According to ‘NBC’ i.e. National Building Code of India 2005, the registered structural engineer shall be competent and proficient enough to prepare the structural, design and details for all buildings and supervise every aspect of it.
A visionary himself, our mentor Mr. Mahadev Desai with his far-sighted approach recommends, rather advices that -One should never economize on the foundation and the best team of consultants (Architect, Structural engineer etc.), as they ultimately prove to be money savers in the long run. It is therefore always recommended to hire a structural engineer/ designer for the safety and well-being of your family as well as your home.
In any construction project, a structural engineer/designer executes important roles and duties, which comprises of various technical activities that needs to be carried out at the construction site. Structural engineering is a specialized field of civil Engineering. It is a vast field of boundless theories and practices. It is a creative field where there is a continual evolvement of fresh ideas, innovation and construction as well as computational technology.
The roles and responsibilities of a structural engineer are the vital and crucial ones. The structural engineering mainly deals with its physical integrity. The key responsibility of a structural engineer is to design a structure which will first and foremost ensure safety and of course, durability for its service span. The structural engineer must have the sound knowledge of physics and mathematics, three-dimensional conceptual skills, and creative problem solving skills, apart from basic civil engineering.

A structural engineer is a licensed professional with keen knowledge of structural behaviour of different type of structures. A Structural Engineer has expertise and will provide guidance regarding the structural soundness of your home. He will guide you in making your home economical, safe, durable and long lasting.
A structural engineer is trained to figure out the behaviour of any building under the impact of various forces like gravity i.e. building’s own load, wind, earthquake, temperature, blast and pressures acting upon the building and decide whether the structure is safe or unsafe under these various forces. Thus, it is important to understand the roles and responsibilities of a structural engineer.Please note – Here, in this article we have restricted our content to home construction.
An Architect mainly focus on aesthetics and functionality of building based on the design philosophy, whereas the structural engineer will suggest the best suited structural system and materials as per your site location, site conditions and also making sure that the structure supports and resist the loads imposed on it.
An architect designs the shape, size, form and language of the building depending upon its utility and functions. But most of the technical aspects essential for the structure are resolved by a structural engineer. It is a combine effort and implementation of knowledge of engineers and architects where the architects are being assisted by structural engineers for accomplishing their vision of a planned building.
Before commencing the construction of a new home, it is important to carry out the structural analysis of the whole building as well as foundations to ensure their reliability. Apart from giving the safe and sound structural system, a structural engineer also renders the following services:
Roles and Responsibilities of a Structural Engineer
01. Role of a Structural Engineer is to Check the Architectural Configuration

Architectural Configuration of a building must always be symmetrical and proportional. The structural engineer will give it a shape with appropriate materials.
Symmetry of a building is necessary as it determines the stability and balance. Symmetrical elements evoke harmony and order in any space.
All the elements of any house/building must be well proportioned i.e. height-depth ratio, area-depth ratio or length-depth ratio. They should neither be extreme tall, nor extreme thin or wide. Everything must be well in proportion.
In case of those shapes or plans which are either not symmetrical horizontally or vertically in compliance to Indian Standard – IS 1893 -1: 2002[370] (Criteria for Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures, Part 1: General Provisions and Buildings), the structural engineer will provide an expansion joint at an appropriate place, making different parts symmetrical in line of codal provisions. This also requires good knowledge of the various building materials.
A structural engineer may evaluate characteristics of different building materials to finalize their suitability for the design of the foundations and their load bearing members. Many architects ignore or are unaware of the threats to the building due to poor configuration and asymmetry. Hence, the design once finalized must be consulted with structural engineer for safety , economy and long life.
To know more about how symmetry of a building affects the structure, particularly during an earthquake. We have depicted the reasons &have mentioned some examples of building failure in the following linked article.
