The foundation of your house is a critical part of its structure as it helps distribute the load and minimizes distress against the foundation soil movement, thereby keeping the building stable and secure. Hence, foundations are critical to the structural safety of a building.
Depending on the depth of the soil in which the foundation is made, there are two types of foundation used in constructing buildings :
01. Shallow foundation – These are used for small and light buildings. They are commonly referred to as spread footings or open footings. There are four types of shallow foundation:
- Individual footing or isolated footing
- Combined footing
- Strip foundation
- Raft or mat foundation
02. Deep foundation – These are used for large structures. There are two main types of deep foundation:
- Pile foundation
- Drilled Shafts or caissons
The foundation used should be sturdy enough to bear the load of the structure. Therefore, large-area footings are needed to spread the vertical load, improving the stability of the building. Different kinds of footings are designed based on the soil type, the type of structure, the site topography, and other local requirements arising during the design process.
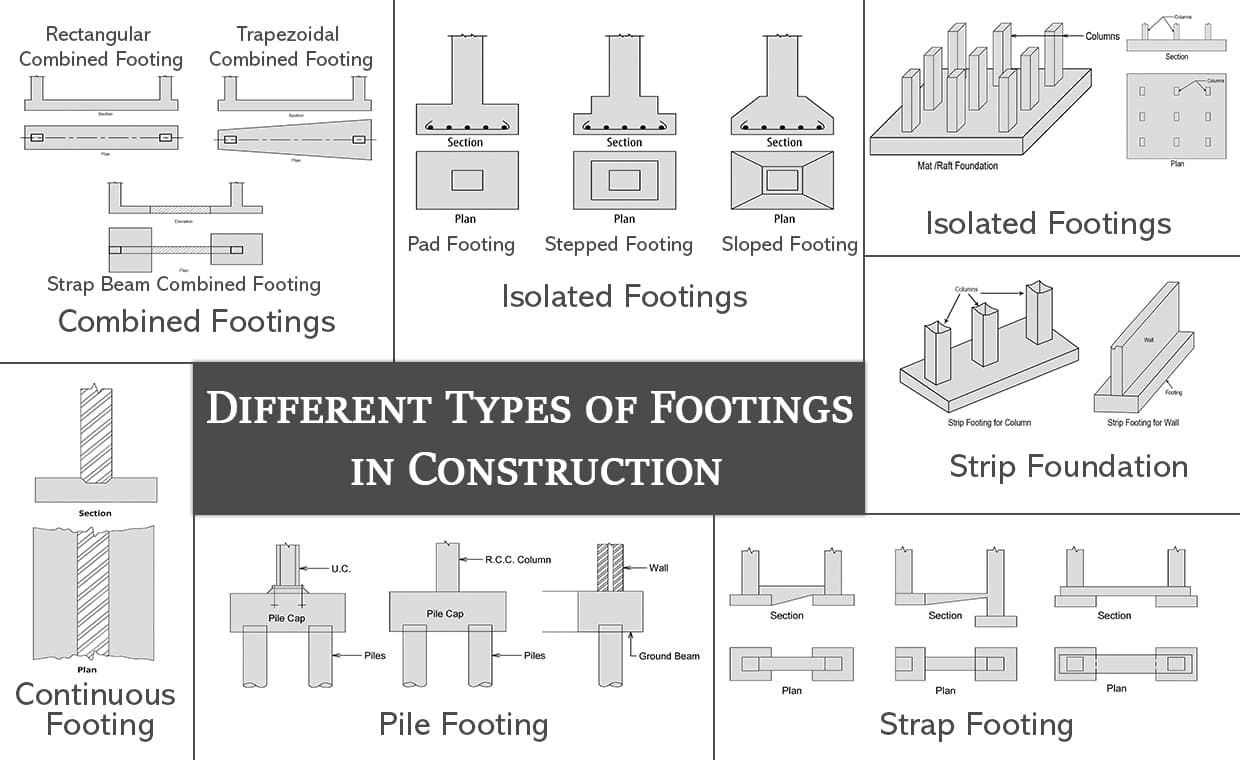
The different types of footings used in construction are described below:
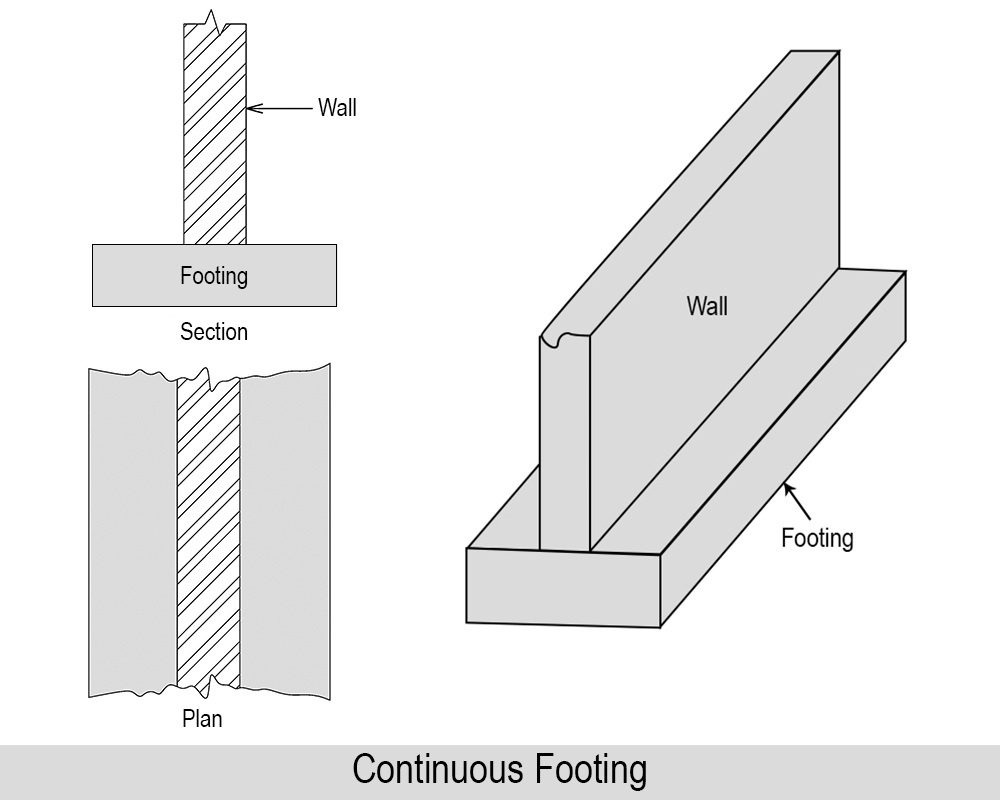
01. Continuous Wall Footing
The footing which supports a long masonry or RCC wall is known as a continuous footing. It can be either simple or stepped.
Generally, width of the footing should be at least equal to twice the width of wall that is rested on it. In this case, the width of the footing is smaller than the length of the footing, offering continuous vertical support to the structure. Basically, it runs throughout the length of the wall. This type of footing is not economical.
Use of Continuous Wall Footing: Continuous wall footings are used to support the foundation walls and load-bearing walls.
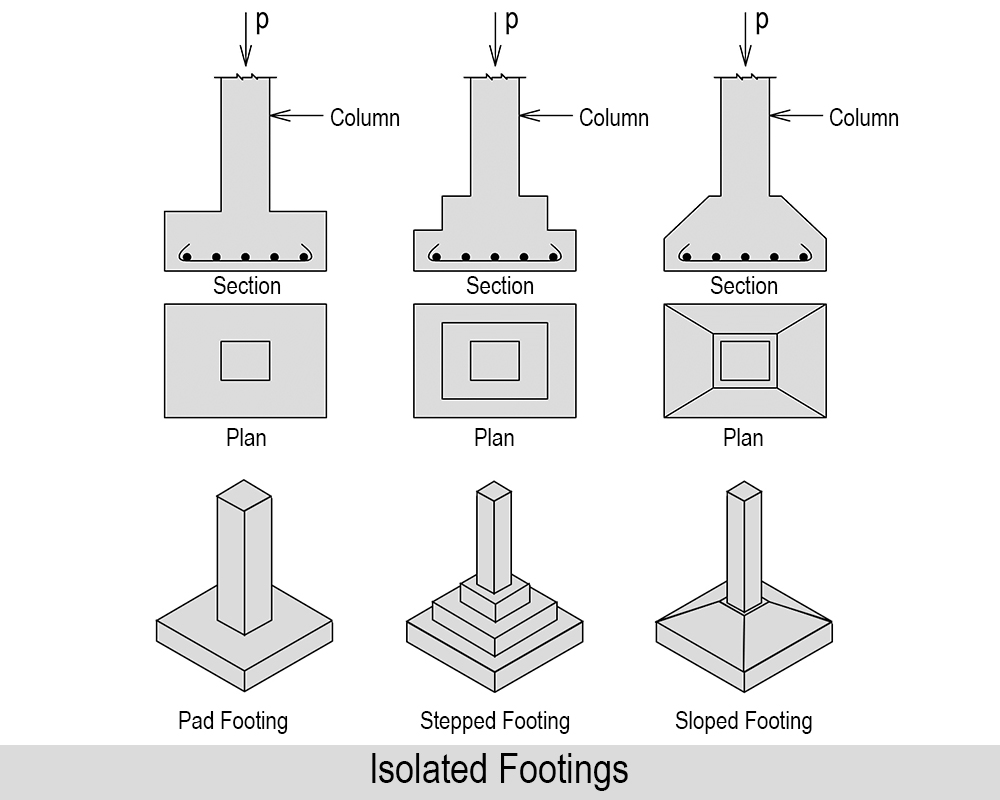
02. Isolated Footing
A footing that supports an individual column is known as an isolated footing. This kind of footing can be Pad, stepped, sloped or with isolated beam and slab. Where good soil is available, these footings are economical.
