A combination of components connected together in such a way to serve a useful purpose is called structure. Structures can be classified in a number of ways: solid, framed structure, shell, membrane, composite, trusses, cables and arches, surface structure etc.
In the world of construction, the term ‘structure’ refers to anything that is built or constructed with interconnected parts at fixed location on the ground. This includes buildings, but can refer to anybody that is designed to bear loads, even if it is not intended to be occupied by people (engineers sometimes refer to these as ‘non-building’ structures – such as tunnels, bridges and so on).
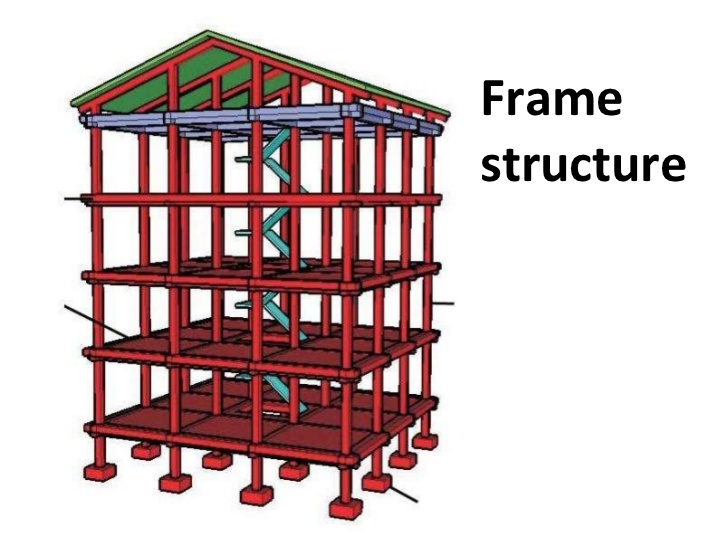
What is Framed Structure?
Framing means to give shape and support to a structure by combining components in building. Hence, a framed structure is a structure having the combination of beam, column and slab to resist the gravity and other lateral loads. These structures are generally used to overcome the large forces, moments developing due to the applied loading. Pole barn homes are a typical example of a frame structure.
Component of Framed Structure and Their Role
Frames are generally used in building and are composed of beams and columns that are either pinned or fixed connected, like trusses. Frames extend in two or three dimensions. Frames can be of any materials i.e. RCC, steel, wood etc. In case of framed structure, the loads of floors, roofs and panel walls are supported by the beams which ultimately transmit these loads to the columns. In framed structure, load transfer path is from slab/floor to beam, beam to column and column to footing, i.e. to ground.
A wall is a member of framed structure, whose length and height are larger than the thickness of it. Walls which are subjected to vertical loads called are load bearing walls. Walls subjected to no loads other than their own weight, such as panel or enclosure walls, are called non-load bearing walls or partition walls. Walls with a primary function of resisting horizontal loads are called shear walls. In framed structure, the walls are normally non-load bearing except shear walls.
RCC non-load bearing, reinforced concrete walls, frequently classified as panels, partitions, or cross walls, may be precast or cast in place. Panels serving merely as exterior cladding, when precast, are usually attached to the columns or floors of a frame, supported on grade beams, or supported by and spanning between footings, serving as both grade beams and walls. Cast-in-situ cross walls are most common as substructures.
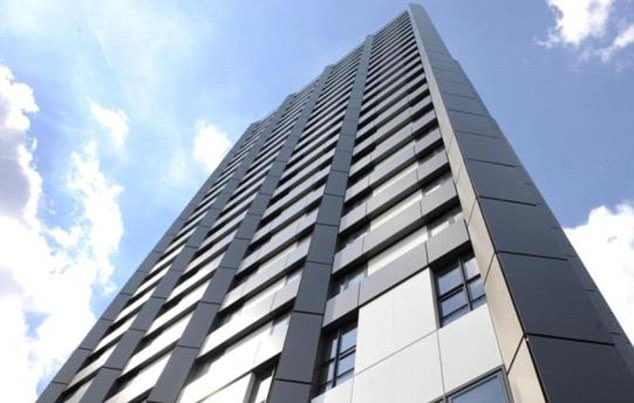

Panel walls can be replaced by cladding panels. Cladding is a term which is generally used for thin sheets required to enclose the framework. The wall cladding can be of asbestos cement sheets, corrugated galvanized iron sheets, copper sheets, thin concrete slabs, panel of glass or wood, tiles, etc. A brief discussion about framed buildings is given below
Types of Frames
There are basic three frames depending on material used in construction:
- Steel Frame
- Concrete Frame
- Wooden Frame
There are also different types of frames depending on the connection between beams and columns.
