Do you know what is the second most-consumed substance in the world after water?
It is concrete. Are you surprised to hear that?
The concrete industry is, in fact, a giant one, having a worth of over $137 billion. Most of the structures you see are made of concrete. Being the most widely used construction material globally, concrete provides the foundation for all kinds of infrastructures.
Each year, its production rate is about 10 billion tons because of its versatile and robust usage.
Concrete is a mixture of cement, fine aggregates, coarse aggregates, and water. In the following sections, you will know about some eco-friendly and cheap alternative aggregates for concrete. These alternative aggregates make concrete more sustainable and environment-friendly.
Why do you Need Alternative Aggregates for Concrete?
With the significant increase in construction work, the demand for concrete is growing day by day. Peak demands are causing a scarcity of raw materials. Besides, studies show that concrete production involves about 10% of the total greenhouse gas emissions.
Considering the raw materials depletion and environmental degradation, sustainable aggregate alternatives became a dire need.
From the next section till the end of the blog, you will get a step-by-step guide to suitable alternative aggregates for concrete.
Aggregate Replacement for Concrete
Concrete replacement materials can be of many types. You can replace the cement in concrete with recyclable materials to reduce energy consumption. The list of waste materials used in concrete can consist of wood ash, fly ash, blast furnace slag, or silica fume.
Such type of ecological form of concrete is known as Green Concrete.
Another effective strategy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by concrete is replacing aggregates. Recently, many reusable and recyclable materials are available for this purpose.
Alternative materials for coarse aggregate in concrete can be rubber, glass, expanded fly ash clay, or plastic materials.
On the other hand, agro-wastes, to industrial by-products, alternative materials for fine aggregate in concrete can be of a wide variety.
In the following section, you will get a brief idea on these aggregate alternatives.
Alternative Aggregates for Concrete
Alternative – 1
Fibrous Concrete or Papercrete an Eco-friendly Alternative of Aggregate in Concrete
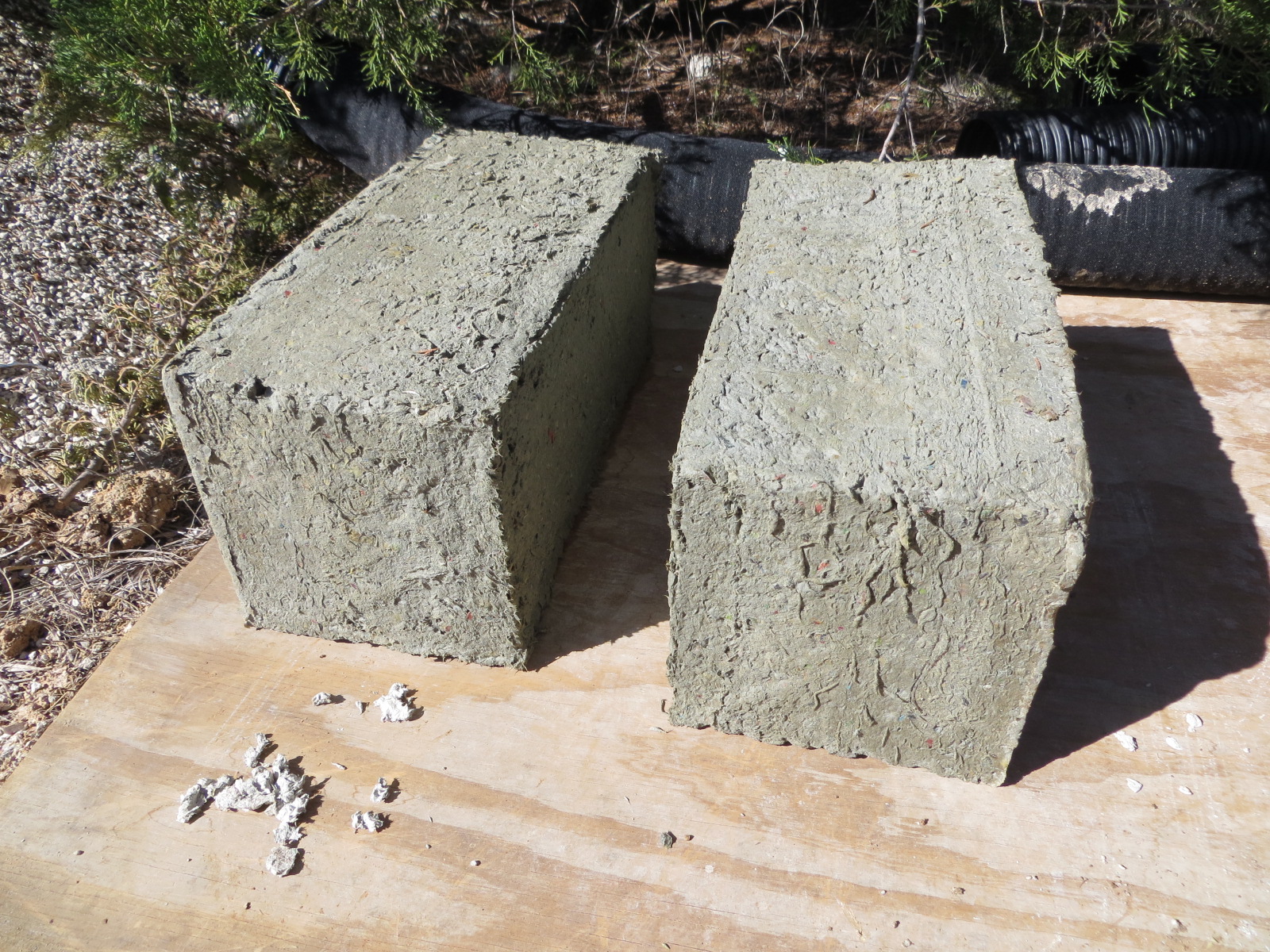