Building Collapse During Earthquake Due To Unsymmetrical Architectural Configuration
02. A Structural Engineer Finalize the Materials of Construction, Particularly of Structural Frame
The structural engineer in consultation with the architect will finalize the construction materials for its load bearing members or say structural frame, i.e. RCC, Steel, Wood, Stone, Bricks, Pre-stressed concrete etc. The design and selection of materials will govern further process in line with codal provisions.
03. Responsibility of a Structural Engineer is to Finalize the Structural System and Type
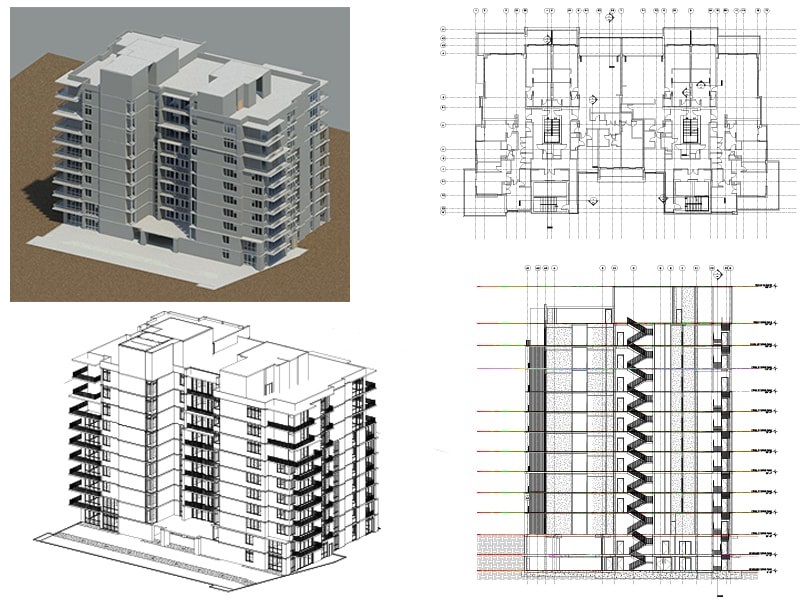
The structural system is the assembly of structural elements like slabs, beams, columns, foundation of a building/house so that they support and transmit the applied loads safely to the ground without exceeding the allowable stresses in any members.
He/she is responsible for finalizing the structural system suitable for the house, taking into considerations the budget and availability of local materials.
04. A Structural Engineer has to Decide Location of Expansion Joints
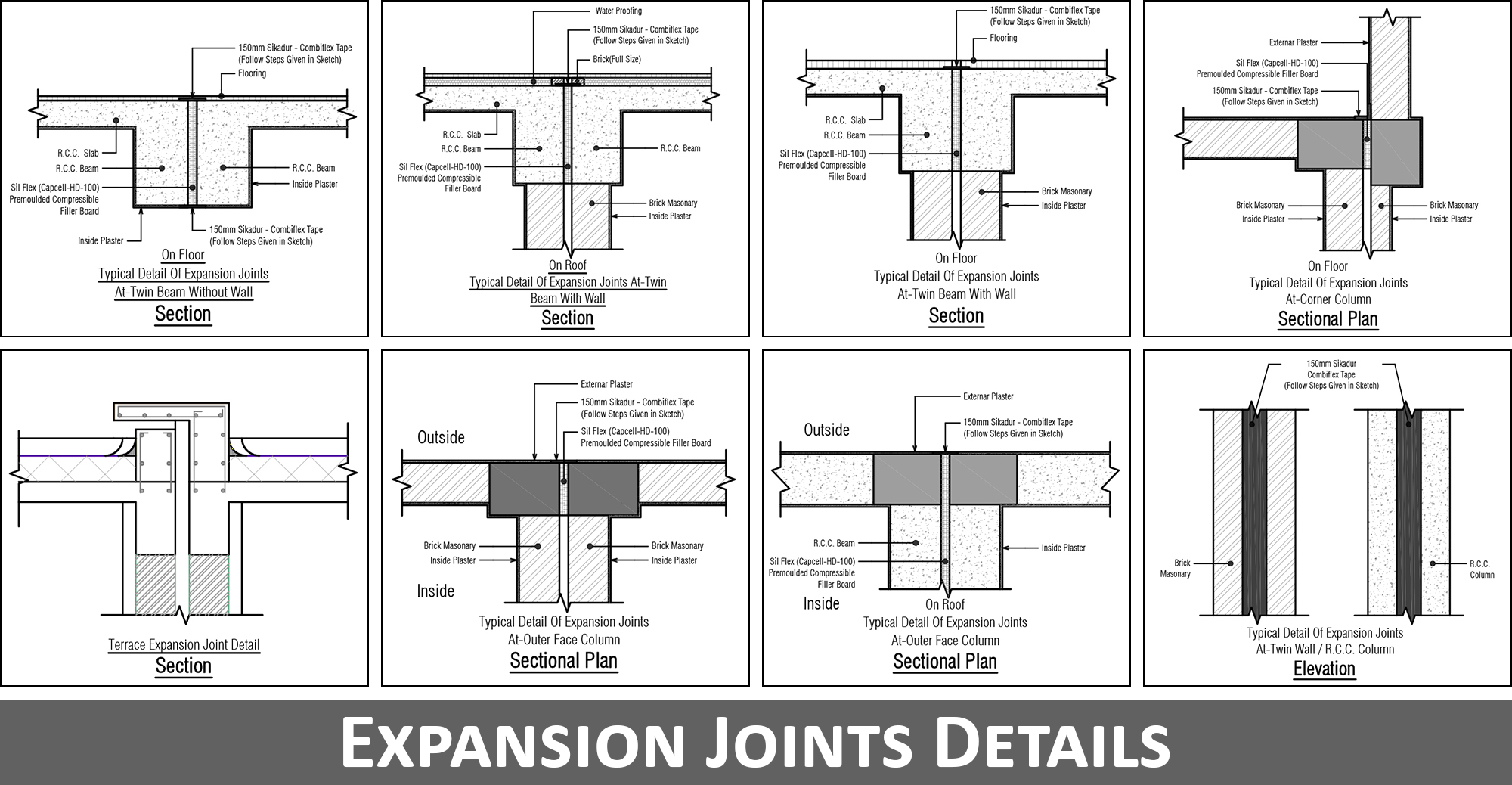
To overcome the effect of earthquake and thermal loads, expansion joints are usually provided to maintain the height-depth ratio, area-depth ratio or length-depth ratio.
Expansion joint also known as movement joint, is an assembly designed to absorb vibrations (i.e. due to earthquake) and temperature changes by holding parts together or by allowing movements without breaking the structure.
A structural engineer authoritatively lends advice concerning the location and width of expansion joint to safeguard building. Small buildings usually do not require expansion joints; both from seismic and thermal load consideration.
Also Read: Joints in Construction: All You Need to Know
05. Site Investigations & Decide the Type of Foundation

The structural engineers are also involved in testing type and the condition of the soil on which the building is going to be raised. This is quite a decisive task. He needs to determine whether the soil is suitable or not for bearing the calculated loads based on the loads appraised by him.
This investigation would further determine the type of foundation system that needs to be designed for the structure. Based on the investigation, if any kind of treatment is needed, it is also decided thereupon. This investigation is conducted by the geotechnical engineer.
