Concrete is a vital material and plays a major role in the quality of buildings or structures. One may say that the making of concrete is easy but it’s not enough. It is important that a concrete mix is correctly designed, batched, mixed and transported, but it is also important to place concrete correctly. The placing of concrete is an essential operation because it largely determines the success of a structure and its durability. Expert contractors also provide concrete placement such as concrete contractors Dallas TX which offers the best materials, and it is assured that your concrete project will be of the good quality. Hence concrete placement must be done in systematic and efficient way to give the best results desired.
Also Read:
What do you mean by Batching of Concrete?
Different Methods for Mixing Concrete
11 Best Methods for Transportation of Concrete
There are various factors that determine which type of concrete placement is most suitable for concreting and are taken into consideration when choosing the method of concrete placement such as,
- Type of construction such as horizontal construction or vertical construction
- Size of construction
- Location of the site
- Weather conditions such as cold weather or hot weather etc.
Placing of concrete in different situations
Here you will get the information regarding which methods should be adopted and which precautions to be taken while placing of concrete in different situations,
Placing of Concrete Within Small Earth Mould

Here you will get the information regarding which methods should be adopted and which precautions to be taken while placing of concrete in different situations,
- In this kind of placing, concrete is placed in a small surface area on the earth such as foundation bed below the walls or columns.
- For the placing, first of all, all the loose earth must be removed from the bed.
- If the surface of the bed is dry then it must be made damp, so the earth doesn’t soak the water from concrete.
- If the foundation bed is too wet than the water and mud must be removed completely to expose the firm bed before placing of concrete.
- Clear all the obstruction such as any root of trees passing through the foundation, some charred or tarred elements because its further growth piercing the concrete at a later time can lead to deterioration of concrete.
Also Read:
Things to Check Before Concreting Footings
How to do Foundation if Water is Present in Pit?
Placing of Concrete within Large Earth Mould

- In this type of placing, concrete is placed in a large surface area on the earth such as road slab and airfield slab or timber plank form work.
- In such concrete placement, before the concreting, the ground surface on which the concrete is placed must be free from loose earth and other organic matters such as grass, roots, leaves etc.
- The earth must be appropriately compacted and made sufficiently damp to prevent the absorption of water from concrete because it makes concrete weak.
- Concrete is placed in alternative bays for the construction of road slabs, airfield slabs and ground floor slabs in buildings.
- In these bays, there are contraction joints and dummy joints which are given for shrinkage. Concrete should be properly dumped and concrete pouring and dragging from one place should be avoided.
- Joints gap are filled with the wooden husk or bitumen to prevent deterioration.
Placing of Concrete in Layers

- In this concrete placement, concrete is placed in the layer and this type of placement is used when the concrete is placed in great thickness such as mass concreting i.e. construction of dam or concrete abutment or pier.
- The layer thickness depends upon the various things like degree of compaction of concrete, using reinforced concrete or plain concrete etc.
- Generally, thickness of the reinforced concrete layer is about 15 to 30 cm. and thickness of the plain concrete layer is about 35 to 45 cm.
- Several such layers may be placed in succession to form one lift and concrete should be placed quickly enough to avoid cold joints.
- Before placing of concrete, the surface of the previous lift is cleaned carefully with water a jet and scrubbed by wire brush and made rough by removing all the laitance and loose material, so that proper bonding can occur between two layers.
Placing of Concrete Within Formwork

- Formwork is the temporary mould into which concrete is poured and formed. It can be said that concrete formwork is the supporting part of the structure. It is generally used for the beam and columns.
- Concrete formwork should be rigid so that it does not get deformed under the pressure of placement of fresh concrete and should be watertight so that the slurry does not leak out because it makes water-cement ratio insufficient
- The surfaces of form have to clean and brushed for every new use of formwork.
- Mould releasing agents such oil or grease should be applied inside of the formwork for easy stripping.
- The joints between planks, plywood or sheets must be properly and effectively plugged so that concrete/slurry will not leak during compaction or any vibration.
- If reinforcement is provided than it should be correctly tied and placed having appropriate cover and reinforcement should be clean and free form dirt and oil.
- Generally, difficulties arise when the concrete is to be poured from a greater height like placing of concrete in the column. It is likely to segregate or block the space to prevent further entry of concrete. To avoid this kind of difficulties concrete is placed by tremie or chute.
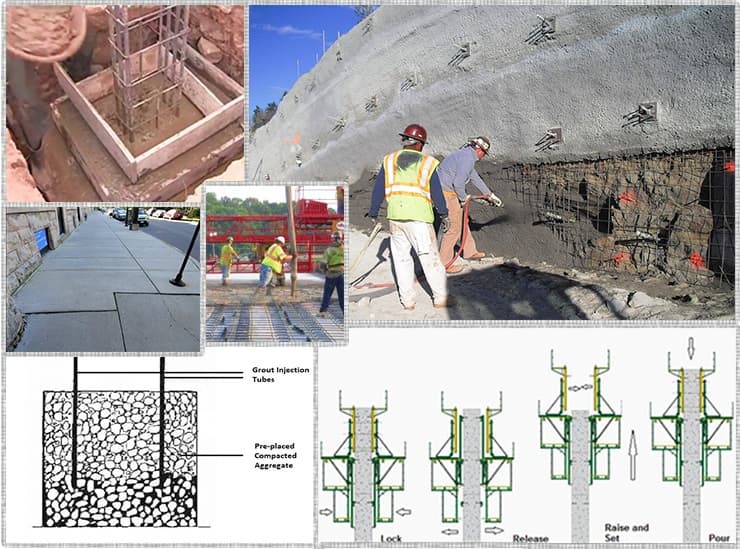
Underwater Concrete Placement