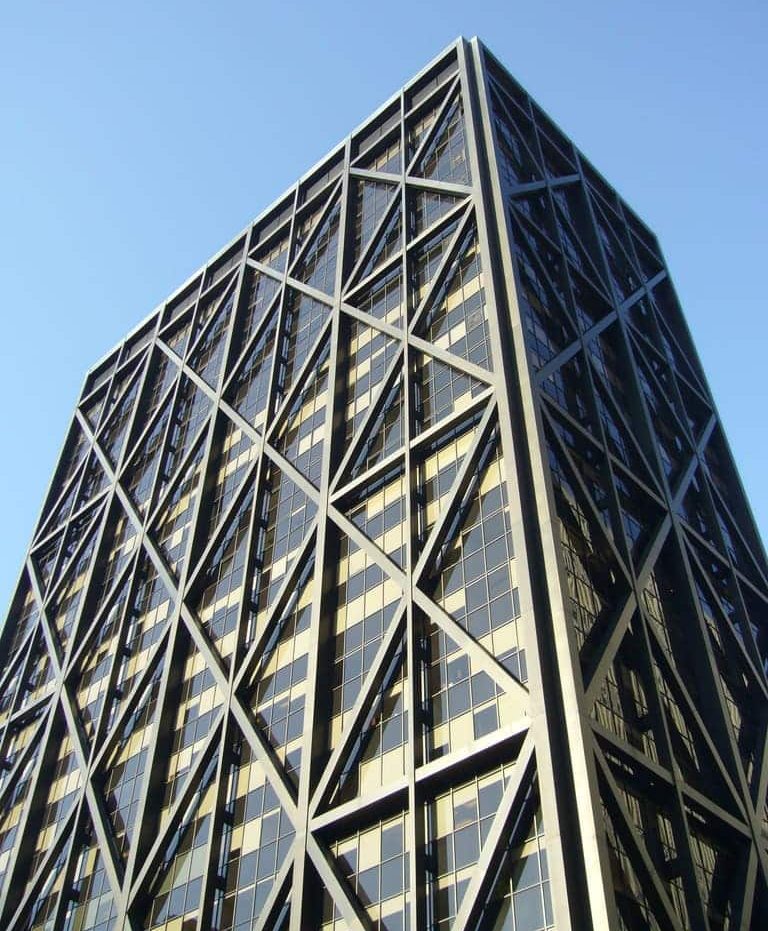

01. Braced Frames – All connection between beams and columns are pinned and there are diagonal bracing members.
02. Moment Resisting Frames – Connections between beams and columns are rigid and there is no diagonal bracing members.
Other types of Frames are:
- Balloon framing
- Space frame
- Portal frame
- “A” shaped framed house
Material Used in Framed Structure
Low-rise framed structures are constructed of materials like wood, steel and RCC. On the other hand, multi storied framed structures are constructed of mild steel.
Advantages of Framed Structure
01. Speedy construction is possible due to its simple geometry. It can be constructed more rapidly than ordinary walled structures. It consists of only columns and beams (or partially the floor slab) as the main structural elements. It is possible to carry out several building construction activities, e.g., construction of frame work of the upper floors and finishing of the lower floors simultaneously. Hence speed in construction in a framed structure can be easily achieved.
02. The strength and stability of the structures is more.
03. Multi storied structures can also be constructed.
04. A framed structure is better resistant to vibration. Framed structure can resist vibrations effectively and hence are ideal for buildings in seismic zones and for factory building.
