Table of Contents
Quick Summary
- Exploring the world of foam glass, this article explains what the material is and why it is gaining attention in modern construction.
- Covers the composition, structure and manufacturing process of foam glass.
- Highlights major properties such as thermal insulation, fire resistance, moisture resistance and compressive strength.
- Lists practical applications in roofing, flooring, refrigeration and wall insulation.
- Compares advantages like durability and eco friendliness with disadvantages such as cost and brittleness.
- Concludes with insights into its growing adoption as a sustainable building material.
Glass is believed to be one of the oldest synthetic materials and exhibits a delicate achievement of human civilization. Glass has been used as a building material since ancient times. Due to the rapid development in the glass industry in recent times, glass has emerged out to be the most versatile building material in the modern times. The first glass object created by man centuries back was that from the natural glass such as obsidian and rock crystal. The manufactured glass dates from pre-historic times in the Far East, India and Egypt. Though its exact place and date of origin is unknown, however, it is believed that the ancient Hindus were well advanced and they knew the method of glass making long before the Christian era.

Time went on and development took place in various sectors. Thus, with the help of innovative techniques developed in manufacturing glass, today it has reached at a stage where glass of different qualities can be produced to suit the requirements of various industries. So here, we are going to discuss on foam glass. Foam glass is also known as cellular glass.
What is Foam Glass?
Foam glass (FG) is a porous glass material consisting of materials such as waste glass and various mineral wastes.
Cellular glass (foam glass) is a glass foam material, which is produced from a reaction between glass and carbon at high temperatures. Foam Glass has a cellular structure. It is impermeable, rigid and well-insulating. The thermal conductivity of foam glass being low, it has a better insulation capacity. Hence, it can be used as a thermal insulator. Because it is entirely made of inorganic materials, foam glass is non‐flammable. In addition to that, foam glass also has high compressive strength, thereby making the material suitable for the insulation of flat roofs which are covered with bitumen or other heavy substances. However, foam glass is not suitable for the insulation of wooden flooring, because it is highly impermeable.
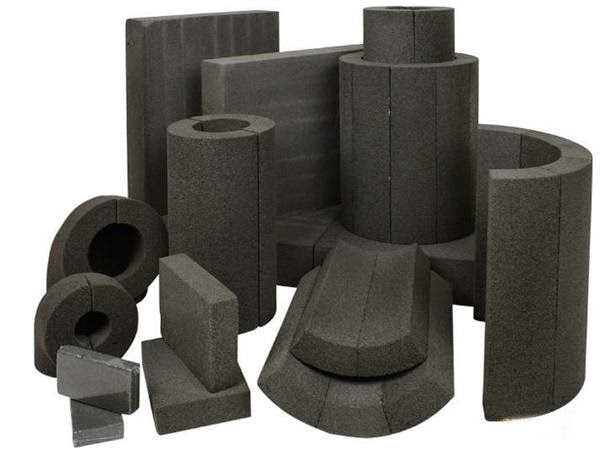