Use of Isolated Footing: Isolated footings are used as shallow foundation in order to transfer concentrated loads to the ground. To know the basic information, read Isolated footing.
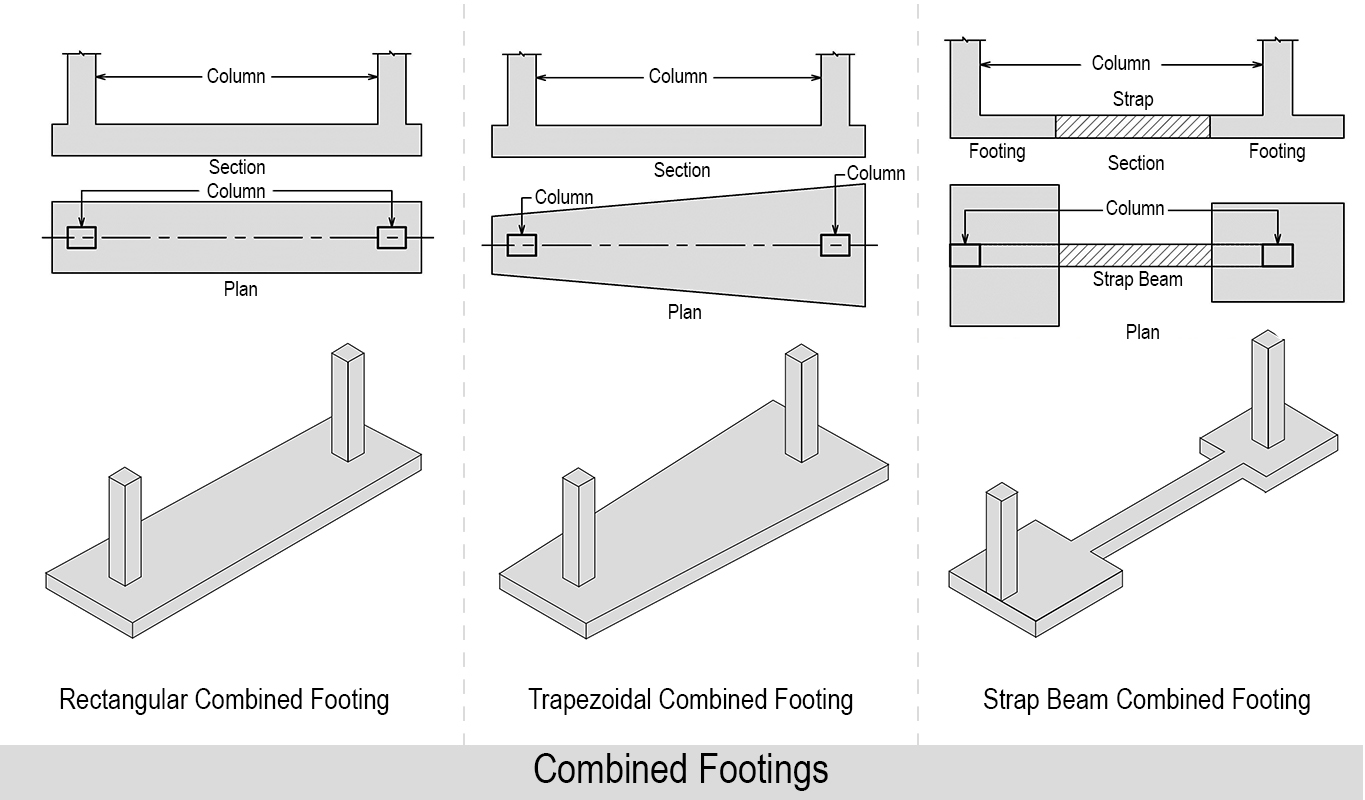
03. Combined Footing
A footing that supports two or more columns is known as a combined footing. It is used when two or more columns are close to each other or two or more individual footings of a column would overlap. Combined footing may be trapezoidal or rectangular in plan. A trapezoidal footing is provided when the load of one column is greater than the other.
