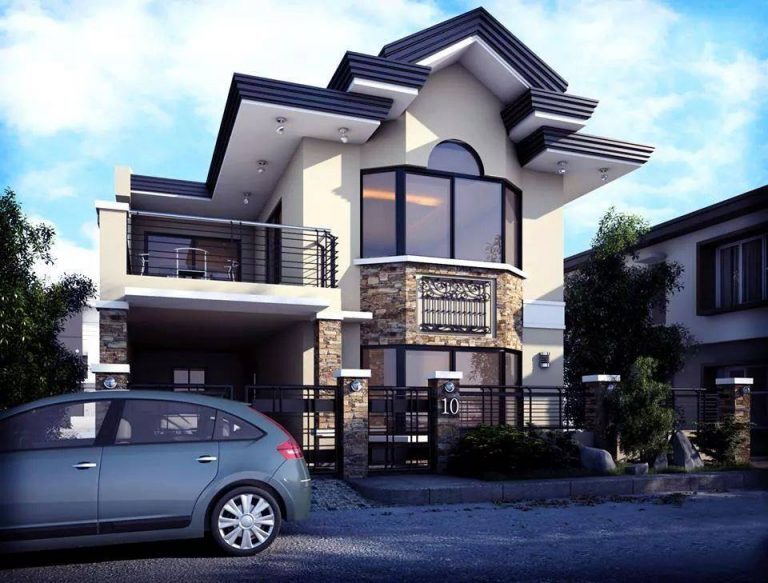

The image shows the exterior view in an aesthetic way in which the building reflects the prospect principle.

One of the other factors of the prospect is to have a pleasant view outside a house from doors, windows, balconies as clearly as possible, as shown in the above image.
03. What does the GROUPING mean in building planning?
The simple meaning of GROUPING was described by ‘S. P. Arora’ & ‘S. P. Bindra’[376] (Author of Building Construction) that it is to organize the different rooms in such a way that they are adequately interconnected with each other to form a functional and practical layout of the house. The accessibility of all the rooms is interlinked with each other, and this provision can be satisfied by grouping.
To understand the theory of grouping, let us consider an example. In a simple sense, the dining room should be near to the kitchen so that both the units can be easily used for the service. Similarly, water closets should be close to the bedrooms and living room but not close to the kitchen.
An idea of the grouping is applicable not only in a residential building but also applies to commercial and industrial buildings. In industries, the storage rooms must be near the road to ease the loading and unloading of the goods.
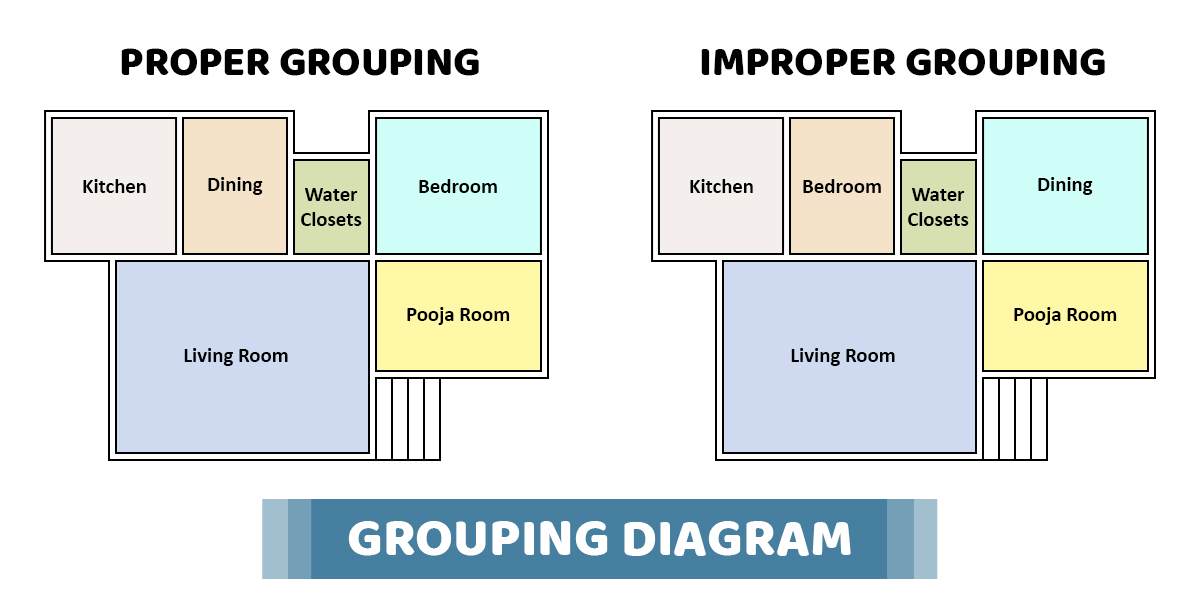
The above figure indicates the common groups of rooms, which should be combined together while planning a residential building.