Raw Materials used for Papercrete
- Paper Slurry
- White lime or sand
- Portland cement
Manufacturing Process of Papercrete
- Add waste paper or paper pulp to a trough of water.
- Soak it for 24 hours.
- Use a mixer to mix the created slurry. Allow this mixing procedure for 10 minutes.
- Let the excess water flow out.
- The ratio of Portland cement to white lime and paper sludge is 1:0.5:4.
- To ensure the workability, add the required amount of water.
Advantages of Papercrete
- It is one of the cheap concrete alternatives.
- You can utilize low tech and reasonable hardware.
- Papercrete is lightweight.
- Workability is good enough, and you can mould it into different shapes.
Disadvantages of Papercrete
- The stiffness is less compared to conventional concrete.
- According to ‘B. Fuller’ (Published in: Structural Properties of a New Material Made of Waste Paper, 2007), the compressive strength of Papercrete is 96 -1.1MPa. Traditional concrete has a compressive strength of 15-70MPa. Very less compressive strength compared to concrete restricts its use.
- Damp resistance is low.
Alternative – 2
Wastes of Plastic as Substitute of Aggregates in Concrete

Raw Materials to Make Plastic Concrete
- Discarded plastic materials
- Cement
- Fly Ash
Manufacturing Process of Plastic Concrete
Undergraduate students from MIT followed this manufacturing process of plastic concrete. The steps are as follows.
- Shred the plastics into smaller flakes.
- Expose them to harmless and short doses of gamma radiation.
- Grind these flakes into a fine powder.
- Mix these plastic powders with cement and fly ash.
Advantages of Plastic Concrete
- Plastic concrete is highly versatile.
- You can meet specific technical needs by tailoring it.
- Lightweight compared to conventional materials.
- One of the essential advantages is that it is quite durable with a longer lifetime.
- It can be resistant to impact, water, and chemicals.
- Electrical insulation and thermal properties are excellent.
- Comparatively cheap production cost.
Disadvantages of Plastic Concrete
- According to ‘Md Hashmath & Md Meraj’ (Published in: Experimental Study on Utilization of Waste Plastic as Aggregate in Cement Mortar, 2015), the bonding capacity of plastic is less. For this reason, the flexural, tensile, and compressive strength of concrete is less.
- The melting point of plastic concrete is low.