Use of Combined Footing: Combined footings are used to transfer loads of closely spaced column to the ground or when the column face the boundary of plot.
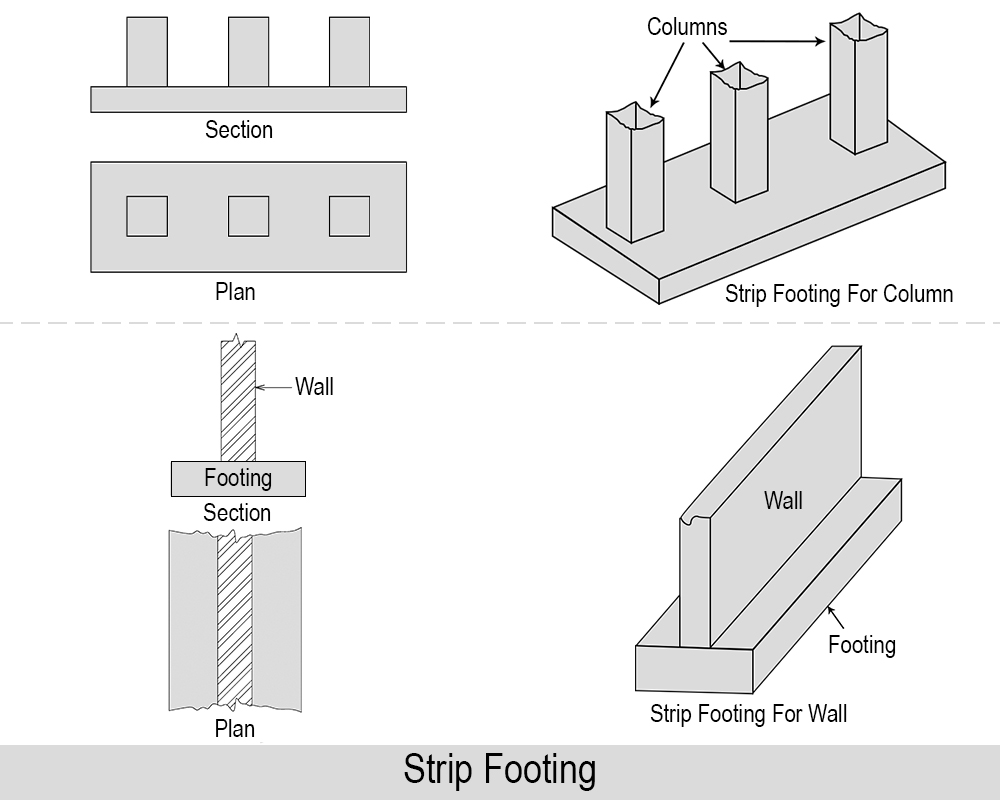
04. Strip Footing
A footing which supports a number of columns in a line has to be a combined footing known as strip footing. It is used when the row of a column is closely spaced and their spread footings overlap with each other. A strip footing is also known as a continuous footing.
Use of Strip Footing: Strip footings are used to transfer loads of closely spaced raw of columns to the ground.
