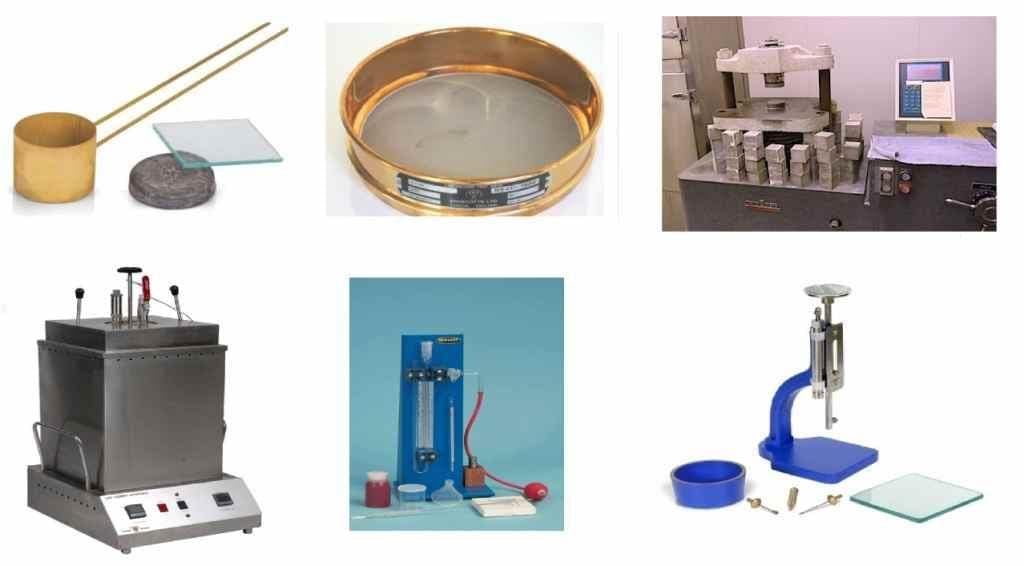
Why should you Test Cement?
Building construction consists of various materials, i.e. cement, sand, aggregate, brick, wood, steel etc. It has more than 100 materials and therefore it is a complex structure. It’s necessary that all the materials perform best because the quality, functionality and life of the structure as a whole, is dependent on the quality of materials used in construction along with workmanship. If any of these materials fail in their desired performance, it adversely affects the performance and durability of the structure.
Role of Different Materials
Every material is intended to perform one or other function as part of a building element. It has to be strong enough and must possess certain properties which may be physical like its weight, density, nature of behaviour with heat or chemicals like its resistance to nature and environment. Each material, therefore, has to have certain minimum properties so as to play its role. Now if we use any material without knowing whether it is good or bad (in term of a common man) it will make your building good or bad. Hence tests are very essential to assume that you are using the right material and your money invested is an investment and not wastage.
Testing of materials is therefore essential in the construction sector as a part of overall quality assurance, as applicable to all materials, because it only ensures the life of the structure/product. There is various kind of test available to ensure the quality of each material.
Here we are discussing various “Tests of Cement”.
Why Testing is Important for Cement?
Cement is the most essential and most popular construction material. Cement contains multiple ingredients like lime, silica, alumina etc. Cement is made by two types of the manufacturing process, i.e. dry manufacturing process and wet manufacturing process. Cement work as a binder in a concrete/mortar and bind the all ingredients together.
Field Test vs Laboratory Test
Most of the tests are performed in the engineering laboratory. But for any project every time you may not be able to test all tests in the laboratory. You need to certify and allow its use by field observations or certain “to do field” on site itself. Such tests of cement are called field tests of cement and anyone who is constructing his/her home must know and use such tests, to get returns on money spent.
Like other materials, cement has a mainly two properties, i.e. physical and chemical. Due to these properties, cement plays a significant role to provide structural strength. Therefore, it’s more important to use standard specified and good quality cement in our construction. To check the quality of cement, there are many kinds of tests conducted on cement on the field and in the laboratory, to test its various properties.