Alternative – 3
Glasscrete or Post-Consumer Glass the Sustainable Alternative of Aggregate in Concrete
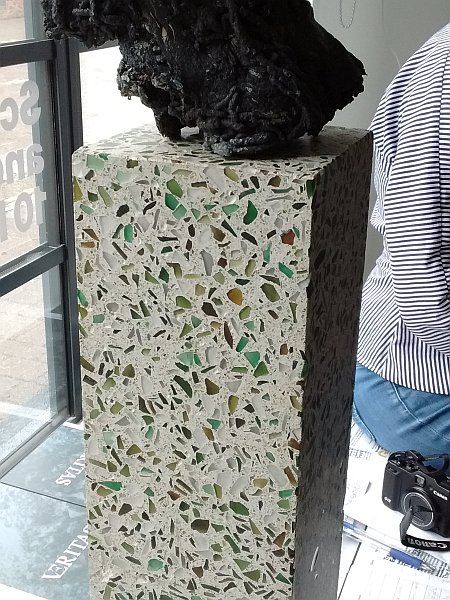

Raw Materials Used for Glasscrete
Glass can be used as a replacement to fine aggregates in concrete. It is broken down into a sieve size of #8 and #4. Few studies produced washed glass sand to gain the Fineness Modulus of natural sand.
Cement, coarse aggregates, and glass aggregates are the constituents of this green concrete form.
Manufacturing Process of Glasscrete
The process of mixing of all components is similar to the traditional concrete. Yet, steps to produce desired glass aggregates involve a long method.
- Wash the broken glass granules to remove harmful organic materials.
- Dry these glass particles in the oven.
- Remove the dried granules and allow them to cool down.
- To obtain glass sand, place these particles in the Los Angeles abrasion machine.
- Store the crushed particles for use as fine aggregate.
Advantages of Using Glass in Concrete
- The workability of concrete with glass is better than that of natural sand.
- The durability of the concrete increases because of using glass.
- Improves the efficiency of concrete.
Disadvantages of Using Glasscrete
According to ‘Jared Robert Wright’ (Published in: Examining Concrete Properties Containing Recycled Glass Cullet as a 100% Fine Aggregate Replacement, 2012), one of the significant issues with glasscrete is Alkali-Silica Reaction (ASR). The silica in glass forms silica gel because of chemical reaction with hydroxyl ions in cement. As this gel absorbs water, it develops cracks in the cement.
Besides, the cleaning process is quite expensive. Any organic residue on glasscrete harms the strength of concrete.
Alternative – 4
Expanded Polystyrene Concrete: Lightweight Alternative aggregate for Concrete (EPScrete)

Raw Materials use for Expanded Polystyrene Concrete (EPScrete)
- Expanded Polystyrene beads of 1mm-3mm diameter.
- Sand
- Cement
- Water
Manufacturing Process of Expanded Polystyrene Concrete (EPScrete)
- In a concrete mixer, place water and add any colorant you want to add.
- Add Portland cement and sand to the mixer.
- Mix the water, cement, and sand mixture thoroughly.
- Add a portion of the Styrofoam beads and keep mixing for a minute. It allows the bead to absorb water.
- Keep adding the desired amount of styrofoam beads and take time to mix it well. If beads become stiff by absorbing water, you can add extra water.
- When the mixture comes to a consistency of low slump and pourable texture, stop mixing.
- Pour this mix into moulds. Place it on a plain surface and cover it with a plastic film. Leave the mixture for curing.
- After 24 hours, remove the entire mix from the mould and allow it to cure completely.
Keep in mind; curing will take about a month. You have to keep the stone damp during this process. It will allow full-strength bonding to occur.
Advantages of EPScrete
EPScrete is 88% lighter than conventional stone-based concrete. Thus, structural support requirements like steel reinforcements and foundation size needs are smaller. Besides, it has good insulation properties.
Disadvantages of EPScrete
Polystyrene materials are sensitive materials. The strength is less than traditional concrete and can be used as light decorative bricks only. You cannot use it to make concrete pavers.