05. Framed structures are very rigid and stable. Framed structures are able to resist tremendous vertical (dead load) as well as lateral loads (wind), earthquake without substantial deformation/deflection.
06. Dead load is reduced due to absence of thick load bearing walls etc.
07. Every floor slab being finished becomes cover to protect the lower floors from rain and sun.
08. Framed structure provides more floor areas without obstacle between columns. A non-load bearing wall between the adjacent columns and a beam over it are supported on a beam. This means that maximum height of a wall is equal to that of story height. Thus, this form of construction requires thin panels which in turn increase the floor area. However, the external walls should be sufficiently thick to withstand weather conditions.
09. Flexible utilization of space. No necessity to construct walls on walls. Any wall can be taken anywhere. Hence, flexibility in use.
10. Adaptable to almost any shape.
11. Framed structures can be easily altered within limits of frame. It is possible to change the position of panel wall to meet the requirements at any time. Thus, greater freedom in planning can be easily achieved.
12. Offsite preparation is possible in framed structure, especially for prefabricated construction using precast concrete or structural steel elements.
13. Acceptable distribution of natural light – window openings can be provided easily on eternal walls.
14. Easy to analyze and design structures including computer aided designs, due to simple geometry, i.e. easy methods of analysis.
15. This form of construction divides building components into two distinct categories, i.e., load bearing and non-load bearing. Non-load bearing members can be constructed with low-cost materials.
16. These structures are most suitable and economical on filled and soft grounds when compared to ordinary walled structures.
Wooden Framed Buildings
Wood offers several advantages like beauty, versatility, durability, high strength to weight ratio, good electrical insulation, low thermal inductance, and excellent strength at low temperatures. It has high shock absorption capacity. It can withstand large over-loads of short time duration. It can be bent easily to sharp curvature. It can receive a wide range of finishes for decorative and protective purposes. When wooden frames are used, the walls are conventionally built with slender studs spaced 40 cm center to center.

Facings such as sheathings and wall board and decking, floor under-layment and roof sheathing are generally available in proper sizes for attachments to studs, joists and rafters with the spacing. Timer studs are usually set in walls and partitions with wide faces perpendicular to the face of wall or partition. The studs are nailed at the bottom to bear on the sole plate and at the top to a pair of horizontal joists or rafters. They may be supported on the top plate or on a header called a rib band. The wood bearing wall constructions are generally either braced to balloon frame or platform frame.
Steel Framed Structure
These buildings are made up of a steel framework which supports all the loads. The columns, the beams, and girders in these buildings are made of steel sections. These buildings should be adequately braced in order to resist the wind and earthquake forces. Fire-resistant materials and other light materials are generally used for the partitions and exterior walls of these buildings. Thus, the steel framed buildings are similar to RCC framed building. Steel, being so much stronger than all forms of masonry, is capable of sustaining far greater load in a given space. Thus less no. of columns properly can be spaced to provide support for the beams spanning between them, thus achieving large column free spaces.