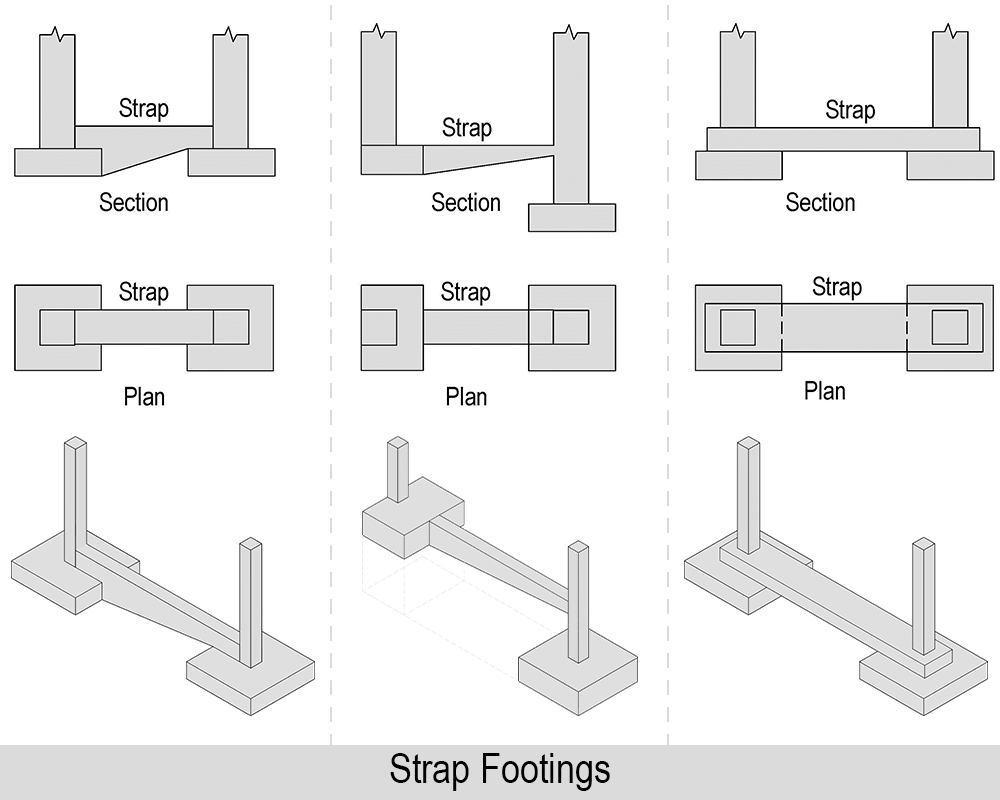
05. Strap Footing
When a distance between the two columns supported on combined footing becomes large, the cost increases rapidly. The strap footing is an economical option in such cases.
Use of Strap Footing: Generally, strap footings are used in conjunction with columns of adjoining property.
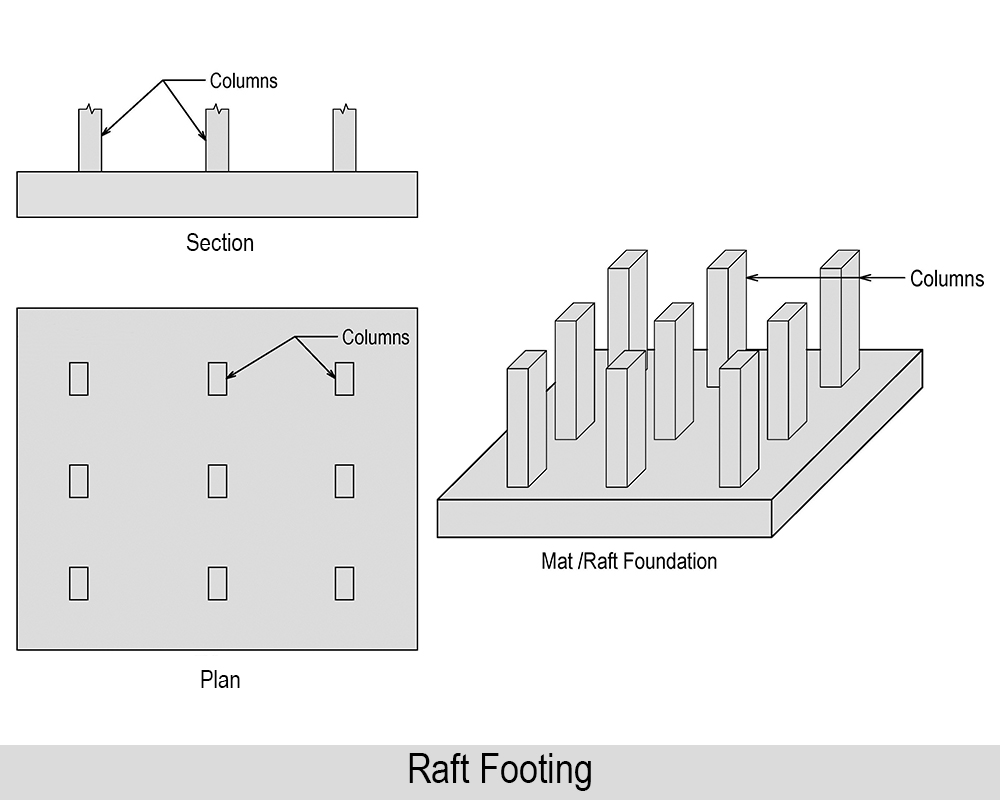
06. Raft Footing
If loads transmitted by the columns in a structure are heavy and the allowable soil pressure is small then footing requires more area. In such a case, it may be better to provide continuous footing under all columns and walls. Such kind of footing is called a Raft Footing.