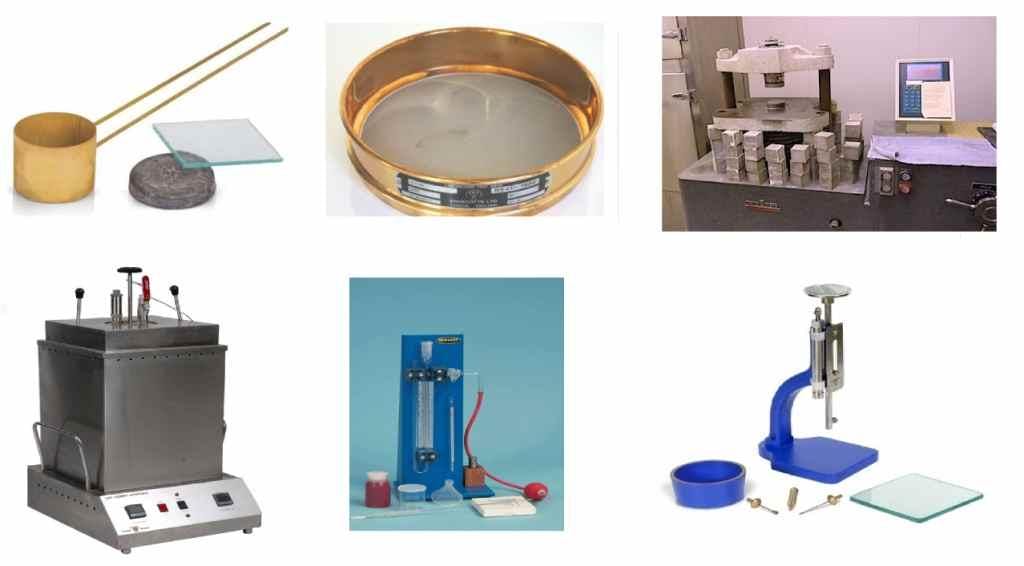

Field Tests of Cement
A field test of cement gives the idea about its basic quality based on its colour, smoothness, touch and feel at first look without any big apparatus. They are the very common and easiest way to check the quality of cement. They are very helpful when the cement is used at the site. Some common tests of cement that can ensure that cement is good at first looks are mentioned below:
- There should not be dust or any visible lumps in the cement
- The cement should float for a few minutes before it sinks on the surface of the water.
- The colour of the cement should be greenish grey.
- It must give you a cool feeling when you insert your hand into the cement bag.
- It should give a smooth feeling when you take a pinch of cement and feel between the fingers
- The cement bag should not have hardened or started to hardening.
Laboratory Tests of Cement
On the other side the laboratory testing determines the physical and chemical properties of cement and has a scientific approach to ensure the quality of cement. It is very important to compile the standard specifications while purchasing the cement and examine the properties for all particular purpose like design mix and so as you can’t test everything on site that’s why the laboratory tests are conducted.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Cement:
The Important Physical Properties of Cement:
- Consistency
- Initial and Final Setting Time
- Soundness
- Fineness
- The Compressive strength of cement etc
Various standard guidelines are available for testing the properties of cement. All the properties affect the quality of cement. Followings are the tests of cement performed in the laboratory to determine the quality of cement.
01. Standard Consistency Test of Cement
Consistency refers to the ability to flow of a freshly mixed cement paste or mortar. Standard consistency sometimes is called normal consistency. This test gives the idea about the requirement of water content to produce a cement paste in a proper manner, neither wet nor dry.
In other words, it gives the minimum quantity of water required to initiate the chemical reaction between water and cement content. The amount of water plays a significant role in cement paste/concrete/mortar. It’s a trial and error type experiment conducted in the laboratory.
(a) Use of Standard Consistency Test of Cement:
The standard consistency test of cement paste is used in the determination of water/cement ratio for the initial setting time & final setting time and soundness test of cement and compressive strength of cement. This actually helps you to decide how much water we should add to gain strength and chemical reaction to develop.
