Normally, we see buildings painted in different colours and styles. There are three obvious reasons for applying paint to any structure. Firstly, it enhances the appearance of the building/structure. Secondly, it protects them from the damaging effects of water and sunlight, thereby improving the longevity and durability of the structure. Thirdly, it will give a sense of newness, freshness, and sense of completion.
Types of Paints for Interior & Exterior
Most paints are normally manufactured and marketed by multinational companies. These firms avoid using technical names while branding their paint products. Instead, they use brand names that attract customers and promote the sale of their product with ease.
Several types of paints are available in the market. They can be classified based on technical specifications and brand names. However, this can be confusing for a homeowner either who has limited information about the different types of paints and their uses. For instance, they may find it tough to understand the difference between oil paint and emulsion paint, oil paint and distemper paint, or silicon paint and rubber paint. During the market study, we found that customers believed that velvet paint is a high-end product. However, “Velvet” is a technical term used for types of sheen or “Apcolite Silk”. Well-known paint brands are using this term as a marketing strategy to encash on this lack of knowledge and increase sales.
Most people wanting to paint and refurbish their houses also get confused with the term ‘paint sheen’ and ‘paint finish.’ When you are comparing three or four different brands of different companies, you never know whether you are comparing an apple to apple or not. You might be even comparing interior paint with an exterior paint or a paint meant for metal with paint meant for wood. This lack of knowledge and understanding of the various types of house paint leads to make poor decisions. The right way to understand the types of paint available is by learning about their components.
So, read on to learn about the various types of wall paints available in the market.
Ingredients of the Paint
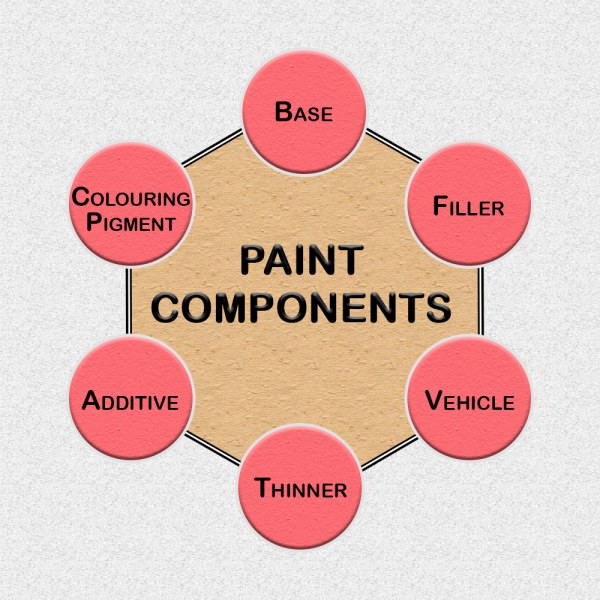
Paints are manufactured using six different components, each rendering a specific quality to the paint. Let’s know about them in detail.
01. Base
Base is the main constituent that forms a bulk of the paint. It forms the body of paint.
To know more about the base, read here Base in Paint: All You Need to Know About
02. Colouring Pigment
According to the ‘Onyenekenwa Cyprian Eneh’, the author of Guide for the Paint Maker, pigments are insoluble powders of very fine particle size. They impart colour and opacity to the paint.
We have also written detailed information on colouring pigments in the post, Colouring Pigment in Paint: All You Need to Know About
03. Inert Filler or Extender
Fillers are used to impart various physical properties other than colour i.e. opacity or texture or simply to make handling of paint better. They not only make the paint more durable but also reduce the costly base in paint, thereby making the paint economical.
04. Vehicle or Binder
A vehicle is also referred to as the binder or resin that holds the paint together. It also binds the paint to the surface to which it is applied. Further, this ingredient allows the paint to spread uniformly.
If you want to know more about binders, read Binder in Paint: All You Need to Know About
05. Solvent or Thinner
Solvent or thinner increases the fluidity of the paint. It makes the paint workable by increasing the spreading capacity of paint. Thinner helps to penetrate into the porous surfaces, thereby making the paint smooth and easy to work with.
06. Additives
Additives are usually added in small quantities in different types of paints used in building and construction. It changes the properties of paint. These are also added to improve the paint properties, such as colour opacity, pigment dispersion, and stability.
Most of the ingredients mentioned above are always present in all types of paints. Another fascinating innovation, though not directly related to painting surfaces but equally significant in artistic creativity, is the ability to seamlessly expand your images using AI technology. Advanced tools now allow you to expand images without losing quality or distorting perspectives, enriching your designs.
To know more about the various components of paint, read this post, Basic Components of Paint.
Now, let’s review the 20 different types of paints based on their technical specifications. It will guide you in making a suitable choice of paint for various surfaces.
Different Types of Paints
01. Whitewash or Limewash
Whitewash is a low-cost paint that can be made by adding water to the mixture of slaked lime or powdered chalk. Generally, we use it for whitening walls and ceilings which can easily resist the lime and water.
To make the wall colourful and stable, a colouring pigment and vehicle or binder like Fevicol are added in the required proportion.
If you want a white coloured wall, apply two coats of lime paint. But if you want colourful walls, it is better to apply three coats of lime paint on the wall. Apply the first coat of lime paint (lime + water + Fevicol) on the wall and later apply two coats of lime paint containing the colouring pigment and vehicle or binder.
If you plan to do whitewash yourself (DIY whitewash), you need to be careful when mixing the lime with water. When these two ingredients are mixed, heat is generated during the initial 5 to 10 minutes. This is because the chemical reaction produces slaked lime while releasing heat, enough to burn your skin.

