Concrete is undoubtedly, one of the most important materials in the field of construction. It consists of cement and coarse as well as fine aggregates (sand). River sand is one of the primary materials used in manufacturing concrete. It also plays a vital role in the Mix design. River sand is found naturally in the river banks or river beds and is often a good extraction site for the sand.

Extraction of River Sand
In the recent times, availability of sand has become very limited because of erosion, depletion of forest and other environmental issues. Due to the rapid growth of construction industry, demand for sand has increased enormously, causing deficiency of river sand in most parts of the world. Additionally, extraction of river sand affects the ecological balance. The other disadvantages of using river sand are given as follows:
- Global scarcity of natural sand
- Growing demands for fine aggregates in construction
- Remotely located sand pits
- Presence of silt and clay in river sand
Apart from these, there are a number of bans against the extraction of river sand. The unavailability of river sand and the requirement for cost reduction of concrete has collectively resulted in finding a new replacement of sand in concrete. Thus, discovering the substitutes for sand has been of great importance in the field of construction.
Materials which can be used as Replacement of Sand in Concrete Mix

Various Materials for Replacement of Sand in Concrete
01. M-Sand (Manufactured Sand)

M-Sand
Due to the depletion of good quality river sand, M-Sand is identified as an alternative to River sand. M-sand stands for manufactured sand. It is manufactured in industries/ quarries by crushing rocks, quarry stones or larger aggregate pieces into sand sized particles. For various construction works, different suitable grades of M-sand are used. The main advantage of M-sand is that, it is cheaper than the river sand. At most of the places, the price of M-sand is half the price of river sand.
Owing to the large advantages of M-sand, it is considered to be the best construction material discovered in the recent times. Thus, it has significantly provided a long-term solution to the construction industry in overcoming the shortage of river sand. But the key is to ensure that the M-sand is procured from a reliable source and should be adequately processed.
When the concrete mix (1:1.82:2.96) of grade M20 was tested for replacing the river sand with M-sand, the concrete mix was found to have better strength and durability when it was compared with river sand. According to the ‘Halesh Kumar B. T. et al.’, (Published in International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering), replacing river sand with M-sand up to 15% gave the highest compressive strength as well as tensile strength value of concrete.
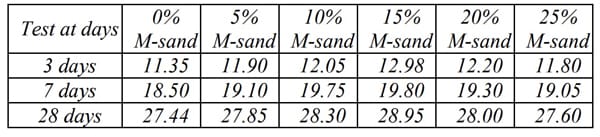
Test Results of M 20 Grade of Concrete that Contains M Sand
Manufactured sand is one of the best alternatives of natural river sand in terms of both strength and durability. It has a better control over gradation and is also free from impurities.
Advantages of M-sand:
- High compressive strength and flexural strength
- Does not contain silt, over-sized materials and marine products
- Eco-friendly
- Much cheaper than river sand (almost half the price), however it will depend upon location of quarry as well as source of river sand.
- Less or no moisture content, hence no problem of bulking of sand due to water in it
Disadvantages of M-sand:
- Cubical, angular and has a rough texture
02. Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag

Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS)
Ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS or GGBS) is a by-product of iron and steel. It is obtained from quenching the molten iron slag from the blast furnace into water or stream. These glassy and granular products are then dried, and grounded into fine powder, which is also used as a substitute for sand. The particle size of granulated blast furnace slag is similar to that of sand. It has a specific gravity of approximately 2.63.
‘Anzar Hamid Mir’ (Published in International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications), carried out tests on cement mortar mix 1:3 and GGBFS (ground granulated blast furnace slag) at 0%, 25%, 50%, 75% and 100% replacement to natural sand for constant w/c ratio of 0.5. In the test results, there was a considerable increase in compressive strength.
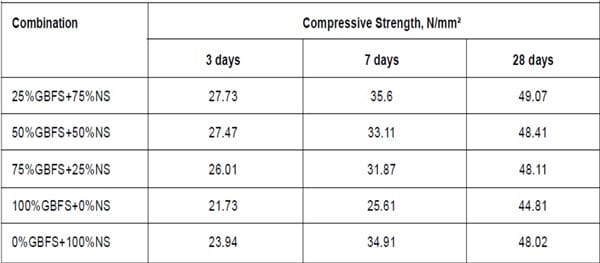
Test Results of Cement Mortar Mix 1:3 Contains GBFS
Thus, GGBFS can be utilized partially as alternative for sand in concrete. But there is also a reduction in workability for all replacement levels. The workability of the mix can be increased by adding suitable amount of chemical admixtures such as super plasticizers.
Advantages of Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag:
- High durability
- Provides more compressive strength to concrete
- Easy availability
Disadvantages of Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag:
- Reduces workability of concrete.
To know in detail the properties of GGBFS, its effect on properties of concrete, its pros and cons, and its applications, read Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag for Concrete.
03. Washed Bottom Ash