Also Read: 12 Major Things To be Considered While Selecting a Site
06. Finalize the Structural Framing Plan
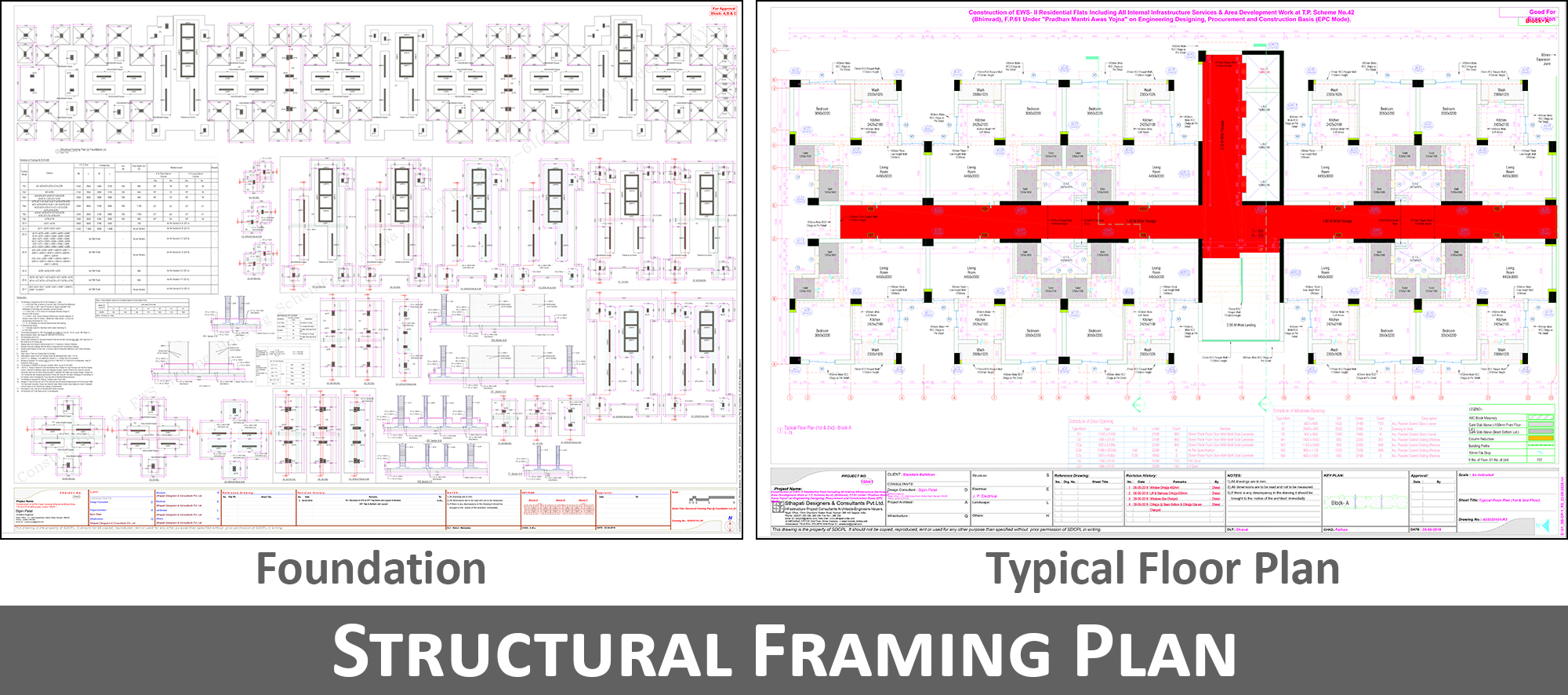
He then prepares the structural framing plan based on the load path for both gravity as well as horizontal loads (earthquake, wind, etc.) ensuring that the frame is erected the way it is supposed to be constructed on site.Structural framing plan: A plan showing arrangements of structural components (i.e. beams, columns, footings, rafters, etc) along with their connections, materials and other respective features i.e. the location and orientation of columns shall be finalized by him. He will also divide the floor into slabs, beams which will ultimately transfer the loads to column/ walls. This is the most important task that he needs to undertake because it not only associated with the functional utility of the structure but more associated with its financial aspect i.e. construction cost.
If the basic framing plan is bad, it would be impossible to control the cost. With fast functioning software, it has now become possible to carry on numerous trials whereas in the past with the lack of such technological support, it all depended on the skill and experience of the designer who could not afford many trials and error then.