(b) Recommended Result of Standard Consistency Test of Cement:
A recommended result of the standard consistency for ordinary Portland cement ranges from 26 to 33%.
(c) Why Standard Consistency Test Fails? & What if Test Fails?
If your test result is more than this value, cement paste may have become extra wet and poor and if less than this value, cement paste may have become harsh. Wet cement paste may lead to bleeding and harsh cement paste may give a rough surface and also cause cracks. This normally does not happen unless there is a manufacturing defect.
If the test value is not in range of recommended result, there are many reasons behind it. The cement may be very fine or coarse, having a manufacturing defect, it might have absorbed moisture from the atmosphere. You can find this reason by conducting the various other tests of cement. In such case consult your engineer or check with your cement supplier or manufacturer.
The recommended result also depends on various standard guidelines of cement, brand of cement and types of cement.
(d) Standard Guideline of Standard Consistency Test of Cement:
There are various standard guidelines available to find out the consistency of the cement. Such as IS 4031 (Part 4)-1988, ASTM C 187, BS EN 196-3:2005, etc.
(e) Apparatus of Standard Consistency Test of Cement:
- A standard consistency test of cement is performed by using vicat apparatus.
- A standard consistency of mortar is measured by the flow table test.
To know more about standard consistency test of cement click here.
02. Initial Setting Time and Final Setting Time Test of Cement
Initial setting time is the time when the cement paste starts losing its plasticity and final setting time is the time when the cement paste completely loses its plasticity. In other words, you can understand that within the Initial setting time, cement paste starts to get converted, i.e. from a fluid state to a rigid state and after final setting time, it completely reachesrigid state. Setting time of cement is essential to know so that cement sets, neither too rapidly nor too slowly.
(a) Use of Setting Time Test of Cement:
Initial setting time of cement paste is important for concreting process, i.e. transportation, placing and compaction of concrete. Suppose it is 30 minutes, we have to place and compact it in 30 minutes of adding water. Do not compact concrete after initial setting time or do not use mortar after initial setting time.
Final setting time test determines safe removal time of scaffolding or sides of the form of concrete (not vertical supports.)
(b) Recommended Result of Setting Time Test of Cement:
The recommended result, for the OPC initial setting time is not less than 30 minutes and final setting time is not more than 600 minutes
(c) Why Setting Time Test Fails? & What if Test Fails?
If your test value is not in range of the recommended results, there many reasons behind it, Such that some chemical composition may have changed during production (manufacturing defect), a fault in the testing apparatus, error in testing etc. In that case, you can test again with accuracy, change your material an apparatus or consult your cement supplier/manufacturer.
Otherwise, you have to take care of the timing of work. If the initial setting time is less than this value, all the process, i.e. mixing, transporting, placing has to be completed within their time otherwise cement paste/concrete/mortar starts to set. If the final setting time is more than this value, you will have to retain scaffolding and the sides of the form, until the cement paste/concrete/mortar is completely rigid and will have to be careful to start the curing.
The recommended resultis different for different types of cement. It mayalso be different as per various national guidelines.
(d) Standard Guideline of Setting Time Test of Cement:
There are various standard guidelines available to find out the initial setting time and final setting time of cement. Such as IS 4031 (Part 5)-1988, ASTM C 191, BS EN 196-3:2005
(e) Apparatus of Setting Time Test of Cement:
Initial setting time and final setting time test of cement is performed by using vicat apparatus.
To know more about setting time test of cement click here.
03. Soundness Test of Cement
Soundness of cement defined as an ability to resist volume expansion after setting. It is essential that cement shall not undergo any appreciable change of volume after setting because otherwise,it will cause cracking, disintegration and distortion of the set and hardened mass.
(a) Use of Soundness Test of Cement:
The soundness test of cement is performed to ensure that after setting, cement will not show any large change in volume or any appreciable subsequent expansion. Otherwise, that will be crack concrete which will lead to corrosion and leakage.
(b) Recommended Result of Soundness Test of Cement:
Recommended result,
Le-Chatelier Method – For OPC maximum expansion is 10 mm.
