Before we understand what timber is, it is essential to talk about wood. ‘Wood’ in simple words can be stated as a hard, fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. Wood has been used for thousands of years by we humans.
Early humans used wood for various purposes, but primarily it was used as a fuel and even as a construction material. For Example, they used to make huts out of wood; they also used it for cooking purpose. Apart from this, wood had a wider range of use even then. This was because it was readily available, and no elaborate or sophisticated tools were required to work with it.
Wood comes from trees. The wood is fine, uniform structural tissue of a tree, and is favored because of its exceptional cutting qualities, durability, rich color, and aroma. It is moderate in hardness yet it is highly workable. The wood obtained from each tree has its potential, specific quality and peculiarity but at the same time, it can be associated with a few flaws as well. This is something crucial which one must take into consideration while understanding the nature of wood.
Wood has been used as a building material for thousands of years, being second only to stone in terms of its rich and storied history in the world of construction. It has evolved in over the ages from natural material to a modern industrial and engineering material. Wood has a unique ability to contribute for well-being of human being both as a material for use and as a key element in the natural world of the forests.
Timber – Lumber:
The word ‘Timber’ is used to describe structural products of wood, while in North America; the word ‘Lumber’ is used. ‘Wood’ is often used to describe the furniture and other non-structural items.
Definition of Wood:
Different experts have defined wood in their own way. According to ‘Christopher Gorse’, ‘David Johnston’ and ‘Martin Pritchard’ (Author of Oxford Dictionary of Construction, Surveying & Civil Engineering), Wood is a naturally occurring material obtained from trees.
According to ‘Catherine Soanes’, ‘Sara Hawker’ and ‘Julia Elliott’ (Author of Pocket Oxford English Dictionary), Wood is a hard and fibrous substance which forms a significant part of the trunk and branches of a tree.
Wood is a natural material that has been used for the construction of buildings, bridges and various other structures since many centuries. Wood can be fabricated into all kinds of shapes and sizes to fit practically any construction need.
Wood is further processed and transformed into timber, lumber etc. These days, with the advances in science and technology, it is rapidly replaced by composite wood materials in which natural wood is just an essential ingredient of a matrix or a laminate.
The latter is found to be more useful and adaptable as woods may be treated chemically, thermally or otherwise as per requirements. Some examples are plywood, fiberboards, chipboards, compressed wood, impregnated wood etc.
Timber is a remarkably a versatile material. Timber is used as a construction material because of its fire resistance, good structural characteristics, insulating properties and moreover, it is economically feasible. Naturally forming long slender elements ideal for framing, it represents one of our oldest building materials. Relatively recent developments in processing and technologies have provided products of timber for a wide range of application. As wooden technologies overcome constraints, timber begins to compete with steel and concrete.
Definition of Timber
According to ‘David Blockley’ (Author of New Dictionary of Civil Engineering), Timber is a wood, which is prepared for building and carpentry use.
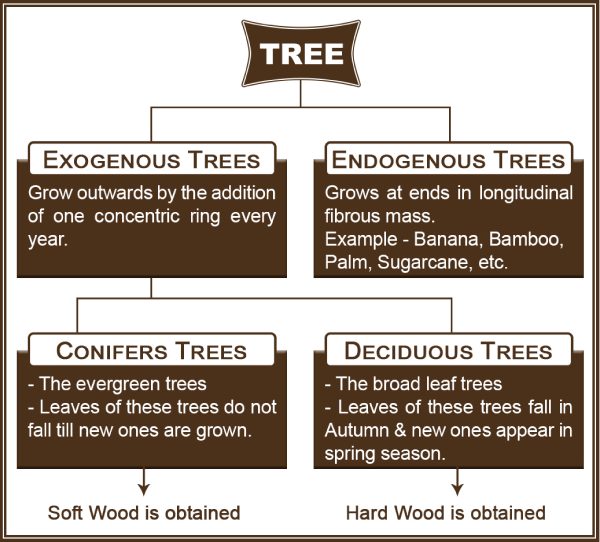
Tree Classification Based on Mode of Growth
Timber is obtained from two broad categories of trees:
- Conifers Trees
- Deciduous Trees
These trees are further classified as softwood and hardwood. The terms ‘softwood’ and ‘hardwood’ do not exactly indicate softness or hardness of particular timbers. In fact, some hardwoods are found to be softer and lighter than softwoods. The main differences between hardwoods and softwoods are botanical, and relate to the way the tree grows.
01. Softwood
- Softwoods are obtained from Conifers or evergreen trees.
- Examples of softwood trees are Chir, Deodar, Fir, Kali, Pine, Spruce etc.
- Softwood has a relatively simple structure with long slender cells with flatted or tapered, closed ends arranged in radial files.
- Softwoods are generally faster-growing and cheaper than hardwoods.
- They are considered less decorative and are typically less prone to moisture movement.
- According to ‘Madan Mehta’, ‘Walter Scarborough’ and ‘Diane Armpriest’ (Authors of Building Construction), Softwood trees mature for harvesting two or three times faster than hardwood trees.
- Approximately 75% of North American forests contain softwoods. Because of their faster growth and relative abundance, softwoods are commonly used for structural framing of the wood building in North America. Hence, in most of the buildings, floor joists, rafters, ceiling joists, studs, sheathing are of softwood lumber.
02. Hardwood
- Hardwood is a dense wood obtained from a broad-leaved tree or Deciduous Trees.