The foam glass is manufactured in the form of rectangular blocks. The finely ground glass and carbon are mixed thoroughly and the mixture is later allowed in a furnace to get melted. At the time of melting, the mixture expands and produces the mass of black foam. The resulting glass material contains more than 350 million inert air cells per m3. The cellular glass floats on water. This mass of glass can be cut like wood. It is rigid, fire-proof and an excellent heat insulator. It can be used as a substitute for cork in air-conditioning and refrigeration industries.
Properties of Foam Glass
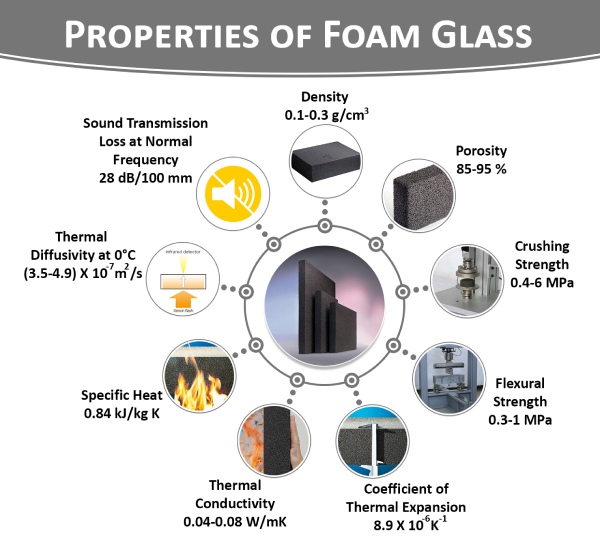
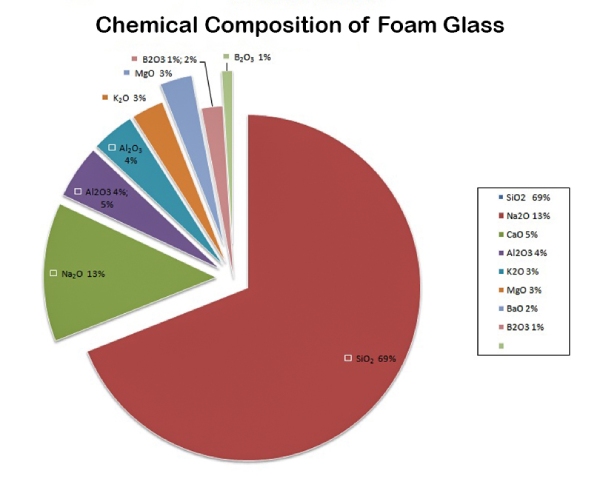
Chemical Composition of Foam Glass
Size & Thickness of Foam Glass
Its thickness varies between 30 mm to 150 mm.
Uses of Foam Glass
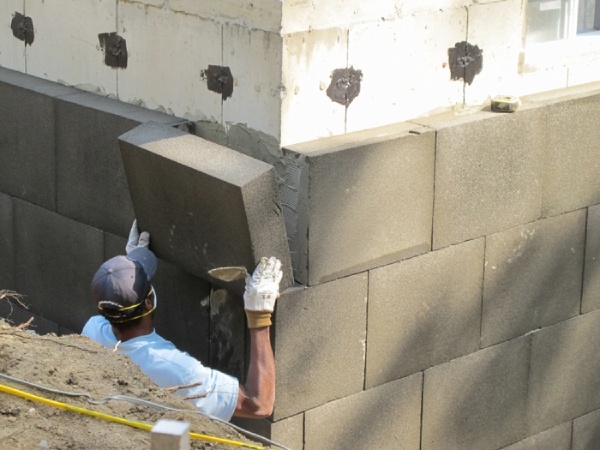

- Used in Refrigeration and Air Conditioning industry, as a substitute for cork.
- Used in Flooring.
- Used as a Substitute for partition.
- Used as a Corning.
- Foam glass is well suited as a rigid insulation material in walls, roofs and traffic areas (floors or flat roofs) where other materials are compressed which usually results in an uneven surface thereby causing the loss of insulating properties. It also acts like a barrier for changes in temperature or for preventing liquids or gases to pass through.
Let us have an insight of Advantages and Disadvantages associated with Foam glass:
Advantages of Foam Glass
01. Foam Glass is waterproof
It is moisture resistant, it therefore does not swell. Foam glass Slab and Board are absolutely damp proof, and do not absorb water either in liquid form or through interior diffusion flows. Hence, the insulation value is retained during the entire service life of a building.
02. Foam Glass is Pest- resistant
It does not rot. It is pest-resistant as it is comprised of inorganic materials which do not support any plant or fungal growth. It is a better option under conditions where insulation is behind a façade or in contact with the ground. If you are thinking to go ahead with it, there will be less chances of damage due to pest.