Autoclave Method – For OPC maximum expansion is 0.8 %
(c) Why Soundness Test Fails? & What if Test Fails?
More than this value indicates that cement might have become unsound. Unsoundness is due to inadequately burnt cement component, insufficiency in fineness of grinding and thorough mixing of raw materials.
If cement is unsound then avoid using that cement because it leads to damage in concrete. You can ask the cement supplier/manufacturer to replace your material as it does not satisfy the standard criteria.
(d) Standard Guideline of Soundness Test of Cement:
There are various standard guidelines available to find out soundness of cement. Such as IS4031 (Part 3)-1988, ASTM C 151-09, BS EN 196-3: 2005
(e) Apparatus of Soundness Test of Cement:
Soundness of cement may be measured by two methods, namely “Le-ChatelierMethod”, in this method le-chatelier apparatus is used and “Autoclave Method”, in this method autoclave apparatus is used.
04. Fineness Test of Cement
By fineness of cement, we mean diameter of its smallest particle. The fineness of cement has a significant effect on the hydration and in increasing the rate of gain strength. The strength of cement is directly proportional to its fineness. Because, smaller the particle of cement, it offers a larger surface area and larger surface area gives more heat of hydration, larger area for bond hence faster the development of strength.
However, the excess fine cement increases the cost of grinding and need more water in hydration. It also affect the workability of cement paste/concrete/mortar and also causes bleeding. Therefore, it’s essential to check fineness of cement according to standard specification.
(a) Use of Fineness Test of Cement:
Fineness test of cement is performed to check the fineness of cement according to standard specifications. The fineness of cement can be measured either by the grain size of cement or by the surface area of cement. Followings methods are used to determine the fineness of cement.
- The sieve Test- Measures a grain size of cement.
- The blain’s air permeability test- Measures a surface area of cement.
- The Wagner turbidimeter method- Measures a surface area of cement.
(b) Recommended Result of Fineness Test of Cement:
The sieve Test- The weight of residue of the cement left on sieve shall not exceed 10%.
The blain’s air permeability test- The minimum value of the specific surface area of cement -225 m2/kg.
(c) Why Fineness Test Fails? & What if Test Fails:
If your test result is more than the recommended value, it indicates that the cement particle is coarser than the specified standard. It happens due to lack of care during manufacturing.
In that case, you should consult your engineer whether to use that cement is or not. If not, then avoid using of that cement and replace it.
(d) Standard Guideline of Fineness Test of Cement:
There are various standard guidelines available to find out fineness of cement. Such as IS4031-PART1-1996, IS 4031(Part2)-1999, ASTM-204-05, ASTMC-115-96a (reapproved 2003).
(e) Apparatus of Fineness Test of Cement:
Followings are various methods and apparatus using to measure fineness according to the various standard guidelines.
- The sieve Test (IS 4031- part-I) – 90 µ size sieve
- The blain’s air permeability test (IS 4031- part- II) – Blaine Air Permeability Apparatus
- Lee and nurse method-air permeability test (BS EN- 196-6: 1992after modified in blain’s method (ASTM- 204-05)) – Lee and Nurse Permeability Apparatus
- The Wagner turbidimeter method (ASTM C- 115-96a (reapproved 2003))- Wagner turbidimeter Apparatus
05. Compressive Strength Test of Cement
The compressive strength of the hardened cement is the most important property. Therefore, cement is always tested for strength before important works. Strength tests are not conducted on neat cement as it causes shrinkage and cracking. Thus, the cement mortar is used in this test. Type and nature of the cement also plays a vital role in the strength of mortar and concrete
(a) Use of Compressive Strength Test of Cement:
The compressive strength of cement gives the idea about the cement strength. It provides strength assurance. Ultimately it will decide how much cement to use and how much strength you will get.