- Examples of hardwoods are Mahogany, Oak, Sal, Teak, Greenheart, ash, beech etc.
- The anatomy of hardwood is more varied and complicated than softwood with thicker cell walls making primary tissue for strength.
- Generally, Hardwoods are used for flooring, finishing, where their higher densities (which give excellent abrasion resistance) are useful.
- Hardwoods are also used for wall panelling, trims, cabinets, furniture because they have a more interesting and varied grain structure.
There are various stages involved in the preparation of Timber from the trees.
Processing of Timber
Mentioned below are the four stages involved in timber processing,
01. Felling of Trees
- To get Timber, the trees are cut down or they naturally fall on the ground. This is known as the felling of trees.
- The essential facts to be remembered in connection with felling of trees are age of trees for felling, Method of felling and season for felling.
02. Seasoning of Timber
- When a tree is newly felled, it contains about 50 per cent or more of its dry weight as water.
- Therefore, it is necessary to remove the water before the timber can be used for any engineering purpose. So, timber seasoning is the process in which timber is dried.
To know more details about timber seasoning, Read – Seasoning of Timber: Basic Info | Objectives | Pros & Cons!
03. Conversion of Timber
The process of cutting and sawing timber into suitable sections is known as the conversion of timber. This process is carried out in timber yard with appropriate machinery at different stages.
04. Preservation of Timber
Preservation of timber means protecting from fungi and insects attack so that the life of timber is increased. The longevity of timber can be considerably increased by treating it with certain chemicals grouped together as preservatives before use. The preservatives may be water solvable salts or oil solvable salts or volatile base salts. The main objective of such treatment is to ensure a longer, trouble-free life of timber.
The objectives of preservation of timber are,
- To increase the life of timber structure.
- To make the durable timber structures.
- To protect from the attack of destroying agencies such as fungi, insects etc.
To know more details about preservation of Timber, Read – What is the Preservation of Timber? – Know More About it!
The quality of timber depends on the environmental conditions of the locality, maturity of the tree, methods of seasoning, process of preservation and time of felling. There are so many characteristics that timber contains and make it suitable for various applications.

Timber
Properties of Timber
- It has uniform colour. Its light colour usually indicates timber with low strength.
- It is durable.
- It is hard.
- It is capable of retaining its shape during conversion or seasoning.
- It provides good insulation from the cold.
- It is capable of taking loads slowly or suddenly.
- A good timber is free from serious defects like knots, shakes, flaws and cracks.
To know more details about timber properties, Read – Properties of Timber as a Building Material
There are many structural and nonstructural applications of timber in building construction. It is essential to clarify the terminology for its various uses.
Uses of Timber as a Building Material
Timber from well-managed forests is one of the sustainable resources. Timber is categorized amongst the world’s most eco-friendly building solution. It ages naturally and is not degraded into toxic product that damages the environment. In addition, timber is renewable as it continually grown in plantations and forests. The various uses of timber are,
- It has good strength and hence used for making load-bearing members like beams, columns, trusses and piles.
- It is naturally available, ready to use and economically feasible. The rough timber is used for temporary works like scaffolding, centering of an arch etc.
- It can be easily cut and converted to any size and shape. Hence it is used for frame and shutters of doors and windows, roofing materials, furniture etc.

Uses of Timber
- It has a very high strength to weight ratio, the capability of transferring both tension and compression forces and is naturally suitable as a flexural member.
- It is also used for temporary bridges and boat construction.
- Timber also benefits from its natural growth characteristics. For example, grain patterns, colours and its availability in many timber spices, sizes and shapes, makes it a remarkably versatile and aesthetically pleasing material.
Timber can be used for so many purposes, but has some advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of Timber
- Timber can be easily shaped and modified. Remaining waste can be recycled. Timber generates very few pollutants compared to other building products.
- Timber can be easily connected using nails, screws, dowels, bolts and connectors. Also, under controlled conditions of temperature and humidity, adhesives may be used to connect the timber element.
- Timber is light in weight and easy to handle in manufacture, transport and construction.
Disadvantages of Timber
- It is likely to crack, wrap, bend and decay, if not properly seasoned and not treated with the preservatives.
- There are many applications for which timber is unsuitable due to durability issues.
- It requires careful regular maintenance.
- It is subjected to risk of fire. Timber can burn making it a less than ideal material to use in applications where fire safety is a concern.
- If not readily available, it proves to be costly.
- It is also susceptible to termite attack if not maintained properly.
To know more details about advantages and disadvantages of timber as a building material, Read – Advantages & Disadvantages of Timber as a building Material
Though at least, Timber is also believed to be a ‘future material’. There are few building materials which inherently possess the environmental benefits of wood. Timber is most widely used building material because it has a range of varied characteristics that makes it suitable for a wide range of application.
Timber is a natural and extensively utilized construction material extracted from trees. Wood has been used for centuries, and it is still a relevant construction material today, because of its versatile properties, its diversity and aesthetic qualities.
There are several inherent characteristics that make timber an ideal construction material. These include its high strength to width ratio, its durability, performance and good insulating properties against heat and sound. Timber is also a renewable resource and can make an essential contribution to the achievement of sustainable building. Timber excels where strength (or stiffness) to weight is more important than absolute strength (or stiffness).
Must Read:
Wood Veneer: All You Would Like to Know!
7 Tips to Remove Colored Stain from Wooden Furniture
Image Courtesy: Image 2

