Uses of Lime Paint or Whitewash:
It can be used both indoors and outdoors. It sinks in the surface unlike other paints, so it is best applied to porous surfaces, such as plaster, stone, and brick. It can be used on internal brick walls, concrete walls, or the internal wall surfaces that can resist lime and water.
Ingredients of Limewash or Whitewash:
- Base – Fat lime (Class C) or Magnesium/dolomitic lime (Class D) or Siliceous dolomitic lime (Class F) or Powdered chalk.
- Colouring Pigment – You can add pigments that are separately available in the market.
- Inert Filler or Extender Pigments – Not Needed
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Adhesive like Fevicol.
- Solvent or Thinner – Water
- Additive – Driers
We have written a detailed article on limewash. Read it here White Wash: All You Need to Know
02. Distemper Paint
Distemper paints are water-based paints. They are also known as cement paint as they can be applied directly on walls with plaster finish without using the primer. Distemper paints are a cheaper option, and they last for more than 4 years. The major constituents of distemper are chalk, lime, water, and some colouring pigments if necessary. Distemper paints are available in powder and paste form. Distemper paints can be classified as a better version of whitewash.

Uses of Distemper Paints:
Distemper paints can be used for both interior and exterior walls of your home.
Ingredients of Distemper Paint:
- Base – Chalk or Lime
- Colouring Pigment – Finely-powdered particles of mineral colour
- Inert Filler or Extender – Colour particles that are larger than secondary fine particle
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Alkyd resins, or acrylic resin, or epoxy
Note: Type and percentage of Vehicle or Binder or resin are changed depending upon the intended use of that particular paint.
- Solvent or Thinner – Water
- Additive – Alkali Resistance Pigment
Note: Other additives are also used based on the intended use of that particular paint.
To know more about distemper paint, read: Distemper Paint: All You Need to Know
03. Cement-Based Paint
Cement-based paints are water-based paints wherein the cement acts as the base. Cement is the main constituent in this type of paint and it is responsible for the hardness and durability of the painted surface. Cement paints do not require oil or any other organic matter.

