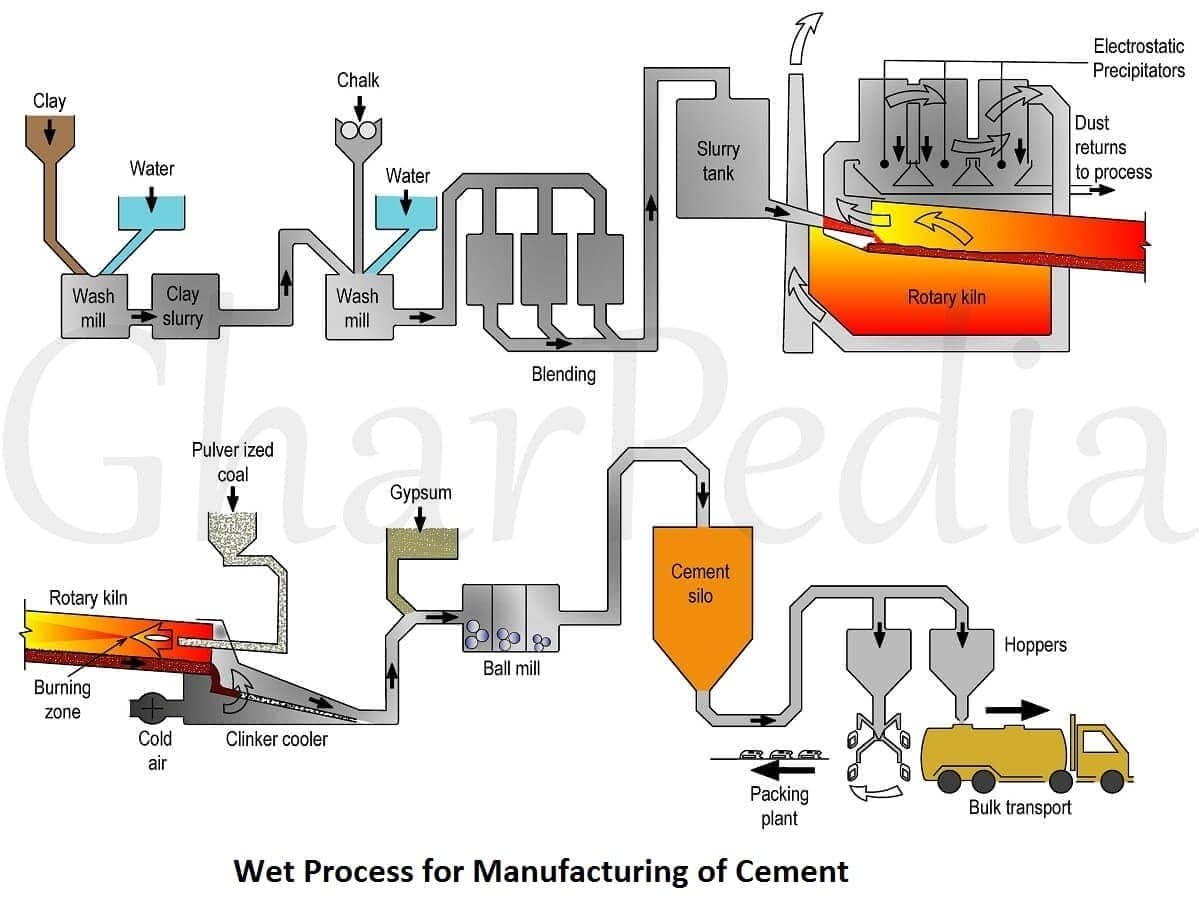
In wet process if chalk is used, it is finely broken up and dispersed it in water in a wash mill. Wash mill is a circular pit consisting of revolving radial arms having rakes which breaks the solid materials into lumps. In similar wash mill, clay is also broken up and mixed with water. Now the two mixtures are pumped so as to mix in predetermined proportion and passed through a series of screens. The resulting cement slurry flows into storage tanks.
Wet Process for Manufacturing of Cement
When lime stone is used, first blast it, then crushed in two progressively smaller crushers and then fed into a ball mill with the clay dispersed in water. The resultant slurry is pumped in to storage tanks.
The slurry is a creamy consistency liquid with 35 to 50 percent water content and some small fraction of material about 2 percent larger than a 90μm sieve size. There are number of storage tanks are provided to keep the slurry. The sedimentation of suspended solids being prevented by mechanical stirrers or bubbling by compressed air.
The slurry with the desired lime content passes into the rotary kiln. This is large, refractory lined steel cylinder having diameter up to 8 m and sometimes as long as 230 m. Steel cylinder is slowly rotating about its axis and it is slightly inclined to the horizontal. The slurry is fed into the kiln at the upper end and pulverized coal is blown in by an air blast at the lower end of kiln, where the temperature is about 1450°C. The coal used in kiln must not have too high an ash content because 220 kg of coal is used to make one tonne of cement. It is worthy when considering the amount of cement.
The dry material undergoes a series of chemical reactions in the hottest part of the kiln and some 20 to 30 percent of the material becomes liquid, and lime, silica and alumina recombine. The fused mass turns fuses into balls of diameter 3 to 25 mm known as clinker. The clinker drops into coolers where it is cooled under control condition. Cooled clinker and 3 to 5 percent of gypsum are ground in ball mill to required fineness and then taken it to storage silos from where the cement is bagged.
The kiln has to operate continuously in order to ensure a steady regime, and therefore uniformity of clinker. The larger existing kiln in a wet process plant produces 3600 tonnes of clinker per day.
The manufacture of cement by wet process is energy intensive and thus uneconomical as compared to dry process and semi dry process.