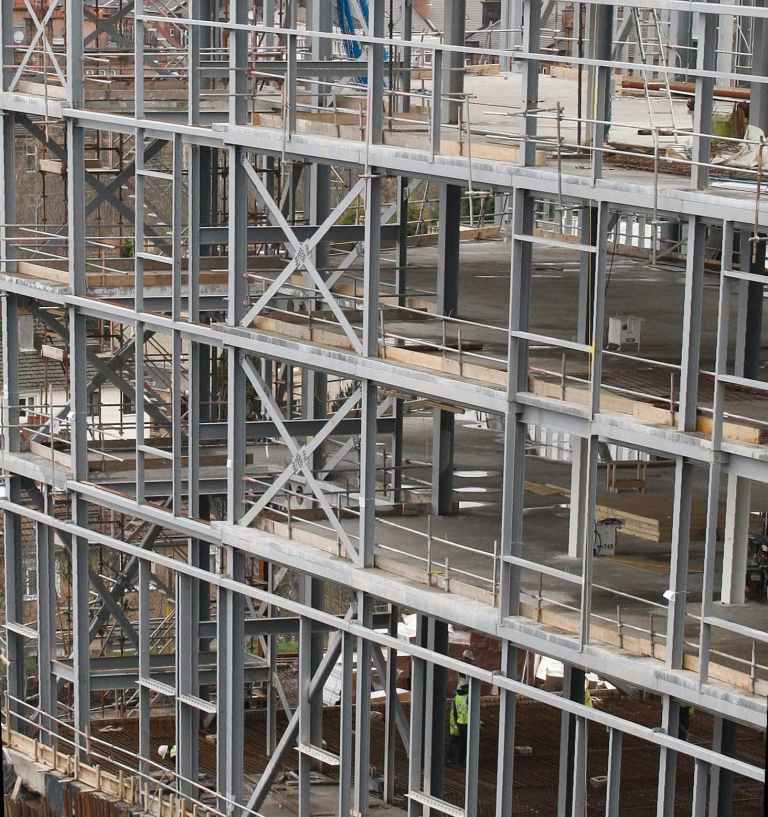

In mild steel framed structures as far as possible curved or circular work are avoided. Columns supporting upper floor loads and roof should be continuous right from the basement foundation. They should be so placed as to support directly the girders carrying heavy walls. The girders should be connected directly into the columns. Skew frames and eccentric loading should be avoided. For achieving economy members subjected to bending should be as deep as possible in the direction of the maximum bending moment. As far as possible, the cleats may be so arranged that they may be riveted mostly at the workshop.
RCC Framed Buildings
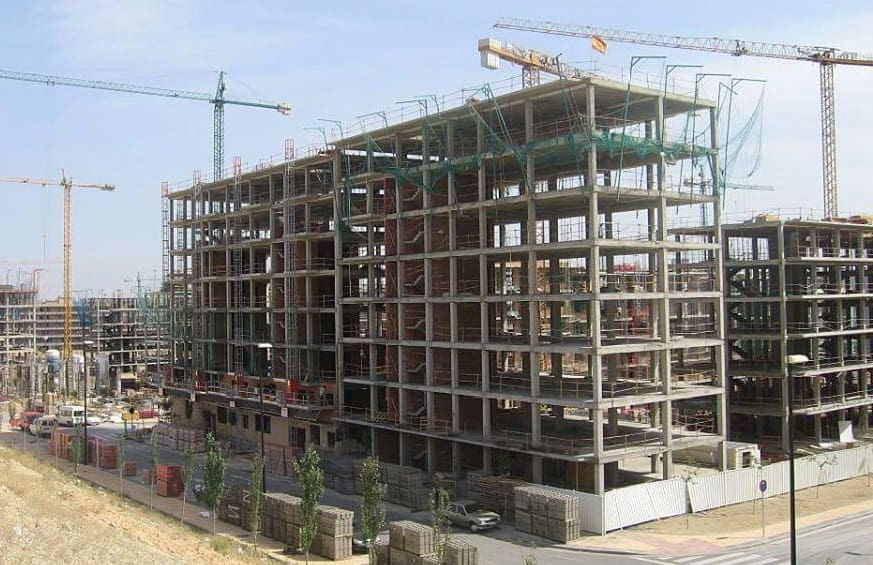

RCC framed structure consists of series of frames which are formed by interconnecting columns and beams at floor and roof levels, so as to form a grid of the beams and girders. Walls are constructed within these frames. Slab, beams, girders and columns are built monolithic ally and rigidly with each other at junction. Thus, in framed building, the loads of the floors, roofs and walls are supported by the beams and girders, which, in turn, transfer these loads to the column below and then to the foundations.
RCC frames are invariably of monolithic construction by which full continuity throughout columns, beams and slabs (of floors and roofs) can be attained. The main advantages of continuous construction are reduced deflections and bending moments in the members which result in the economical construction of buildings with adequate safety.
Due to numerous advantages framed structures are constructed all over the world. Reinforced concrete began to be introduced as a common material in frame construction since 1960. Today, the potential new building methods, such as space frame technology and composite construction is also being realized, and will change the shape of tomorrow’s buildings.