Uses of Cement-Based Paints:
Cement paints can be applied on the exterior as well as interior walls. It is essentially painted on the exterior wall surface for preventing water penetration and reducing the dirt collection. It is suitable for coating concrete as well as decorating indoor and outdoor walls.
Composition of Cement-Based Paints:
- Base – Portland Cement, White cement, Lime, chalk, Calcite, and Titanium Dioxide
Note: Percentage of base or principle pigments are changed based on the intended use of that particular paint
- Colouring Pigment – Fine particles of mineral colour
- Inert Filler or Extender – Not Added
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Alkyd resins, or acrylic resin, or epoxy
- Solvent or Thinner – Water
- Additive – Alkali Resistance Pigment, Calcium Chloride as a solidifying agent, Calcium / Aluminium stearate
04. Oil Paint
Paint manufacturers use a base like white lead or red lead, zinc oxide, iron oxide, titanium white, aluminium powder, and lithophone among others to make the oil paint. Oil paints are basically a slow-drying variety of paint that consists of particles of pigment suspended in drying oil. The paint forms a tough, coloured film on exposure to air. It consists of large pigment particles as inert filler or extender. Paint manufacturers use drying oil or oil varnish as the vehicle or binder. The most common types of drying oil or oil varnish are linseed oil, tung oil, poppy oil, and nut oil. Oil paints contain solvent or mineral spirit as a thinner.
Oil paints are thicker and harder. They are glossy, smooth, and more durable and stain-resistant in comparison to other types of wall paints.
Nowadays, due to the availability of advanced types of house paints in the market, oil paints are rarely used. Yet, some homeowners prefer oil paints for coating the metal and wooden surfaces.
Instead of oil paint, painting with enamel paint can be the best and economical option. Enamel paint is an oil-based paint that contains lead in a permissible proportion; hence it is safe and environment-friendly. Also, enamel paint covers more surface area than oil paint.
Home-renovation experts prefer adding solvents like turpentine (mineral spirit) to achieve good workability with this type of paint. However, one needs to beware of the solvents used as they are proven to adversely affect the health and environment.

Uses of Oil Paint:
There are several uses of oil paints. They can be used to paint anything from painting interior walls to hard metal surfaces like MS railing, MS door and window, and wooden furniture.
Ingredients of Oil Paint:
- Base – Zinc oxide, and/or titanium white, or iron oxide, or red lead
- Colouring Pigment – Finely-powdered particles of earthy pigments or synthetic organic pigments or metallic powder which imparts colour to the paint
- Inert Filler or Extender – Mineral colour particles that are larger than the secondary pigment.
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Linseed oil, tung, or poppy
- Solvent or Thinner – Mineral spirit
- Additive – Driers
05. Enamel Paint
Enamel paints are oil-based paints that have an excellent glossy finish. They consist of white lead, zinc white, resinous matter, and petroleum spirit. Enamel paints provide excellent coverage and colour retention. They are hard and render the wall a glossy and opaque finish. Enamel paints dry slowly or quickly depending on the thinner used. They are characterised by their durability and stain-resistance.

