All structures are so designed that they can withstand all natural as well as man-made hazards. The building, therefore, needs to have materials with a property such that they can resist such hazards. For resisting a fire all the materials must not be combustible but should have such properties that they can withstand fire for a larger duration. So that the residents can come out or can be evacuated by the time the fire is extinguished or their life is endangered.
To take care of such provisions all states have their own standards for fire-resistance of buildings based on fire tests. In India, National Building Code classifies the construction into four classes, namely, type 1, type 2, type 3, and type 4, on basis of fire – resistance offered by building components for 4-hours, 3-hours, 2-hours, and 1-hour fire resistance respectively. All the structural components of a building should be constructed in such a way and of such materials that they withstand fore as an integral member of the structure, for the desired time period according to the type of construction, in case of fire, so that during such time it allows occupants to come out and also the building does not collapse during such time.

Fire Resistant Construction
To obtain fire resistant construction, use of combustible material like wood, cardboard, baled cotton, plastic, fabrics etc. should be avoided while to construct the structural elements.
To achieve fire resistant construction, due considerations should be made in design and construction of the following structural element of a structure.
- Walls and columns
- Floor and roofs
- Wall openings, and
- Building fire escape elements, e.g. staircase, corridors, entrances, exits etc.
01. Walls and Columns
Walls
The load bearing walls or column of masonry or RCC should be thicker in section so that they can resist fire for a longer time and also act as vertical barriers for the passage of heat and fire and give minimum smoke.
- If the construction is of solid bearing walls, bricks should be preferred to stone.
- If it happens to be a framed structure then R.C.C frames are preferred to those of steel frames.
- If the use of steel only is to be made due to specific demand then it should be protected by embedding it in concrete or by covering it with some other fire–insulating material, such as burnt clay blocks or terra-cotta.
- Walls of lightweight concrete are preferred to dense concrete as far as fire resisting qualities are concerned.
- Both load-bearing and non-load bearing walls should be plastered with fire resistant mortar to get the fire-resistant construction.
- Normally, 20 cm thickness of the common wall (i.e. wall separating two building) is sufficient from fire-resistant point of view but it should be raised above the roof level by at least 90 cm.
- The partition walls should similarly be of fire-resistant materials such as, R.C.C or reinforced brickwork, hollow concrete, burnt clay tiles, reinforced glass, asbestos cement board, or metal lath covered with cement plaster.
- In case, wooden partitions are employed, they should be covered with metal lath and plaster. A cavity wall construction also offers good resistance against fire.
Columns
The desirable fire grading is of 4 hours for columns and girders whereas for beams it is of 3- hours, depending upon type of structure. Therefore, as already mentioned, RCC framed structures are preferred to steel structure for fire resistance.