Alternative – 5
Crushed Rubber as Aggregates in Concrete
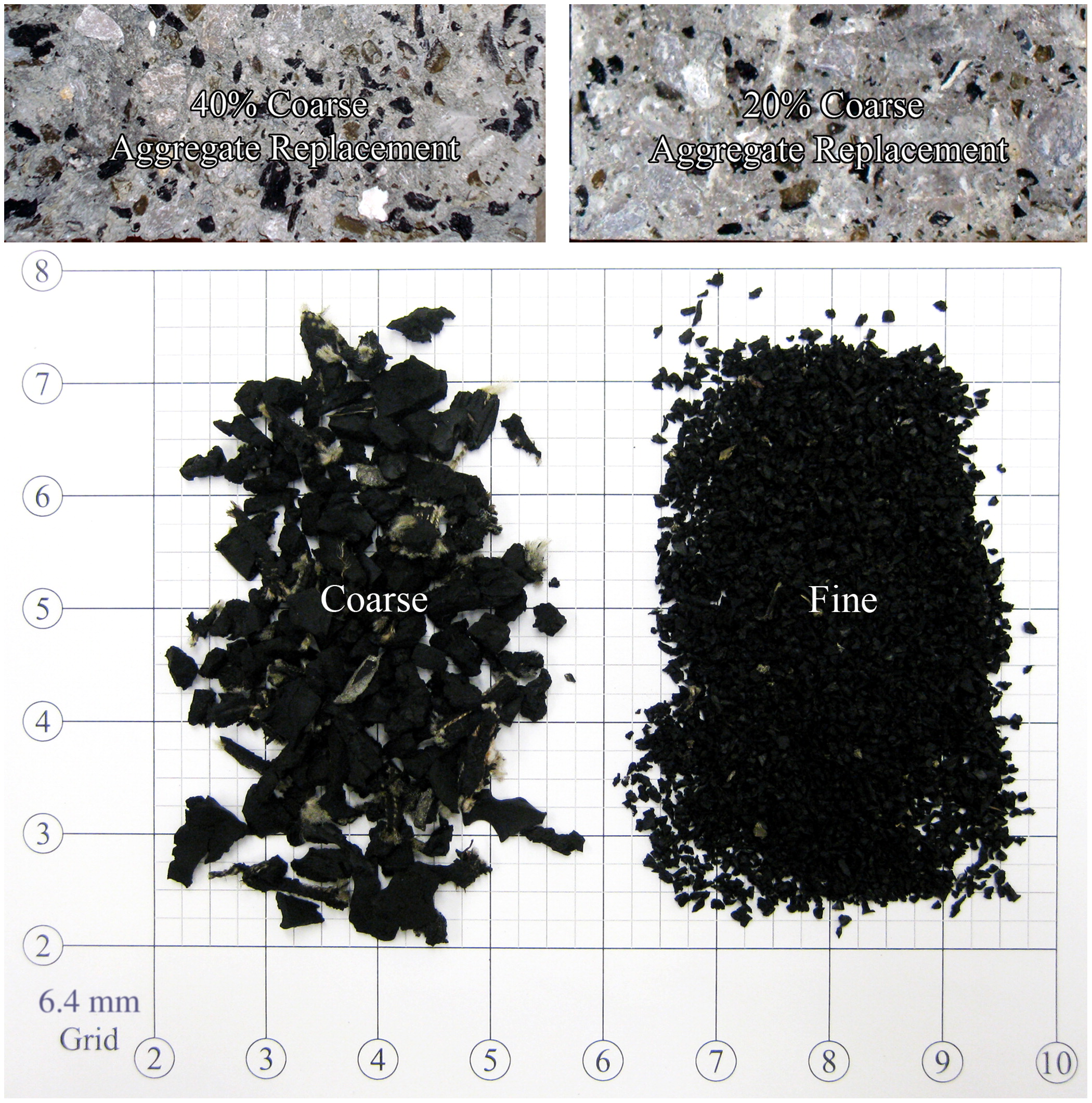

Raw Material used for Crushed Rubber
Did your vehicle tire reach the end of the usable life? In that case, you can use it as a replacement for coarse aggregates in concrete.
The vehicle tires ground up to 3-10mm size to form crumb rubber.
Pros and Cons of Crumb Rubber
The addition of rubber to concrete resists the failure and shattering of concrete. But during its mixing, the air is trapped in the mix. It results in low compressive strength of the concrete mix.