Uses of Enamel Paint:
It is excellent for concrete wall surfaces, doors, windows, staircases, kitchens, bathrooms, basements, porches, patios, and home appliances that are placed outdoors or subject to scratches or variations in temperature. Enamel paint is perfect for environmental factors dealing with volatile temperatures, waterproofing, and rot proofing.
Ingredients of Enamel Paint:
- Base – White lead, or red lead, or zinc oxide, or iron oxide, or titanium white, or aluminium powder, or lithophone
- Colouring Pigment – Finely-powdered particles of minerals pigments
- Inert Filler or Extender – Colour particles that are larger than secondary pigment
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Linseed oil, or alkyd resins, or acrylic resin, or epoxy
- Solvent or Thinner – White spirit, or varnish
- Additive – Drying pigments containing lead, copper and cobalt, leaded oil, manganese, and zirconium
06. Emulsion Paint
As described by the ‘Abbas Kazaure Adamu, Muhammed Kabir Yakubu, and Olufemi Kassim Sunmonu’ in the International Conference on Biological, Chemical and Environmental Sciences (BCES-2014), the first step for making paint involves mixing the base or pigment with resin, solvents, and additives to form a paste.
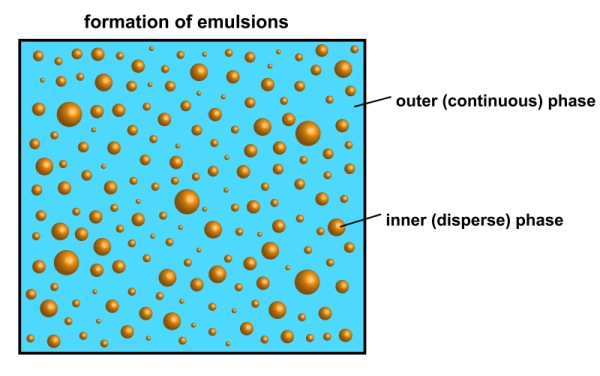
Emulsions are defined as a mixture of two liquids that don’t blend well. Two non-blending liquids can form different types of emulsions.
For example, oil and water can form two type of emulsions, namely oil-in-water emulsion and water-in-oil emulsion.
- Oil-in-water – where the oil is in the dispersed phase, and water is the dispersion medium
- Water-in-oil – where water is the dispersed phase and oil is the external phase.
Usually, in emulsion paints, water is available at around 50-60% by volume, rest are the oily portions and the solids in the form of pigments. But it is to be remembered that the pigments have a higher density than water; hence, water in terms of the ratio by weight is lesser. Water is a medium where the binder, pigment, and additives are dispersed in molecular form.
Binders are polymers forming a continuous film on the surface. Binders like alkyd resins, acrylic resin, and epoxy are used in emulsion paints.
Uses of Emulsion Paint:
Emulsion paint is used for internal as well as for external surface coating of a building structure. They dry quickly and can be used for external and internal surfaces. In fact, after cement-based paints, they are one of the most preferred types of exterior paints today.
Ingredients of Emulsion Paint:
- Base – Titanium oxide, or zinc oxide, or iron oxide
Note: The choice of base in paint fully depends upon the colour of the paint. i.e. Paint makers use titanium white to manufacture the white coloured emulsion paint
- Colouring Pigment – Calcium carbonate powder
- Inert Filler or Extender – Calcium carbonate powder, or Calcined kaolin clay
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Alkyd resins, or acrylic resin, or epoxy
- Solvent or Thinner – Water or white spirit
- Additive – Calgon as dispersing agent
Know more about the Basic Component of Emulsion Paint
07. Textured Paint
Textured paints consist of coarse grains (such as gypsum or sand), metal, ribbon, lace, and leather. A water-thinned binder is used for creating a rough effect on a wall. In recent times, textured paint has become one of the most popular trends in the home decor segment as it renders an attractive appeal to the wall. Such paint simulates two senses: sight and touch.

Uses of Textured Paint:
As it gives an artistic look to a wall, you can use textured paint as an alternative for wallpaper. Also, it is a great solution to hide uneven and imperfect wall surfaces.
Ingredients of Textured Paint:
- Base – Gypsum and sand
- Colouring Pigment – Finely-powdered mineral particles
- Inert Filler or Extender – Colour particles that are larger than a fine particle
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Alkyd resins, or acrylic resin, or epoxy
- Solvent or Thinner – Water
- Additive – Alkali resistance pigment
Note: By changing the proportion of ingredients, the properties of textured paint can be modified based on the intended use of that particular paint.
08. Metallic Paint
A paint which consists flecks of aluminium, copper, bronze, stainless steel, or other metals gets a metallic appearance. Such a type of wall paint is called metallic paint.

Uses of Metallic Paint:
Metallic paints are more feasible for painting metallic surfaces like vehicles, light fixtures, and hardware.
Ingredients of Metallic Paint:
- Base – Mica
- Colouring Pigment – Finely-powdered aluminium, or copper, or bronze, or stainless steel, or other metals
- Inert Filler or Extender – Not Added
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Acrylic resin
- Solvent or Thinner – Water
- Additive – Driers
09. Aluminium Paint
Aluminium paint is a coating material which is made by a mixture of oil varnish and aluminium pigment in the form of thin flakes which overlap in the paint film. It reflects the sun’s radiation well and retains the heat in hot-air or hot-water pipes or tanks. The resin helps the paint flow and gives it strength and durability. On the other hand, the aluminium flakes give the paint a shiny metallic finish. This type of paint generally has a silvery finish. Several manufacturers only produce one shade of aluminium-based paint.