07. Structural Analysis and Design
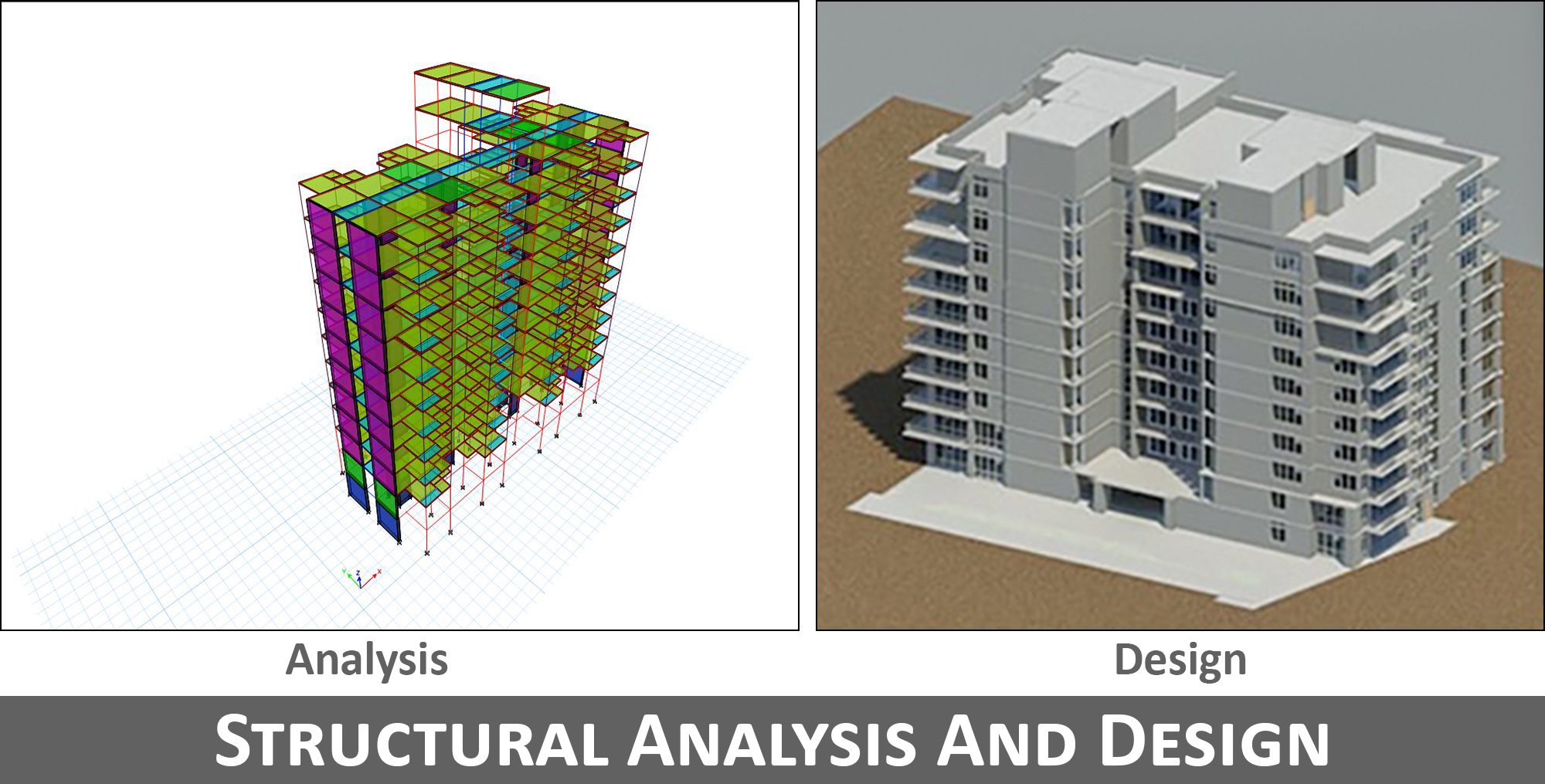
a) Structural Analysis:
- Analysis of a structure involves its study from the viewpoint of its strength, stiffness, stability, and vibration and ultimately response of all elements.