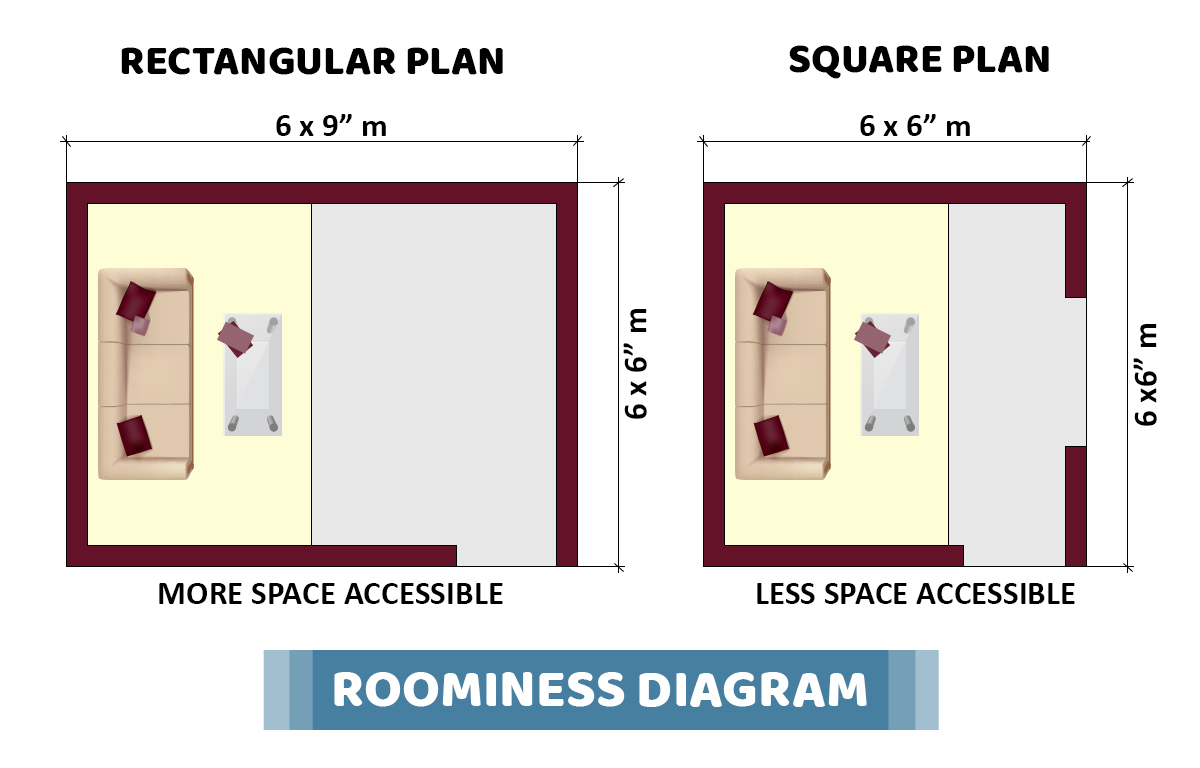
04. How ROOMINESS can be a principles of building planning?
The meaning of ROOMINESS is to maximize the advantage of the available space from the minimum dimension of a room. Both the size and shape of the room play a vital role in providing roominess.
Here are the few points to understand the roominess practically.
- A square room seems small in size when compared to a rectangular room.
- It is always advisable to plan a rectangular room with a proportion of 1.2 to 1.5 times the ratio of the length to the breadth. The increase in ratio due to length gives the tunnel experience as it looks longer.
- Also, the height should neither be too high nor tooless that the ceiling becomes a hindrance.
- Floors, ceilings, walls, ceiling, lifts, furniture, and all such elements should be appropriately placed to offer more space in the rooms.
Are you worried about what should be the advantageous size of different rooms? Here we come up with the solution by providing a link to know the same.