Other Substitutes of Aggregates in Concrete
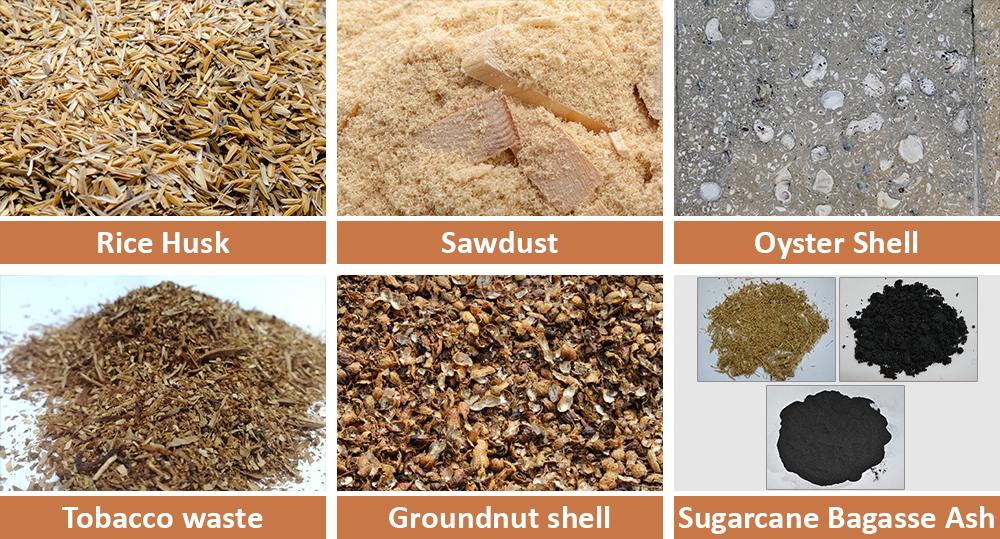

Alternative aggregates for concrete are evolving day by day, followed by modern research and technology. Besides the materials mentioned in this blog, you can also use some waste materials to replace concrete aggregates.
The list of waste material used in concrete comprises of;
- Rice husk
- Sawdust
- Oyster Shell
- Tobacco waste
- Groundnut shell
- Cork
- Sugarcane Bagasse Ash
But concrete made with these agro-wastes lacks in gaining the required strength. This field has a vast scope of research since you need eco-friendly and cost-effective aggregates.
Note: at this place we can start the extra information!!!!
Compressive Strength of Concrete
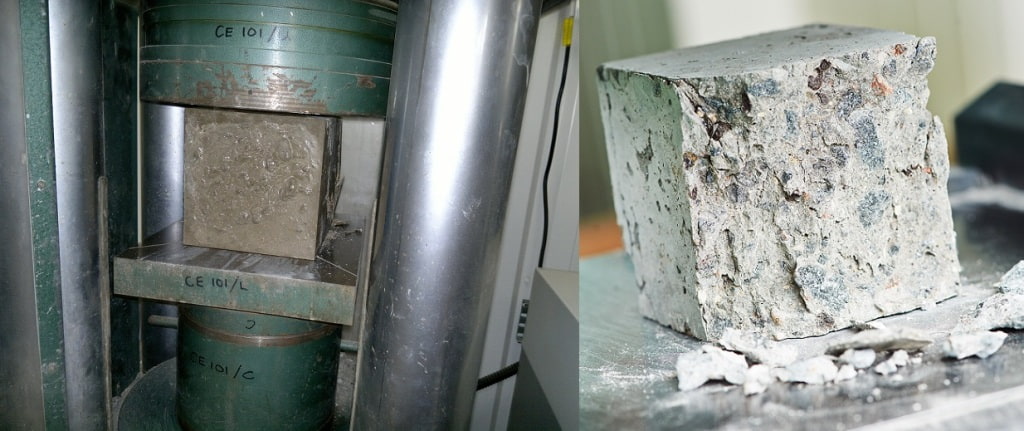

Compressive strength is one of the most critical metrics of concrete that every designer needs to know.
It is a performance measure for concrete. The compressive strength is expressed in Mega Pascals (MPa) in the S.I. Units and pounds per square inch (psi) in the U.S. customary units. The value can vary from 2500 psi to 6000 psi (i.e. 150 kg/cm2 to 400 kg/cm2) according to different requirements.
Before selecting the alternative aggregates for concrete, it is necessary to know about the required concrete compressive strength. If your alternative aggregates do not meet the strength criteria, those will not be suitable for use.
You can read our blog in detail to know how to measure the compressive strength of concrete.
Effects of Aggregates in Concrete
Do you think what the effect of aggregates properties in concrete is?
You cannot overemphasize the necessity of using the best quality and right type of aggregate in concrete.