Use of raft footing: It is widely used when soil has low load bearing capacity. To know more, read the basic information of raft foundation and also know the various types of raft foundation.
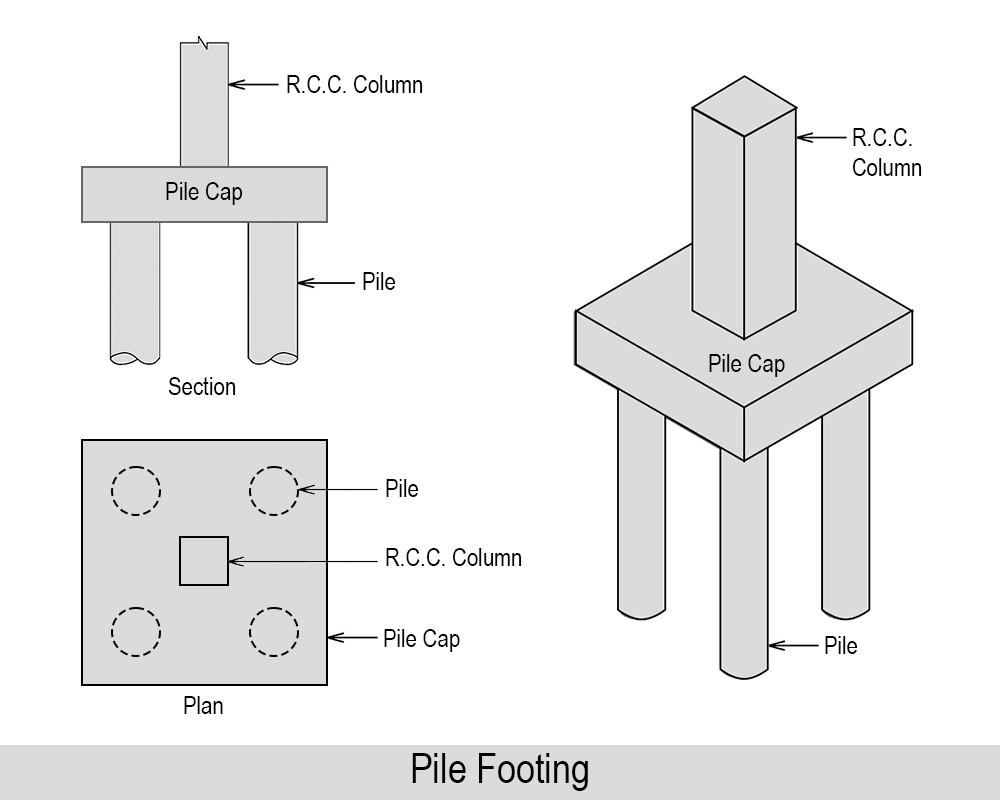
07. Pile Footing
According to ‘Richard L. Handy & M. G. Spangler’ (Author of book called Geotechnical Engineering – Soil And Foundations Principles And Practice), When the soil has a low bearing capacity or the ground water level is high, pile footings are applied. Piles are common while building foundation for bridges, dam etc. in walls.
Use of Pile Footing: Piles are used as deep foundation where the soil is very week and has higher groundwater table.
As Stated by ‘Allen P. Nangan II, Tomas U. Ganiron Jr & Doyce T. Martinez’ (Authors of the Scientific World Journal called Concrete Foundation Systems and Footings), when a load is gradually applied on a foundation, settlement occurs which is almost elastic, to begin with the ultimate load.
Shear failure occurs when a plastic yield of surface develops under the footing, extending outward and upward to the ground surface, and catastrophic settlement or rotation of the foundation occurs. Which may fail the foundation of the house.
There are multiple reasons that may cause the failure of foundation. To know more, read the various reasons of foundation failure. Selection of right foundation depends on the various important factors.
Summing up, footing plays an important role in the stability of the house. Right foundation makes your house long lasting
