05. How CIRCULATION act as a principle of building planning?
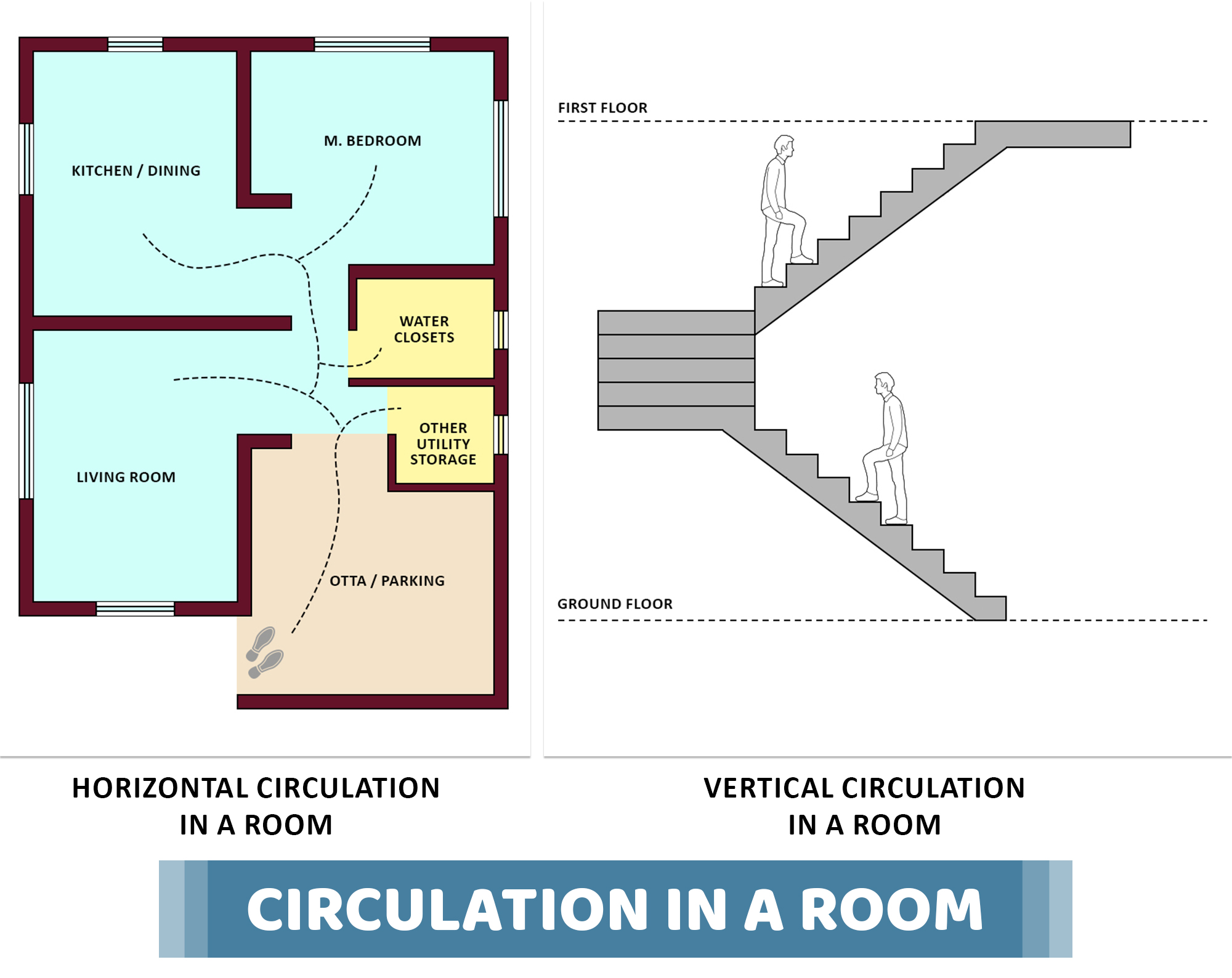
Well, it was clearly mentioned by ‘G. S. Birdie’ & ‘T. D. Ahuja’[44] (Author of Building Construction & Construction Materials) that the internal access in a room in both ways i.e. in horizontal and vertical directions of a building is defined as CIRCULATION. The movement from one room to another on the same floor can be described as horizontal circulation. Likely, the movement from one floor to the other floor is termed as vertical circulation. To have the efficient circulation in a building, passages, corridors and foyer etc should be provided in such a way that these elements are neither too narrow nor too large. They must have good lighting and ventilation.Some better options are highlighted in the diagram which reflects the ways of good circulation in a house.
