Scaffolding is a temporary platform used to elevate and support workers and materials during the construction, repair, or cleaning of a structure; it consists of one or more planks of Suitable size and length, with different methods of support, depending on the form and usage.
The outside plastering work always starts from the top of the building and is finished at the bottom.
Scaffolding is an integral part of almost all the construction projects, and it has been used since the structures have been built commonly needed to get access to structures at height during the construction process. Scaffolding serves many different purposes.
At other times it is necessary to support significant loads from building materials, such as bricks, blocks, stucco, or cast-in-place concrete, which is known as ‘shoring’ instead of ‘scaffolding’.
Types of Scaffolding of External Plaster
Even though there are various types of scaffolding available, new types of scaffolding materials often come out.
Following are some of the most popular scaffolding types around the world which include:
- Single scaffolding
- Double scaffolding
- Cantilever scaffolding
- Suspended scaffolding
- Trestle scaffolding
- Steel scaffolding
- Patented scaffolding
External Scaffolding
There is various materials use for scaffolding. It depends upon the availability and cost of the material. Material which is easily available and of low cost is widely used for scaffolding. In India, wood is easily and readily available and is quite cheap and cost-efficient. So, wooden poles and bamboo are commonly used. In other countries easily available material with low cost is used and may change from country to country.
Precautions to be Taken for Scaffolding of External Plaster
Here are some precautions needed to be taken for scaffolding of external plaster.
- Use good quality material.
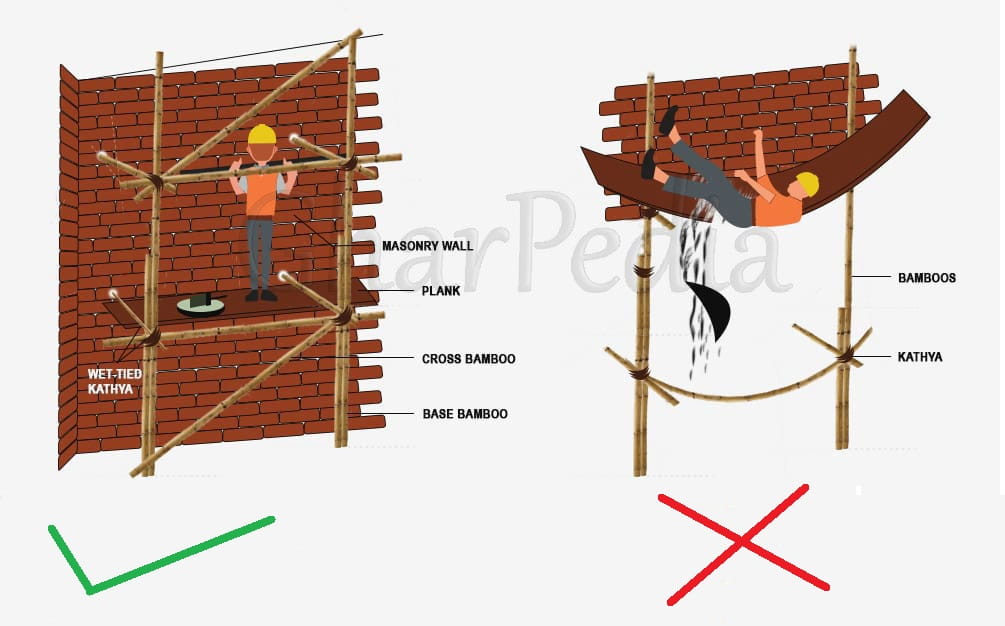
- Bamboo, kathya (ropes) & wooden planks should not be old and weak, so as to avoid probable accidents.
- Erect the base bamboo on a hard and firm ground, with minimum anchorage of 5cm in the ground.
- Kathya should be wet while tying, for better tightness.
- Check whether the scaffolding is in plumb position (vertical position/perpendicular to the ground) or inclined.
- Ensure that every junction of the scaffolding is well tied.
- A defective scaffold must be removed from service.
- Holes in masonry for bamboo support should be made at skirting level to avoid leakage/ seepage in a wall from the holes.
- Scaffolding erection should be carried out with the help of skilled workman so that the structure possesses the required stability.
- Platform surfaces should be secured and cleaned.
- Ensure that all the planks are laid for making the platform on scaffolding strong enough to take the mason’s live load. In some case two masons are required to work at a time, then put double plank instead of a single one.
- All plank rested on the scaffolding must be tied with wet kathya.
- Locate the holes/openings for taking mortar ghamelas from room to outside at the skirting level.
- Ensure that the scaffolding is used within a week after its erection.
- Scaffolding should be removed step by step, from top to bottom, as the work finishes.
- Keep 90 cm distant between the scaffolding and the wall to be plastered, for sufficient working space for the mason.
- All platforms should be at least 18 inches (45 cm)
- Ensure that all supporting bamboos are passed through the wall and tied internally, with other vertical and horizontal bamboos. Half anchorage in the wall for support should not be allowed.
- Proper wedges in the masonry hole for tightness of bamboo should be provided.
- Kathya should be removed systematically during de-scaffolding, for reuse.
- While removing the scaffolding, ensure that no one is working under that particular area, so as to avoid accidents.
- Inspect the scaffolding before and after use.
- Scaffolding, material and workers must be at least 10 feet away from living power lines.
Do Double Scaffolding & Avoid Damp Walls & Patches in Walls
In case of single scaffolding, holes are provided to support bamboo planks for scaffolding process. This hole is then filled up, and this becomes the reason for the leakage in the building as this is the patched up portion. This easily allows the water to enter through the wall and damage the wall plaster and paints for its life.
Double scaffolding is, therefore, an important structure, which will not take support on the wall but will have a different setup.
Therefore double scaffolding is always recommended as compared to single scaffolding while doing external plastering.


