The Structural systems or structural frames can be defined as the assembly of inter-related or inter-dependent elements which forms a complex structure, and they are designed and built for resisting different loads.
Building Structural Systems
The structural systems are the combinations of elements which serve a common purpose. The elements of structural systems can be related to the bones of the human body. If bones are weak and not properly aligned and integrated into the human body, then the human body would not be able to work or perform well. In the same way, if the structural systems are not proper then it would not be able to take loads.
The functions of Structural Systems are to resist loads acting on structures and provide a skeleton in the building which encloses and subdivides space to provide a protected environment.
A building can also be understood as a physical embodiment of a number of systems and subsystems integrated with each other forming building as a whole.
The structural system for a building particularly consists of a stable assembly of structural elements designed and constructed to support and transit applied loads safely to the ground where in its each member has a unique behaviour under the applied loads.
The structural systems as the whole are divided in into different systems:
- Load Bearing System
- Framed System
- Shell System
- Strut and Tie
Related:
What is a Load Bearing Frame Structural System?
What is a Reinforced Concrete Frame Structure?
What is Shell Roof?
Roofs Constructed with the Combination of King & Queen Post Roof Trusses
All the Structural Systems have different advantages and disadvantages. So depending upon the natural environmental condition and loading condition the proper structural system has to be chosen by the Structural Engineer.
The structural engineer should choose it based on the following properties:
- State of Equilibrium
- Adequate Strength
- Geometrical Stability
- Adequate Rigidity
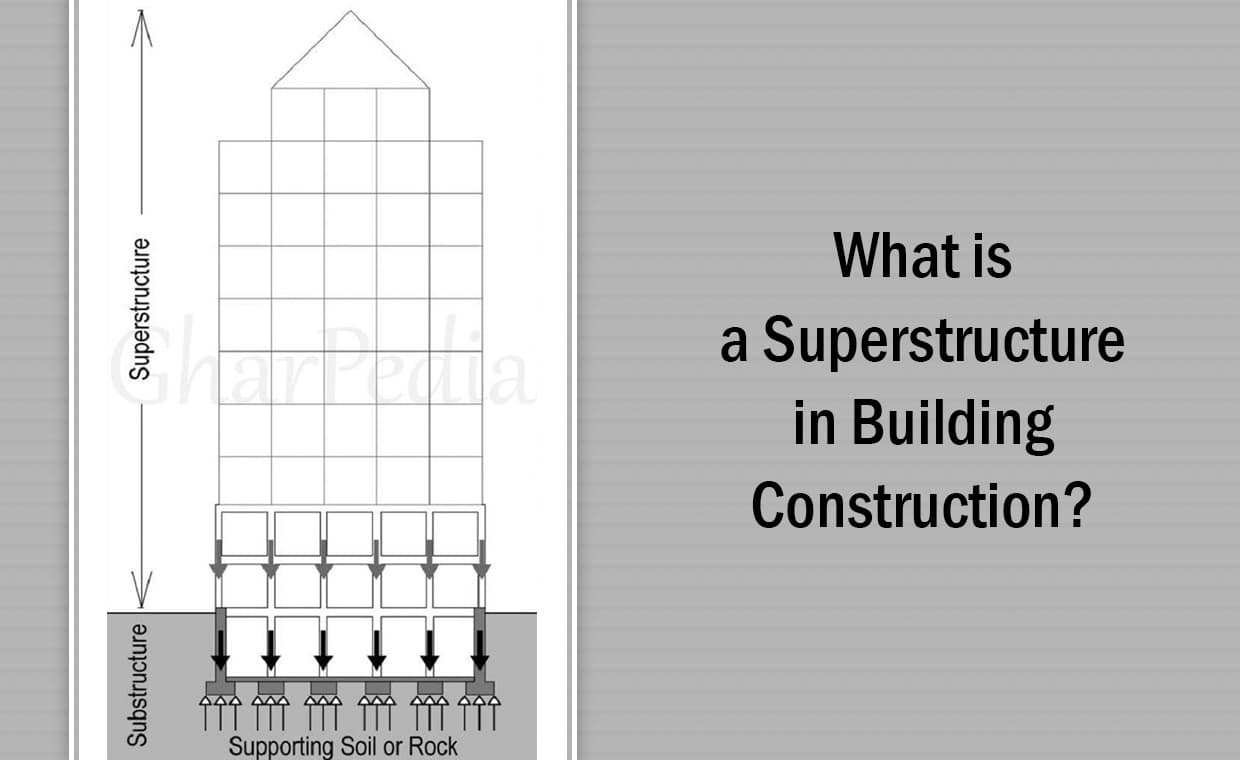
The structural systems can further be categorized between Substructure and Superstructure.
Substructure:
The substructure is the portion of a structural system that is below the ground level. It includes foundations, columns, walls below ground level, basement slabs, bridge piers and abutments, and the base of retaining wall. The purpose of the substructure is to support superstructure and transfer the load coming from superstructure to ground below.
In the substructure, one of the most important elements is the foundation. The foundation system must be designed to transmit the loads from the superstructure structural system directly to the ground in such a manner that settlement of soil for the completed building will be within acceptable limits.
Superstructure:
The superstructure is the portion of a structural system above the ground surface and visible after completion of the project. It includes beams, slabs, columns, domes, shells and walls above ground, steel frames, bridge deck, and the wall of retaining wall etc.
Also Read:
What is a Framed Tube System?
What is a Frame with Shear Wall Structural System?
What is the Difference between Column and Shear Wall?
In most of the buildings, the superstructure consists of floor and roofs, horizontal members that support them and vertical members that support the other components. The superstructure is designed to transmit its loads to the foundation system in the manner anticipated in the design of the foundations.
The superstructure of the building is loaded with different loads and the different loading conditions. Hence instability of the structure may occur.
One way to provide lateral stability is to incorporate in the diagonal members called bracing in the structural system. By providing bracing, columns and beams work together to carry the lateral loads downward.
Another way is to rigidly connect beams to columns to prevent a change in the angle between the beams and columns, thus making them work together as a rigid frame to resist lateral movement.
Another method is to provide long walls known as shear walls in two perpendicular directions. Lateral forces on the building can be resolved into forces in each of these directions. The walls then act like vertical beams (cantilevers) in transmitting the forces to the foundations.
So from all the above discussion, it is seen that it is also important to protect the structural system against damages, including the fire. For fire protection, steel bracing can be encased in fire-resistant floors, roofs or walls. Similarly, columns can be encased in walls and beams may be encased in floors. Or fire-resistant materials, such as concrete, mineral fiber or plaster may be used to box in the structural members.
It is the choice of a right structural system which will render the optimum use of the building at an optimum cost. One has to choose the right structural system striking balance between its intended use and functions and of course the cost associated with it. Space, i.e. volume, height, column or obstruction free area, i.e. long span/short span etc. will decide the right structural system. And having chosen the right structural system, it is the structural/geometrical configuration of placing all structural elements, which will yield the most economical design, i.e. optimum cost of the building.
Must Read:
Queen Post Truss: All You Need to Know
King Post Truss: All You Need to Know
Difference between King Post Truss & Queen Post Truss



