- As steel columns are liable to twist or buckle or distort under intense fire, they should be protected by use of insulating materials such as concrete, hollow clay tiles, bricks, metal lath followed by plaster etc.
- In modern buildings, the columns are made fireproof with concrete and covered in
- The combination of terra-cotta and concrete is most suitable for fireproofing of a steel column.
- Sufficient cover reinforcement in RCC members like slabs, beams or columns should be provided to enable them to function satisfactorily, under fire for a maximum possible time. The less is the cover, the less is the safety.
- It has been recommended for a structural component like columns, girders, trusses, etc. to have a cover of at least 50 mm outside the main reinforcement.
- The fireproofing treatments, which can be possibly be given to concrete and steel columns construction.
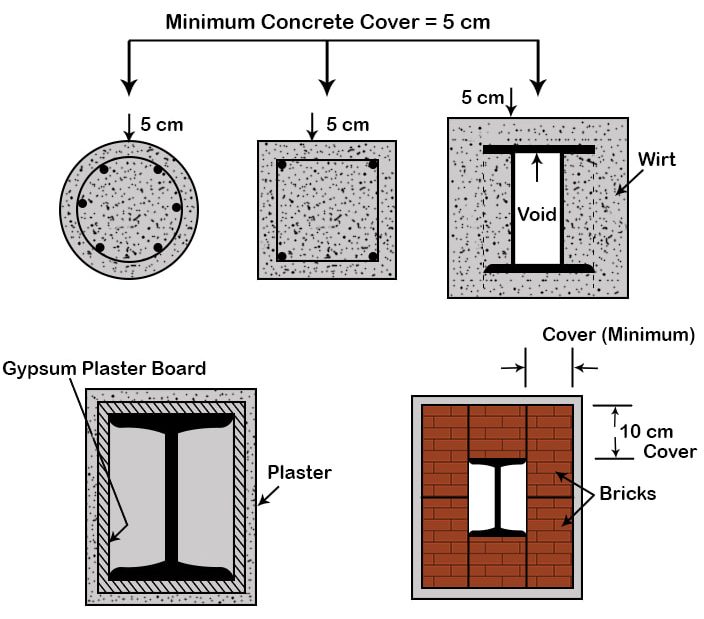
Following are the minimum thickness of cover recommended in R.C.C element:
- Column: 25-35 mm
- Beam: 25-35 mm
- Slab: 20-30 mm
- Footing: 50 mm
- Retaining wall: 30 mm
- Shear wall: 25 mm
- Stair: 25mm
Below is the table which gives a minimum thickness of wall for different fire grading:
Wall thickness for fire grading (for fire resistance ratings):
- Construction and Materials
- Minimum thickness in centimetres (excluding plaster for a period of)
Bricks and Solid Block Construction
| 6 hrs. | 4 hrs. | 2 hrs. | 1 hr. | ½ hr. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01. Bricks of clay, concrete or sand-lime built as a solid wall: No Plaster | 20 (8”) | 20 | 20 | 10 | 10 (4”) |
| (a) Built as a cavity wall | 25 (12”) | Note: The minimum thickness that can be built with cavity wall is 25 cm and hence less thickness is out of question | |||
| 02. Concrete Blocks: Built as a cavity wall 10 cm outer leaf, inner leaf of solid or hollow concrete blocks…. | 10 | 7.5 | Note: The minimum thickness that can built with concrete block is 7.5 cm so less thickness is out of question. | ||
| 03. Reinforced concrete: With minimum concrete cover to a reinforcement of 2.5 cm…. | 20 | 18 | 10 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
02. Floors and Roofs
Floors
The floors and roofs should be made of fire resisting materials as they act as horizontal barriers for spreading of heat and fire in a vertical direction.
- Flooring with a material, like concrete, ceramic tiles and brick, is regarded to be most suitable from the viewpoint of fire-resisting qualities. The use of terrazzo, marble and slate as floor surfaces is also quite satisfactory.
- In case, if the usage of combustible materials, like wood, cast iron, rubber, linoleum, cork, carpet, etc. in flooring, becomes unavoidable due to financial or practical considerations, then the following points should be taken into consideration
In case of wooden joist floors, joist at a greater spacing should be used to limit the deflection within allowable limits in the event of fire accidents.
Fire stops or barriers on wooden floors should be provided at suitable intervals.
- While using combustible materials, such as cast iron, wrought iron, carpet, etc., they should be protected by a covering of various insulating material such as ceramic tiles, plaster, tera-cotta, bricks, etc.
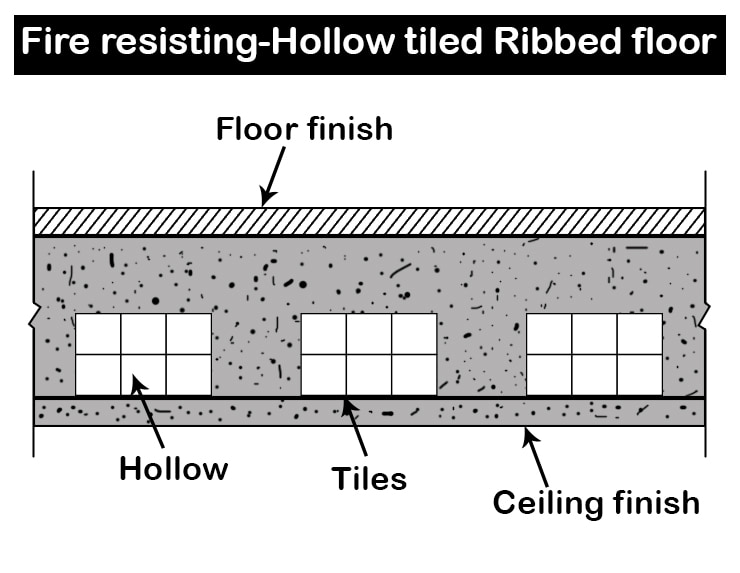
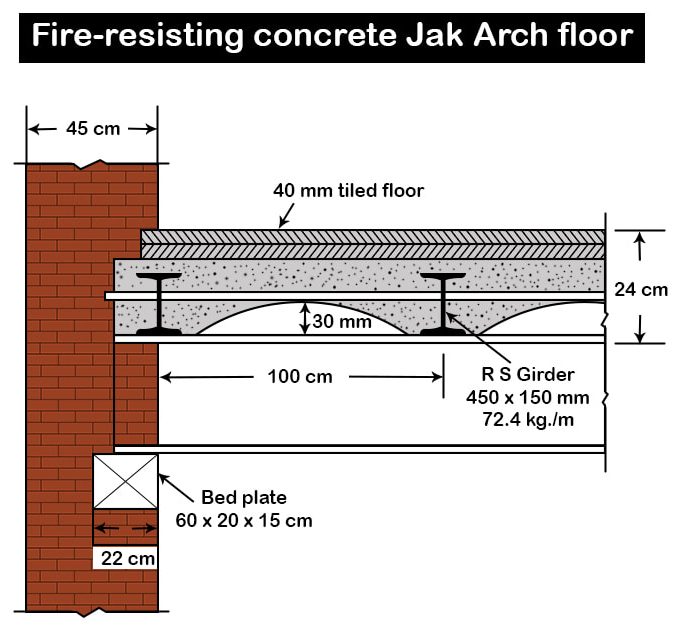
- For fire resistant construction, the floor such as concrete jack arch floor with steel joists embedded in concrete, hollow tiled ribbed floor, RCC floor etc. should be used.