06. What is Flexibility in building planning?
Flexibility means “to allow use of the particular element in another way possible to fulfil a specific purpose. An element is initially designed for one particular reason, but later the same element is used differently.”
Let us take an example to understand the concept of the flexibility. One storey residential house has a dining and drawing hall on the ground floor, separated with a fibre partition wall in it. For various events and gatherings, both dining and drawing hall can be combined and converted into a banquet hall by removing partition wall. Also, future expansions of converting one unit to another must be kept in mind as it is one of the basic principles of construction.
07. What does Privacy means in building planning?
Privacy is an important factor that needs prior attention. Usually, the privacy can be considered in two ways:
01. Internal Privacy: This deals with the privacy inside a house, amongst the rooms. It covers the privacy between rooms and water closets, corridors, passage lobbies etc.
02. External Privacy: Privacy of a building with respect to other buildings and the things outside the building- such as streets, roads, etc., is external privacy.
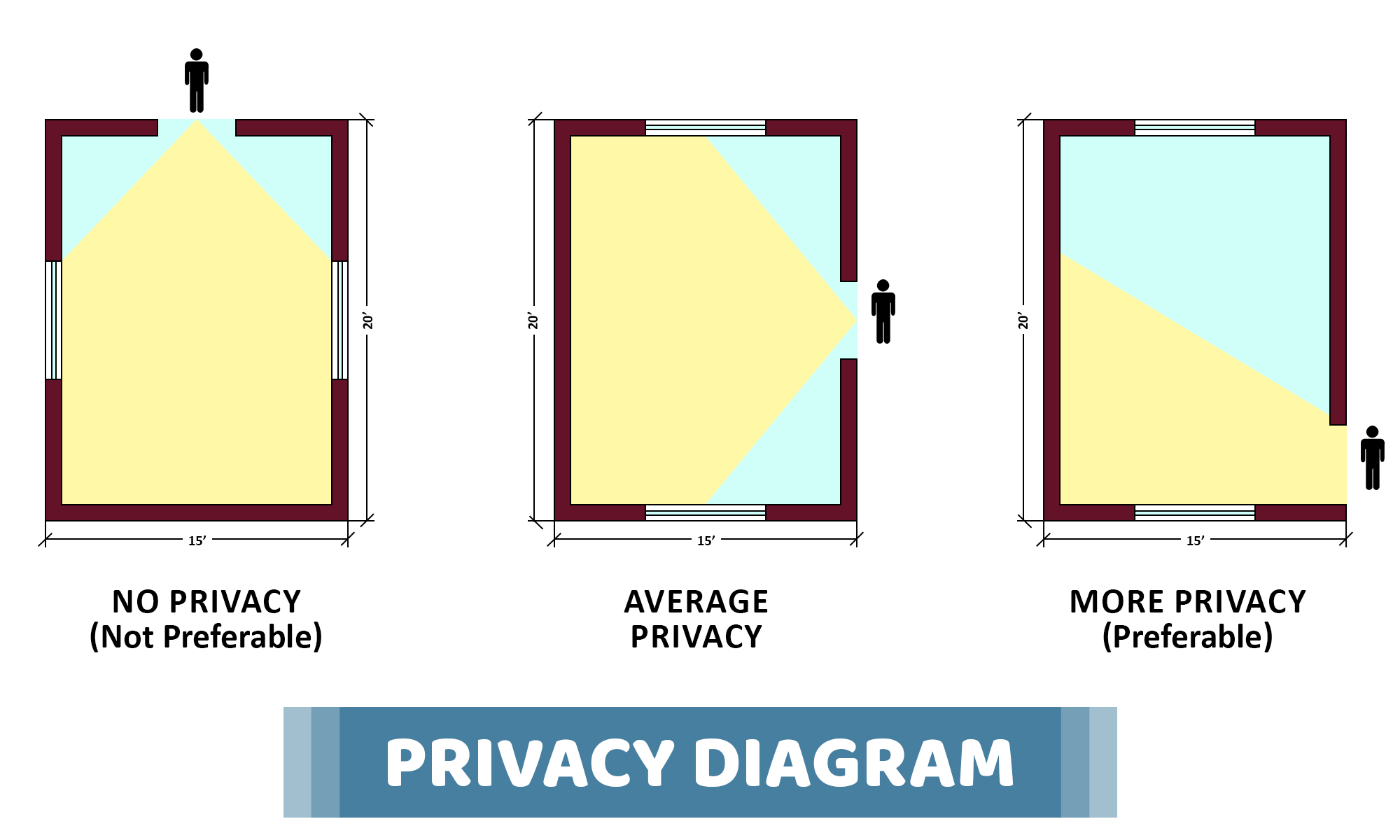
Above diagram suggests the few methods recommended for attaining privacy. Privacy can be achieved by suitable appointment of the door, windows, ventilators and curtains.