Here are a few common questions you may want to know about aggregates.
What Percent of Concrete is Aggregate?
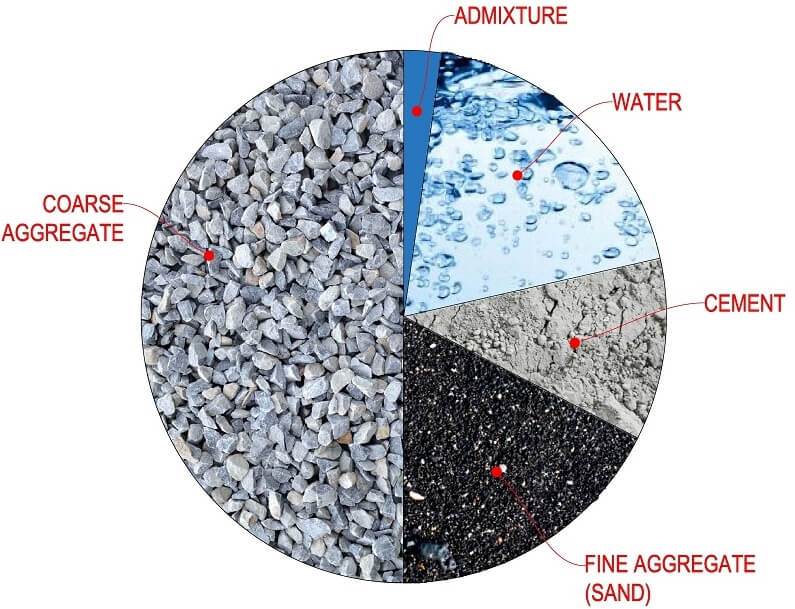
The PCA (Portland Cement Association) manual states that, in general, aggregates occupy 70 to 80% of the total volume of concrete.
What is the Effect of Aggregate Properties on Concrete?
Aggregate shape and its texture can affect the properties of freshly mixed and hardened concrete. Besides, its specific gravity, size gradation, moisture content, and bulk unit weight can directly affect the strength, durability, and concrete workability.
- Smooth and rounded aggregates make concrete more workable.
- The aggregate size distribution determines the paste demand for workable concrete.
- To develop the water-cement ratio, the moisture content of aggregates plays an essential role.
For all these reasons, aggregates are vital to determine the optimum strength and workability of concrete.
If you want to know how aggregates play an important role in concrete, read this article.
What are the Different Types of Aggregates Used in Concrete?
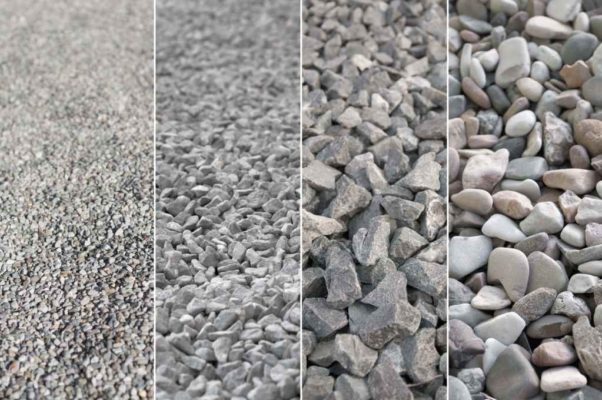

Aggregates classes consist of two broad types. These are as follows, according to the PCA manual.
- Coarse Aggregates – Comprises of a combination of crushed stone or gravels. The particle size is more significant than 5mm and ranges between 9.5-37.5mm.
- Fine Aggregates- Comprises of a combination of crushed stone or natural sand. The particle size is smaller than 5mm.
Before you select the best alternative aggregates for concrete, go through its pros and cons – select materials depending on the type of structure you want to construct. To solve any of your doubts, leave your message in the “Ask Your Query” section.
Image Courtesy: Image 2, Image 3, Image 4, Image 5, Image 6, Image 7(a), Image 7(b), Image 7(c), Image 7(d), Image 7(e), Image 7(f), Image 9
Author Bio
Rubaina Rahman – Rubaina Rahman completed her graduation with a major in structural engineering. At present she is doing her masters on the same subject. From her passion to write blogs, she started her career as a part time content writer in civil engineering and construction genre.