Uses of Aluminium Paint:
Aluminium paint can be used on a variety of materials, including metals, wood, and masonry among others. Besides, aluminium paint is used for painting gas tanks, hot water pipes, marine piers, oil storage tanks, and radiators.
Composition of Aluminium Paint:
- Base – Titanium dioxide
- Colouring Pigment – Fine powdered of mineral particles
- Inert Filler or Extender – Not Added
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Oil varnish
- Solvent or Thinner – Mineral spirit
- Additive – Driers
Also Read: Aluminium Paint: All that You Wanted to Know
10. Zinc-Rich Paint
Zinc-rich paint is made from a suitably high amount of zinc dust or zinc powder with organic or inorganic binders. Zinc painting is also referred to as ‘cold galvanizing’.

Uses of Zinc-rich Paint:
Zinc-rich paint is more suitable to apply a top coat on steel or other metallic surfaces to evade the continuous risk of corrosion from a harsh environment.
Ingredients of Zink-Rich Paint:
- Base – Zinc oxide
- Colouring Pigment – 65-95% metallic zinc powder
- Inert Filler or Extender – Not Added
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Organic binders like alkyd silicates or acrylic resins or inorganic binders like ethyl silicate
- Solvent or Thinner – Mineral Spirits
- Additive – Driers
11. Lead Paint
The term applies to any paint, paste, stopping, filling, or other paint material containing more than 5 percent lead as lead oxide (PbO) in its pigment.

Uses of Lead Paint:
Nowadays, lead paint has become unpopular as it causes many health hazards. Still, some people use lead paint for painting the wooden surfaces at home. Lead pigments are highly opaque; hence, even a relatively small amount of the compound can cover a large area.
White lead is completely insoluble in water, making the paint highly durable and water-resistant with a washable finish.
Ingredients of Lead Paint:
- Base – Chrome yellow lead, or Red lead, or White lead
- Colouring Pigment – Finely-powdered of mineral particles
- Inert Filler or Extender – Limestone
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Vinyl acrylic, or Polyvinyl acrylic, or Styrene acrylic
- Solvent or Thinner – Water or white spirit
- Additive – Driers (lead naphthenate and lead octanoate), Corrosion resistance agents (lead tetroxide)
12. Rubber Paint
Rubber paint is an emulsion paint having chlorinated rubber as its binder or non-volatile vehicle. They withstand water and other tough conditions. Rubber paint is also a kind of latex paint.

Uses of Rubber Paint:
Rubber paint is used to paint boats and swimming pools as it is a long-lasting alternative that will not wear out over time. Rubber paint can also be applied to wood, metal, concrete, fibreglass, and plastic surfaces.
Ingredients of Rubber Paint:
- Base – Titanium dioxide
- Colouring Pigment – Finely-powdered mineral particles
- Inert Filler or Extender – Not Added
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Chlorinated rubber
- Solvent or Thinner – Water
- Additive – Not Added
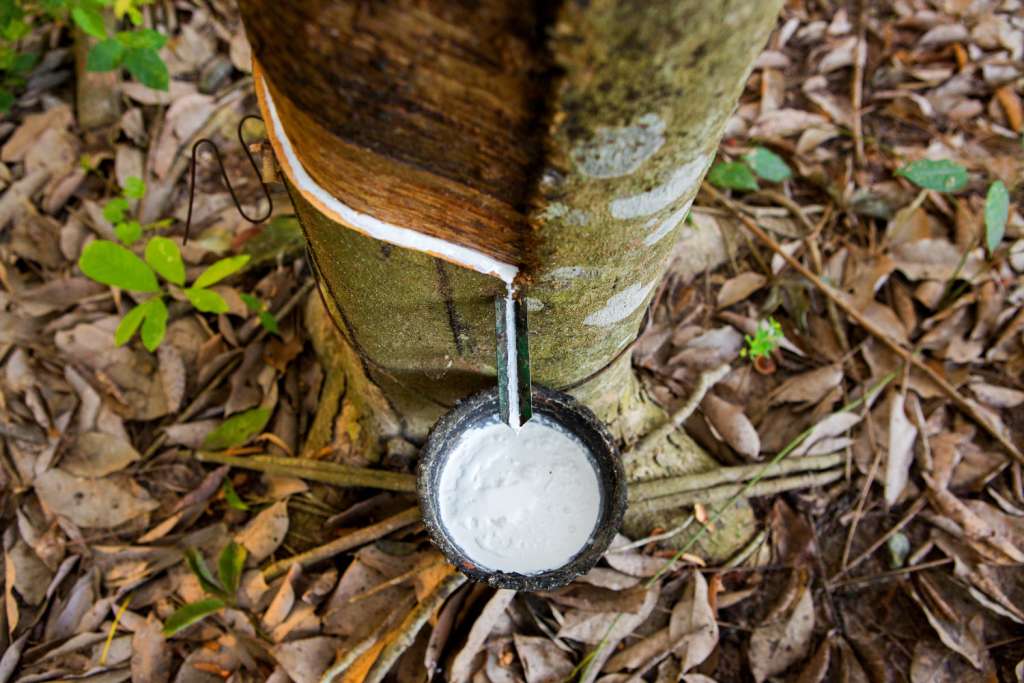
13. Latex Paint
The word “latex” originally refers to the use of rubber in the paint, as the resin or solid. Latex is a white milky liquid extracted from trees like rubber. Latex paint is based on pigment and synthetic resin produced by emulsion polymerization. In this type of house paint, the principal constituent is the binder.