Check out the techniques to improve and maintain the privacy in a home.
Apart from doors and windows as discussed earlier, curtains are the commodities which bring privacy. Here’s link of an article which will help you to figure out all about curtains.
08. How FURNITURE influence principles of building planning?
In the opinion of the ‘Y. N. Raja Rao’ & ‘Y. Subhramanyam’[377] (Authors of Planning & Designing of Residential Building), according to rooms’ functions, the type of furniture varies. The architects and planner must consider the furniture’s relative positions to avoid the congestion of space. The furniture should match the purpose of the room and justify the effective use of a room and furniture as well.

There are many points to consider while choosing furniture for your house. The link below will give you tips for the furniture in living room.
09. What is SANITATION in building planning?
The maintenance of hygiene in a building is crucial. Light, ventilation, and sanitary conveniences, are essential factors that provide good sanitation in a building. Adequate sanitation can be achieved by placing doors, windows, and ventilators appropriately. Installing exhaust fans, lighting lamps, suitable absorbent flooring, and improvised plumbing equipment can lead to better sanitation.
It is studied that for proper lighting, the least area of window should not be less than 1/10th of floor area in residential building. This ratio can be raised to 1/5th for buildings other than residential ones.

The above image relates to the necessary features that sanitation units should possess in it.
Some useful guidance to keep your home clean and hygienic for better health is given in link below.
10. What is the importance of ECONOMY in building planning?

The economy is also one of the major factors to keep in mind while planning a structure. The building should not be too expensive. However, having said that, the cost cutting should not happen by compromising on the safety and the building principles. Often, the cost of the construction at the initial stage is higher as standard designs and materials are used, but it reduces the cost of maintenance and repair in the future.
11. What is ELEGANCE in building planning?
The elegance has a direct connection with the appearance and layout of a plan. It has become a trend nowadays to construct attractive elevations, which gives a pleasant sense of visibility. Straight, it depends on the materials used for construction in the exterior portion and relies on the positions of the door, windows, chhajja, balconies, and many such factors. All these components aim to enhance the look and thus it is necessary to give more footage to it while building planning.

12. What are the PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS in building planning?
While designing and planning a building, there are several practical points to be considered for better results. These practical considerations are briefly mentioned as follows:
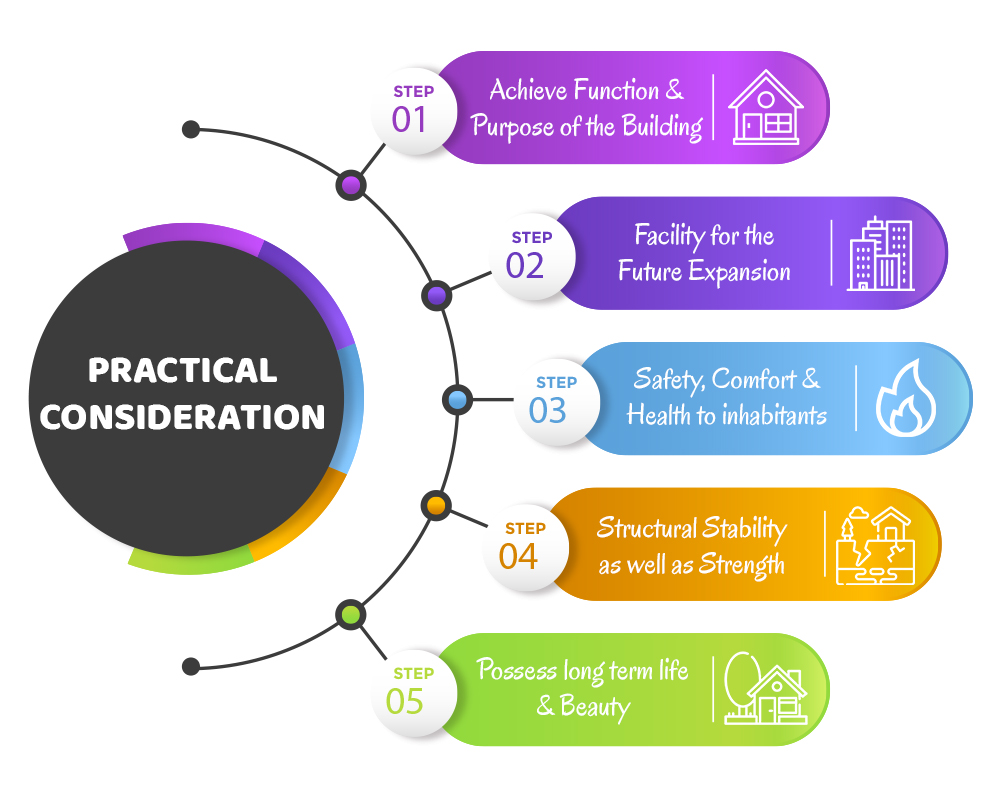
Apart from understanding these twelve principles, there are two more factors which are important to consider while planning a building. They are as follows:
- Local Bye-Laws
- Strength, Material and Life of a Building
Local Bye-Laws:
You must have come across the word Bye-Laws while construction planning. Basically, building bye-laws are rules and regulations that must be followed while planning. If you violate those bye-laws, the government authorities can take lawful actions against you.