- Before designing any member, he has to carry out structural analysis. In the current time, the software such as ETABS, STAAD, SAP etc. performs this task. But with the progressive trend that influences technology timely, new software are being developed to evaluate structures at various conditions of loads such as wind, earthquake etc.
- In the analysis, the structural engineer first assumes dimensions of all the structural elements, loads, material properties, and support conditions. The sizes are generally assumed either from experience or by thumb rule which has been arrived at empirically.
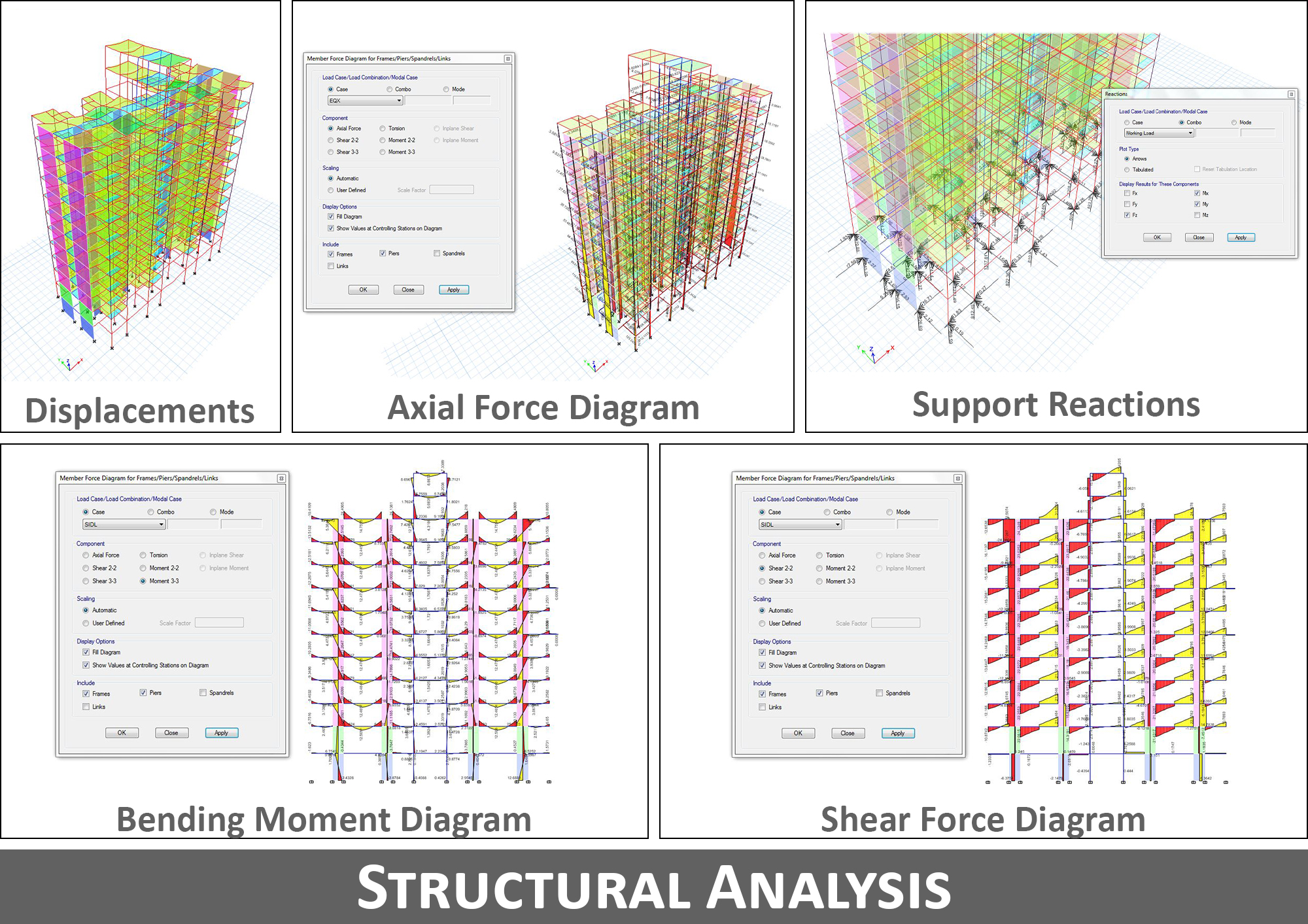
- The response means to find out support reactions, shear forces, bending moment, torsion, deflection, stress, strains etc. which the particular member would undergo due to the applications of loads.