(b) Recommended Result of Compressive Strength Test of Cement:
Recommended test result, for OPC
3days compressive strength is around 50%, 7 days compressive strength is around 70%, and 28 days strength is around 100 %. Suppose You have OPC 53 Grade cement for testing than the result should be after 3 days -26.50 N/mm2, after 7days – 37.10 N/mm2, after 28 days- 53 N/mm2.
(c) Why Compressive Strength Test Fails? & What if Test Fails:
If your test result is not in range of recommended result, there are many reasons such as improper mixing, an improper proportion of cement, sand and water, improper curing, some defect in cement or sand, error in experiment procedure etc.
In that case take proper care during performing the test. Check whether that all any defects in cement or sandand check properties of those material.
(d) Standard Guideline of Compressive Strength Test of Cement:
There are various standard guidelines available to find out the compressive strength of cement. Such as IS4031 (Part 6)-1988, ASTM C 109, BS EN 196 – 1:2005
(e) Apparatus of Compressive Strength Test of Cement:
Compressive testing machine and the cube mould (Size 70.6 mm*70.6mm*70.6 mm) is used to performed to compressive strength test of cement.
To know more about compressive strength test of cement click here.
The Chemical Properties of Cement
Cement contains multiple ingredients as its raw material like lime, silica, alumina, iron oxide etc. These ingredients interact with one another in the kiln during the manufacturing process and make a complex compound.
Chemical properties have a major effect either beneficial or adverse on the quality of cement. It depends on their limiting value in cement. Followings are the chemical properties of cement and their limiting value.
Material Composition
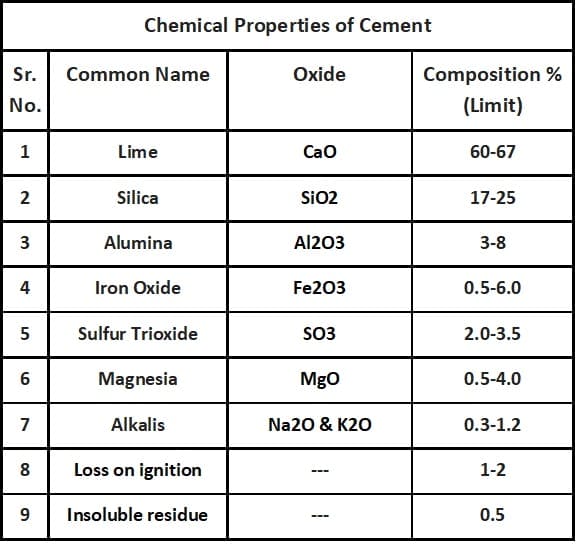
Chemical Properties of Cement
Effect of Variations in chemical components:
- MgO (Magnesia): The excess amount of MgO leads todetrimental expansion. This expansion occurs due to the hydration of free MgO in hardened concrete. MgO should be limited to 4%.
- Free CaO: Free Cao gives the same effect as MgO. Free Cao shows a large volume expansion after hydration which leads to the disintegration of hardened concrete.
- Na2O & K2O (Alkali Oxides): The excess amount of alkalis gives alkali-aggregate reaction which results in disruptive expansion.
All these will harm the structure.
- Loss on Ignition: Loss on ignition means, “pre-hydration or carbonation” of cement occurring due to prolonged or improper storage. Pre-hydration of cement degrades the performance of concrete/mortar, particularly strength and setting times. Carbonation causes a change in strength, porosity, pore size distribution, and chemistry in cement paste/concrete/mortar
The tests of cement we performed to ensure that the cement is of the desired quality and that conforms to the requirements of the relevant national standards. It is desirable for the purchaser or for an independent laboratory to make an acceptance test or, more frequently, to examine the properties of cement to be used for simple and special purpose.
Also Read:
Which is the Best Cement for House Construction?
Things to Keep in Mind Before Purchasing Cement
For How Long Period Cement can be Used? (From Date of Manufacture)
Image Courtesy: Image 1(a), Image 1(b) – civilsnapshot, Image 1(c), Image 1(d), Image 1(e), Image 1(f)
