Washed Bottom Ash
The bottom ash is an agglomerated ash particle which is formed in the pulverized coal furnaces. They are obtained from the thermal power station. It is typically grey to black in colour and is angular in shape. It has a porous structure on the surface. Bottom ash is subjected to washing, to remove the carbon and unwanted material from concrete.
There are various tests conducted on M10, M20, M30, M40, and M50 concrete mixes respectively by the researchers, and it was found that the compressive strength of the concrete with bottom ash reduced considerably with the increase in percentage of washed bottom ash.
The durability of the concrete is not affected by replacing river sand with washed bottom ash, it only enhanced the characteristics of the concrete. The cost of this concrete is less than conventional concrete and the concrete becomes environment friendly on replacement of river sand with washed bottom ash. According to the ‘Anzar Hamid Mir’ (Published in International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications), approximately 30% of washed bottom ash can replace the river sand by its weight.
Advantages of Washed Bottom Ash:
- Increases the split tensile strength of concrete
- The density of concrete linearly increases
Disadvantages of Washed Bottom Ash:
- Availability is limited only to power plant area
- Has zero plasticity
04. Sheet Glass Powder

Sheet Glass Powder
Glass is an amorphous material with high silica content which makes it partially pozzolanic under certain conditions. Sheet glasses are used in windows and doors and if it is once broken, it cannot be fixed. Hence, it should be powdered and used as a sand substitute in the concrete mix. The recycled glass powder enhances the aesthetic appeal of the concrete.
‘S.P. Gautam et al.’ (Published in Journal of Academia and Industrial Research), conducted a few tests for a concrete mix of 1:1.67:3.33 and the results showed that when the fine aggregate is replaced by 10% of glass powder, the compressive strength is increased. However, it was observed that the compressive strength increased marginally up to 20% due to glass powder replacement. Beyond this, its value starts decreasing.
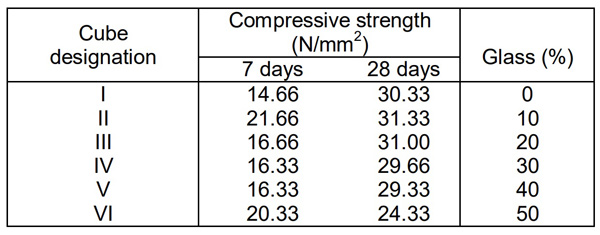
Test Results of Concrete Mix of 1:1.67:3.33 Contains Glass Powder
Hence, the optimum level of replacement of river sand with sheet glass is 10%. Thus, sheet glass powder is also one of the replacements of sand as fine aggregate.
Advantages of Sheet Glass Powder:
- Increases compressive strength of concrete
- Tensile strength is increased
Disadvantages of Sheet Glass Powder:
- Compressive strength is decreased as the age of curing increases
- It does not change the property of concrete
05. Construction and Demolition Waste

Construction and Demolition Waste
Construction and Demolition waste is nothing but the waste of dead mortar, concrete, stones and other building materials that are generated during the construction or demolition of a building. It consists of non-biodegradable and inert materials such as stones, concrete, mortar, metal, wood, plaster etc. These wastes are heavy and bulky with high density. The waste materials are then collected and separated according to the type of material. It is then subjected to grinding and sieving to obtain a finely graded powder.
According to the ‘K. Radhika and A. Bramhini’ (Published in International Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology Research), when tests were conducted on the cement mortar of M20 grade by increasing the percentage of construction and demolition waste in the mix, it was found that, the compressive strength increases up to a certain percentage. The tensile strength of the concrete also increases, if the replacement of fine aggregate is up to a certain percentage. Hence, one can replace the river sand up to 25%-50% in the concrete mixes. This type of replacement has a lot of advantages to the environment as well as human kind. Therefore, replacement of river sand with construction and demolition waste is recommended.
Advantages of Construction and Demolition Waste:
- Increases the compressive strength of concrete
- Recycling of waste is achieved
- Eco- friendly
- It is cheap and easily available
- The density of concrete linearly increases
Disadvantages of Construction and Demolition Waste:
- Decreases the density of concrete
- It does not change the property of concrete
06. Quarry Dust