Roofs
For fire resistance of roofs, the flat roof should be preferred to sloping roofs or pitched roofs and all the considerations made above for floors also hold true in case of roofs.
- In case, the use of sloping roof is restricted due to some reasons, then the trusses should be of either R.C.C. or protected rigid steel should be used with a covering of asbestos cement sheet.
- Regarding ceilings, they should be either directly attached or suspended from the floor joist. The ceiling should be made fire resistant by fixing asbestos cement boards, fibre boards, metal lath with plaster to their framework.
03. Wall Openings
From fire resistant construction point of view, firstly the opening in the walls should be restricted to a minimum and secondly, they should be protected by suitable arrangements in case of fire.
If properly protected these openings also serve as means of escape in a fire. Otherwise, they provide the passage for the spread of fire in the horizontal direction. Doors and windows should be made of suitable fire-resistant material. These days wire-glass panels are preferred for windows.
The following points should be taken into consideration for protecting the openings:
- Solid timber doors having a minimum thickness of 4 cm should be used where some degree of fire-resistance is desired.
- All those openings which are used for communication should have double fire-proof doors and other openings may have single fire-proof doors.
- Any window exposed to the roof or other structure should be protected by fireproof shutters.
- If any structure has a separation less than 6 meters from adjoining structure, then all doors, windows or exposed side should be made fireproof.
- All escape doors should be in such a way so that it provides free circulation to the people in passages, lobbies, corridors, stairs, entrances, etc. and are made up of fire-proof materials.
- Windows if carried down the floor should have a suitable barrier, like projecting slab beyond the outer face of the building.
04. Fire Escape Elements (e.g. Stair-cases, Corridors, Lobbies, Entrances, etc.)
- All these firescape elements should be constructed of fire-resistant material and well separated from the rest of the building.
- Doors to the staircases, corridors and lifts should be made of fireproof materials.
- Staircases should be located next to the outer walls and should be accessible from any floor in the direction of the exits from the building.
- The fireproof doors to these emergency staircases should be fixed in such a way so that they can be closed from inside only. Such an arrangement will help the people to leave and evacuate the building safely and quickly in case of fire accident.
- In single storey building, provision of an accessible fireproof window should be large enough for leaving the building.
- In the case of multi-storeyed structures, the number and placement of the staircase should be decided in such a way so that it provides equitable distribution of the population of the floor overall the staircases. Local norms should be followed.
- All internal staircases should be made of fire resisting material such as RCC and various other fire resisting materials.
- A ‘straight flight type’ staircase should be generally provided where possible because if the fire occurs user can easily move from that place.
- The minimum clear width of a staircase in residential buildings shall not be less than 1m.
External Stairs
All external stairs like fire escape stair, spiral stairs, steep ladders and ramps are treated as supplementary means to the internal staircases.
01. Fire Escape Stairs
- Fire escape stair should be “straight flight” having a width of not less than 75 cm and treads of 15 cm and width, not more than 20 cm.
- The number of risers should be limited to 16 per flight.
- All stair ladders and landings should be provided with robust, non combustible handrails at a height not less than 100cm.
- The ramp should also be projected over the roofs by hand-railing and they should not have a gradient of more than 1 in 10.
02. Spiral Stairs
- Spiral stair should be limited to be used in the buildings with a low density of population. The spiral stair should be made of non-combustible material and should have diameters not less than 1.5 meters and height not exceeding 9 meters.
03. Steep Ladders
- Steep ladders are used in buildings having a very low density of population where the use of fire escape stairs and spiral stairs is quite impractical.
- The width of ladders should not be less than 45 cm and grips projecting 100 cm above the top of the rungs should be provided.
- Landings at the approach and an intermediate stage should be provided where ladder height exceeds 6 meters.
- Ladders used with a height exceeding 9 meters should be provided with guards to form an enclosure for refuge in the event of a fire accident.
- Ladders should preferably, be located at least 10 cm away from the wall and not steeper than 600 to the horizontal.
Conclusion
All of the above points are very important for fire resistance construction. Ensuring all these will save you as well as your loved one’s life, in case of such accidents/ hazards which may occur during the life of a building. If you think some points are missed out or you have any information on this topic other than listed in this article please do share with us.
Also Read:
Acrylic Finish VS Laminate Finish: Select the Best for your Kitchen Cabinets!!!
Smooth Faced Plaster V/S Sand Faced Plaster
Importance of Vernacular Architecture




