It should be noted that every state and city has its own local bye-laws. The building bye-laws provide standards to implement such as minimum plot size, carpet area, built-up area, the minimum height of the building, distance from the main road, safety measures, water supply, drainage, sanitary facilities, lights and ventilation, outdoor and street parking, structural designs. It should be noted that the bye-laws are in tune with the recommendations provided by the National Building Code (NBC). Thus, the authorizations of bye-laws should be obeyed in order to get approval and permission for the construction and avoid future complication. Local bye-laws do not only deal with the new constructions but also guides renovation, alteration, demolition, changing occupation, development of the land.
Strength, Materials and Life of a Building:
Strength:
The materials used for construction of the building will decide the life of the building. The materials should have enough durability, load carrying capacity, and must be easy to handle, and store and should have high strength. Talking about the strength, as per engineering concepts, almost all materials have to deal with and undergo tension, compression, deflection bending, flexural and shear forces, and have to withstand all climatic conditions. The factor of safety must be observed before designing any component or element. You are advised to follow Indian Standard Codes which mark out specifications and workmanship which impact the strength to different building materials. It is also advised to use only those materials which follow IS practices and bear ISI marks.
Materials:
As described in the National Building Code, all materials must satisfy the Indian Standard Codes.
The National Building Code suggests that all the new or alternative materials used for the construction of the building must reassure the essential conditions. This condition includes the provision of the general appearance, dimension and dimensional stability, structural stability including strength properties, fire safety, durability, thermal properties, mechanical properties, acoustical properties, biological effects, optical properties, environmental aspects, working characteristics, ease of handling, consistency, and workability. However, it is recommended that the materials used must be tested in laboratories. Trials in the fields also must be carried out and historical studies should also be carried out to ensure the quality of the material. Therefore, it is advisable to follow the National Building Code while choosing the materials and attain safety.
Life of a Building:
Having considered all the above important attributes a common question that arises is how long a building will survive and sustain and will remain serviceable? It is generally said that, a building has a 100 years life, but this is not always true. The life of a building does not only deal with the physical life but also focuses on economic as well as functional life. Before we move forward, let’s first understand what the physical life, economical life, and functional life of a building mean?
(a) PHYSICAL LIFE:
The period for which the components of a building and building itself can hold without undergoing any failure or collapses.
(b) ECONOMIC LIFE:
The period for which the cost of maintenance of the building does not outweigh the cost of construction can be termed as economic life. This also means the period during which the building yields financial returns.
(c) FUNCTIONAL LIFE:
The period during which the building serves its purpose of the construction to the beneficiary is termed as functional life.There are several factors on which the life of a building depends. The materials used in building, type of building, location of the building, methods of construction, and loads on building are prominent factors affecting life. There are calculations and specifications provided in the Indian Standard Codes to find the design life of a building.
Conclusion
Overall, it can be concluded that before designing a house, it is obligatory to follow these general principles of residential planning. The principles of planning and designing have been examined even in commercial, industrial, recreational, and other structures. These principles provide an overall idea of arranging the elements in a creative way to accomplish successful building planning and happy and healthy life.





