- Structural analysis is important because it can check whether anticipated specific structural design will be able to withstand external and internal stresses and forces. Thus, he will determine forces acting on the structure. He will also determine internal forces (Structural Analysis) and then calculate final size of members (slabs, beams, columns, footings, lintel, etc.) and design connections to avoid failure or excessive deformations.
b) Structural Design:
A structural engineer carries out the structural design procedures that include designing sections of structures to resist the loads, so that the built structure can withstand the expected loads safely. The ultimate output of structural design consists of shape and size of different structural elements.
Most of the structural designers need to study, understand and work with analysis software. Nowadays it is essential for them to have knowledge of both: programming and technical details.
The structural engineer however must be able to comprehend and interpret the output of the software in order to authenticate the validity of the values provided as output by the software.
Some organizations do not depend solely on the results of the software; they do a separate man-made calculation for judging the software based on their experience.
In the article below, Gharpedia has also explained the difference between both the terms – structural analysis and structural design.
What is the Difference Between Structural Analysis and Structural Design?
08. Detailing of the Structural Elements is also a Responsibility of A Structural Engineer
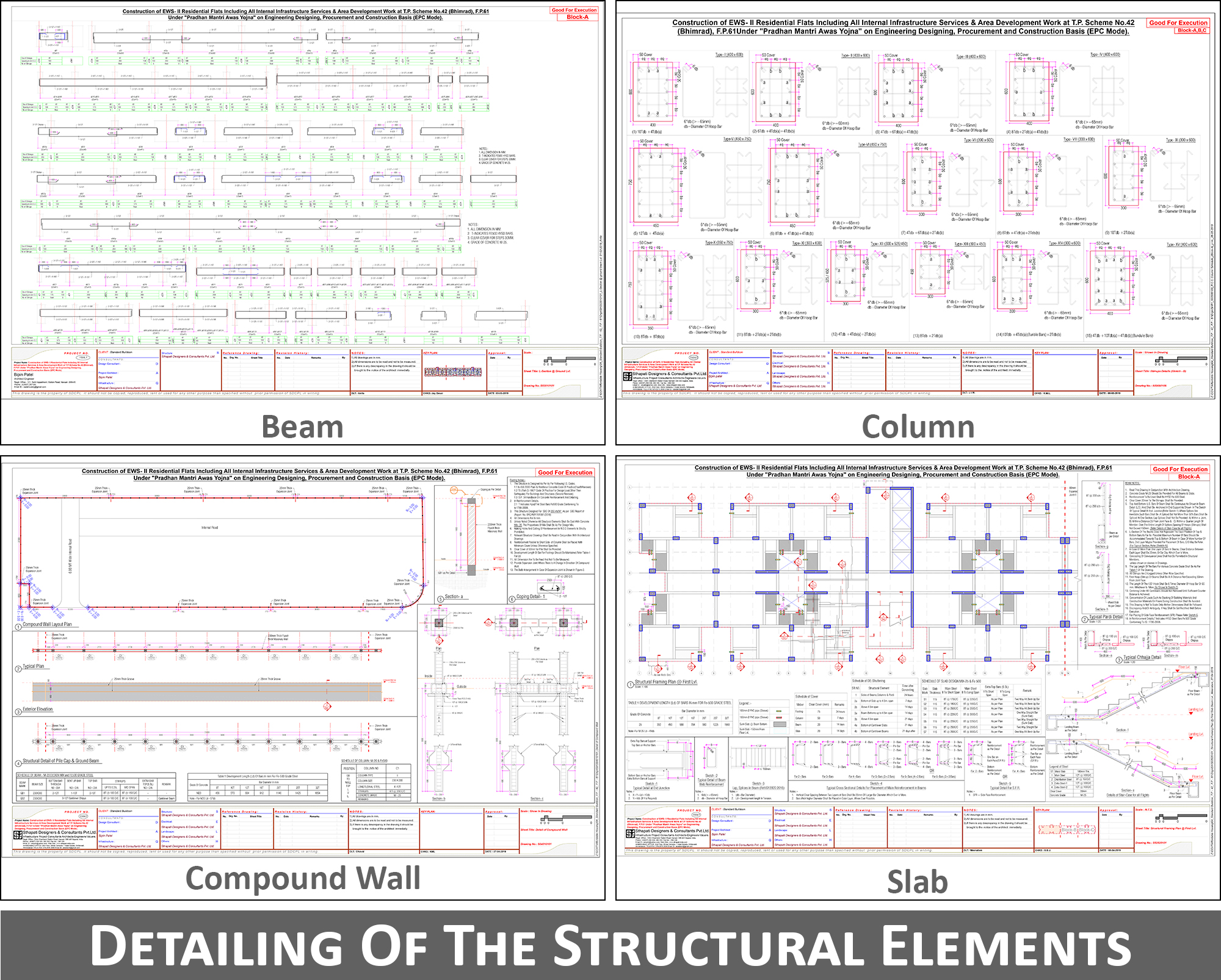
A structural engineer is eventually responsible for detailing of all the structural elements. The design has to be translated into documents and drawings so that accordingly the workers at site can be instructed regarding what & how to do the work.
Structural detailing of R.C.C member includes dimensioning structural elements (beam, slab, column, footing and wall), dimensioning rebars, spacing of rebars, positioning of rebars, laps, covers etc.
Structural detailing of steel and timber works includes dimensioning of sections, shape of sections and connection details. There are strict codal provisions to be followed for almost all joints and connections and the structural engineer to have sound knowledge of the same.