- There are various methods available for the underwater concreting such as the bottom dump bucket method, toggle bagged method, replaced aggregate method (grouted aggregate method), tremie method, pump and pipeline method etc
- Bottom Dump Bucket Method – In this method concrete is taken through the water in a water-tight box or bucket. On reaching the final place of deposition the bottom of the bucket is made to open by some mechanism and the whole concrete is dumped gradually. This method will not give a satisfactory result as a certain amount of washing away of cement is bound to occur.
- Toggle Bags Method – Toggle bags method can be considered as one of the oldest methods of underwater concreting. Toggle bags method is used for small works or repair works. In this method, wet concrete is placed inside the bags and are squeezed out by a diver at the site or place (underwater). The reusable canvas bag is used for this method which is filled with concrete and is lowered to the site which is underwater and then the concrete is discharged.
- In some situations, dry or semi-dry mixture of concrete i.e. cement, fine and coarse aggregate are filled in cement bags and such bagged concrete is deposited on the bed below the water. This method does not give satisfactory concrete because the concrete mass will be full of voids interspersed with the putrescible gunny bags.
Preplaced Aggregate Method (Grouted Aggregate Method)

- Preplaced aggregate method is used when the normal underwater concrete placement is difficult.
- Forms are used for this method and it is packed with well-graded aggregates and injected with mortar to fill the voids.
- Cement mortar grout pipe is injected through pipes (tubes), which extends to the bottom of the aggregate bed. Pipes are slowly withdrawn as grouting proceeds.
- In this method, less cement mortar is required for concreting because aggregate all packed densely than the ordinary concrete.
Tremie Method

- Tremie method is used for the underwater concrete placement and below the ground level concrete placement.
- In the tremie method, concrete is placed by gravity through a long vertical pipe which is called tremie pipe. Tremie pipe is a pipe having a diameter around 20 cm and adjustable length with a funnel-shaped hopper at the top end.
- A funnel-shaped hopper is fitted to facilitate pouring of concrete.
- The bottom end of the tremie pipe is closed with a plug, thick polyethylene sheet or other material and taken below the water and made to rest at the point or location where the concrete is going to be placed
Pumps and Pipeline Method

- Pumped concrete is widely used and more reliable method for the concrete placement of underwater concrete as well as multi-storied buildings, bridges, tunnel etc.
- In the pump method, its working starts with the suction stroke which sucks the concrete inside the pipe.
- The piston is provided for the suction and delivery of concrete.
- To match the pump and requirements of placing rate, it’s important to choose the correct diameter and wall thickness of the pipeline.
- For horizontal placement of concrete, the large diameter of pipelines is suitable and for the vertical placement of concrete, a smallest possible diameter of pipelines is suitable.
- How far concrete can be pumped, depends upon the various criteria such as the types of pump and the concrete mix design like workability etc.
- If the high-pressure pump is selected and we also give special attention to concrete mix design than concrete can be pumped to a height (vertical) over 400 m and a horizontal distance of over 2000 m
Special Concrete Placement
(a) Slip Forming

- Slip forming is a continuous placement and consolidation of concrete. In this technique, concrete is poured into a continuously moving form.
- Slip forming is used both for vertical construction such as tall structures i.e. chimney and silos and horizontal construction such as road pavement. Of course, slip forming is suitable for uniformly shaped structures.
- In Slip forming method, concrete is continuously placed, compacted and formwork is dragged (slipped) up by number of hydraulic jacks.
- The rate of dragging (slipping) the formwork will vary and it will depend upon the temperature and strength development of concrete to withstand without the support of formwork.
- Low slump concrete is used for this technique.
(b) Shotcrete or Guniting

- In shotcrete method concrete is applied by spraying through a nozzle by means of compressed air with fine aggregate and sand are used in shotcrete or guniting.
- Normally, the materials are dry mixed and the water is injected just before entering the nozzle. Wet concrete can also be sprayed.
- Shotcrete is very well suited for the construction of thin section and lightly reinforced section. Its more economical than regular concrete because of less requirements of formwork and requiring small portable plant for manufacturing and concrete placement.
Placing of concrete is very important for construction quality. Hence, it is necessary to take particular care in all technical and climatic parameters. According to this information you can determine which method of concrete placement is more suitable or viable for your construction and which precautions you need to exercise.
Don’t forget that after your concrete has been set, you’ll want to seal the concrete so that it is protected from moisture and freeze/thaw cycles. Learn more here.
Also Read:
Concrete Pouring During the Rain
Things to Check Before Concreting RCC wall (Shear Wall)
Things to Check Before Concreting Beams & Slabs
Things to Check Before Concreting Ground Beams & Plinth Beams
Image Courtesy: Image 2 – youtube, Image 4, Image 5 – ridgeend, Image 6 – unesco, Image 7, Image 9

