Quarry Dust
Quarry dust can be partially used as an alternative to river sand, as fine aggregate in concrete production. It is basically a by-product of stone crushers produced during the crushing and screening process of coarse aggregates. The replacement of river sand with quarry dust enhances the compressive strength of the concrete to a limited extent. Which gives even better workability and strength when it is mixed with ingredients like fly ash. It has to be properly screened and processed to provide more strength to the concrete. Quarry dust is abundantly available and can be effectively used.
According to the research of ‘Sumit L. Chauhan & Raju A. Bondre’ (Published in International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering), they conducted a test for concrete cubes with 30%, 40% and eventually 50% replacement of sand by quarry dust for M20 and M25 mixes. The concrete mix design ratio for M20 concrete was taken as 1:1.5:3, whereas the mix ratio for M25 concrete was taken as 1:1:2. The experimental results showed that the addition of quarry dust as fine aggregate ratio of 30%, 40% and 50% was found to enhance the compressive properties. The results of compressive strength test for quarry dust mix concrete (28 days) were as follows:
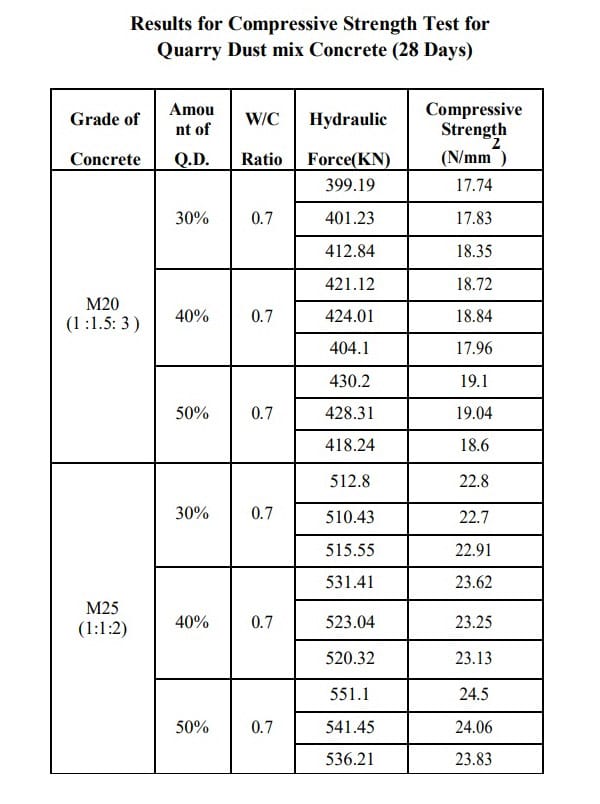
Test Results of M20 & M25 Grade of Concrete Contains Quarry Dust
The test result shows that, as the percentage of quarry dust gradually increases, the compressive strength of the concrete also increases. However, the percentage of quarry dust should not exceed beyond 50%. The specific gravity of quarry dust is almost as same as the river sand. According to the value of compressive strength collected, the value is high and it shows that the quarry dust is suitable to be used as partial sand replacement. All the collected values of compressive strength surpass the minimum value of compressive strength for normal concrete which is 7N/mm. Hence, quarry dust can be used as sand alternative in concrete mix for construction industry.
Advantages of Quarry Dust:
- Good permeability
- High Compressive strength
- Enables improved workability
- Reduces cost
Disadvantages of M-sand:
- Shrinkage is more
- Comparatively high-water absorption
Summing up, looking at environmental depletion and over exploitation of natural resources like natural sand is a threat to human civilization. It is therefore, our duty to preserve mother earth by preserving natural resources. River sand is one of the most exploited natural resource in construction industry. Even if you save few percent by replacing it with other materials it will be a great contribution by us. This will be more significant when you achieve this by using the materials which can be used in place of river sands, for instance, industry waste like blast furnace slag and sheet glass powder. You achieve two things at a time, an environment friendly construction material along with achieving a better concrete.
As Sthapati Designers & Consultants Pvt. Ltd. (SDCPL), we have used blast furnace slag as coarse & fine aggregate in our project of concrete road in Jhagadia Industrial Estate in Gujarat 10 years ago. Therefore, we feel proud in recommending the same.
Hope the knowledge of such materials as a replacement of sand in concrete will help you to choose the best one for your project as well as will give the chance to contribute to green development.
Also Read:
Green Concrete: Its Application, Advantages & Disadvantages
8 Eco Friendly Building Materials Utilised in Green/Sustainable Buildings!
Pozzolanic Materials: Eco Friendly Substitute of Cement Ingredients
Image Courtesy – Image 1 – unep, Image 3 – kovaibuilders, Image 4, Image 6, Image 7, Image 8, Image 9, Image 12
Author Bio
Arfa Falak – My name is Arfa Falak and I have my graduation in BE (civil). I live in Bangalore. I am an aspiring design Engineer.