09. A Structural Engineer Prepares Structural Drawings
He/ She will later prepare structural drawing, based on which the contractor will execute work on construction site.
Structural drawing includes the following:
- North
- Setting out dimensions
- Plans, Sections and elevations with dimensions and levels.
- Notes on specifications, finishes, etc.
- Structural Framing Plans and Details
- Foundations Plans and Details with Sections
- Column Beam and Slab Details with Sections
- Wall Sections
- Reinforcement Drawings incl. Bar Bending Schedule (Many times prepared by contractor)
- Length, shape and number of each type of reinforcing bar, details of lap etc.
- Details of Joints
- Detail of miscellaneous structure like Chhajja, pardi, lintel
For each element, he/she has to prepare separate structural drawings. For illustration purpose structural drawing of column splice detail is shown below.
10. It is the Duty of a Structural Engineer to Conduct Periodical Site Inspection

Frequent visiting of construction site also comes under the duties of a structural engineer. He/she must visit the site or arrange regular / timely visits to check whether the work is carried out as per design and drawings.
11. It is Utmost Important for a Structural Engineer to Communicate with Other Members

Since the structural engineers are the ones who conceive and develop the design ideas and details, he/she can only visualize the happenings on the site and can make out whether the structure is taking the shape as desired or no. For this, he/she has to share his ideas and communicate with other team members of the project.
The structural engineer has to coordinate with other team members like architects, PMC/site engineers, geotechnical engineer, MEP consultant, landscape architects, project manager etc. Proper communication allows the members to relay accurate information preventing misunderstandings, confusions and errors.Above listed are the roles and responsibilities of a structural engineer. Thus, one must be vigilant enough while making the selection of a structural engineer as the safety and life of home/building depends on him.