03. Higher Compressive Strength
It is in-compressible even with long-term loads due to its cell geometry without deformation. It can be used as load-bearing thermal insulation without risk. It can withstand load which crush most other insulating materials. In a properly designed piping system i.e. underground water distribution system, liquefied natural gas, steam and chilled water carrying system, commercial and ductwork pipework, etc, the insulation eliminates the need of special treatment at pipe cradles. The high compressive strength makes it especially appropriate for green roofs, roof decks and parking decks.
04. Foam Glass is Incombustible
It is unburnable i.e. fire-proof. It is classified under incombustible material as per European Standards EN 13501: A1. It does not burn under the influence of high temperatures. Service temperature range of foam glass is -273°C to 200°C. If a home catches fire, the insulator will prevent the spread of flame. Foam glass insulation system has been tested for preventing fire spread through wall penetrations. Depending upon the thickness and the material used, it provides fire resistance to fire-wall pipe penetrations for up to two hours, for pipes of up to 600 mm diameter according to DIN4102-11.
05. Foam Glass is Vapour-tight
Foam glass is vapour-tight because it consists of hermetically sealed glass cells. It cannot soak through and already contains the vapour barrier. As it is quite impervious to moisture (vapour and water), it does not support mold growth, blocks radon, and keeps out termites and rodents from wall.
06. Foam Glass is Dimensionally Stable
Cellular glass is dimensionally stable because glass neither shrinks nor swells. It has low coefficient of expansion. While using it in roofing system, dimensionally stable foam glass protects the adhering waterproofing. This eventually supports and enhances a long service life of the whole roof system.
07. Foam Glass is Acid-Resistant
Foam glass is resistant to organic solvents and acids. The wall or roof of homemade from such insulated material will not be damaged by aggressive atmospheric medium.
08. Foam Glass is Easy to Work with
Cellular glass is easy to handle or work with because it consists of thin-walled glass cells which can be easily cut with simple tools like a saw blade or hand saw. However, you need to be very cautious while working with the foam glass as it may cause damage to your hand or eyes. Therefore, it is advised to put on protective wears while you work with it. By using foam glass, you can insulate the exterior of your home with less effort.
09. Foam Glass is Ecological
Foam glass is manufactured using at least 60% of recycled glass. It is also free of environmentally damaging flame retardants and gas propellants. After using foam glass as thermal insulation, it can be reused as filler in landscaping or thermally insulating granulates. It is ecologically sensible recycling through re-use.
Disadvantages of Foam Glass
01. Foam glass or cellular glass insulation is fragile and brittle.
02. It is susceptible to vibration-induced damage.
03. The cost of this insulation is high compared to other insulations with similar insulation properties.
04. Installation costs are more due to the fragile nature of the material.
Manufacturing of Foam Glass
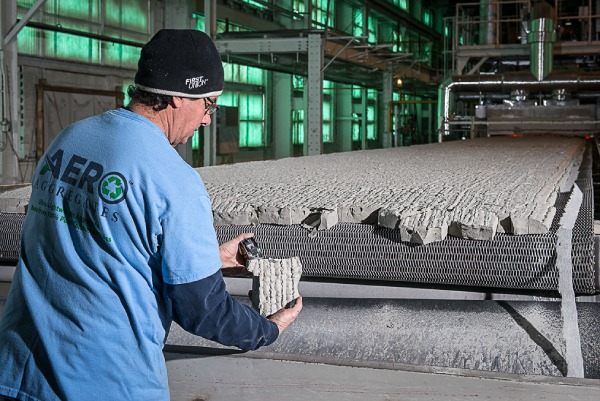

- Foam glass is in the form of rectangular blocks.
- It is produced using a process that traps gas bubbles in the glass, creating an expanded material with a spongy consistency.
Steps involved in preparing Foam Glass
- First make sure that recycled glass material is cleaned and later crushed using industrial glass crusher.
- Enough glass is used to fill the glass furnace to capacity for time and cost efficiency.
- Glass having a similar expansion coefficient for the best results is used i.e. the temperatures at which the glass melts and re-solidifies.
- Crushed glass is mixed with powdered cullet that adds strength to the glass with a carbon-based material such as coal powder.
- The carbon thus reacts with the glass to produce carbon dioxide, which develop a foam consistency with a volume approximately 15 times that of the original crushed glass.
- The crushed glass mixture is placed in the heat tolerant kiln forms with an anti-sticking agent.
- The kiln forms are loaded onto the roller conveyor with a high temperature tunnel furnace.
- The glass is heated at 1,000 to 1,300 degrees Celsius.
- It is then slowly cooled or annealed.
- Gases allow the glass to expand while heating and then stabilize during cooling.
Conclusion
According to ‘Francis D. K. Ching’ (Author of Building Construction Illustrated), Cellular glass insulation or foam glass insulation is fire-resistant, impervious to moisture, and dimensionally stable, but has a lower thermal-resistance value than foamed plastic insulations, which are flammable and must be protected with a thermal barrier when used on the interior surfaces of a building.
For more than seventy years glass foam production technology has been established as a valid method both for obtaining products having a unique combination of properties (with particular reference to high insulation capability, very low density, excellent resistance to fire, water impermeability, high compression strength, and dimensional stability) and for recycling growing quantities of glass waste. Glass foams are modern building materials which are reasonably competing these days with various other conventional materials for application in thermal insulation. The continuously decreasing price owing to improvement of process technologies and the growing introduction of waste as raw materials as well as the advantages coming from energy saving through a better insulation capability, will certainly increase the application possibilities for this material in the near future.
Apart from this article on foam glass, we have also written articles on various glasses available in market. Please check this list,
FAQs: Foam Glass
1. What is foam glass?
Foam glass is a rigid, lightweight insulation material made by heating crushed glass with a foaming agent to create sealed air cells.
2. What is foam glass used for?
It is used in roofing, flooring, wall insulation, refrigeration systems and industrial piping.
3. Is foam glass waterproof?
Yes, foam glass is completely waterproof and does not absorb moisture.
4. What are the main advantages of foam glass?
It is fireproof, vapour tight, chemically resistant, dimensionally stable and has high compressive strength.
5. What are the disadvantages of foam glass?
It tends to be brittle, costly and can be damaged by vibration, making installation more challenging.











