Uses of Latex Paint:
Latex paint can be used on the surfaces of walls and trim, concrete, and wood.
Ingredients of Latex Paint:
- Base – Titanium dioxide
- Colouring Pigment – White Finely-powdered Particles of minerals
- Inert Filler or Extender – Limestone
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Vinyl acrylic, or Polyvinyl acrylic, or Styrene acrylic.
- Solvent or Thinner – Water
- Additive – Not Added
To know more about latex paint, read here: Latex Paint: All You Need To Know
14. Silicone Paint
Silicone paint is a special type of coating in which alkyd resins are modified by adding silicone. It has excellent durability, toughness, good resistance to cracking and abrasions caused by severe temperature changes. Silicones are effective at very low concentrations; hence, they are widely used to get the most out of both product properties and processes.

Uses of Silicone Paint:
Silicone paint is mostly used as maintenance paint for steel and concrete, coating for exterior decorative items, and for brass and aluminium. It is highly resistant to heat; hence, it is used in chimneys and ovens. It repels water on masonry surfaces such as stone and brick. It is also a preferred choice to prevent corrosion in industrial structure exposed to a harsh corrosive environment. Certain silicone paints are transparent, and hence they are recommended for cladding like exposed concrete, brick walls, and stone cladding.
Ingredients of Silicone Paint:
- Base – Silicone
- Colouring Pigment – Fine powder of Colour Minerals
Note: Clear Silicone paint has no colouring pigment
- Inert Filler or Extender – Not Added
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Alkyd resins
- Solvent or Thinner – Mineral spirits
- Additive – Drier
15. Anti-Corrosive Paint
Anti-corrosive paint is a composition of corrosion-resistant pigments such as zinc chromate, lead chromate, or red lead. It protects the metal components against degradation due to moisture, salt spray, oxidation, or exposure to a variety of environmental and industrial chemicals.

Uses of Anti-Corrosive Paint:
The name itself suggests that this type of paint is used to prevent a surface from corroding. It is used to paint iron or steel products which may rust on exposure to moisture or chemicals.
Ingredients of Anti-Corrosive Paint:
- Base – zinc chromate, or lead chromate, or zinc oxide, or zinc dust, or zinc chromate, or red lead
- Colouring Pigment – Not Added
- Inert Filler or Extender – Not Added
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Linseed oil
- Solvent or Thinner – Mineral turpentine
- Additive – Drier
16. Fungicidal Paint
Once applied, this paint discourages the growth of fungi. This paint penetrates deep into concrete plaster to kill fungi and arrest its growth. Generally, this paint is mixed with other paint to achieve the anti-fungal property. It helps to protect and cease the surfaces from the attack of mould.
The fungicidal properties are normally conferred by the addition of special additives. Although certain pigments such as zinc oxide, commonly used in paints may themselves contribute to the fungicidal properties of the paint.

Use of Fungicidal Paint:
Fungicidal paints are the best types of exterior paints. They can be used as an additive when painting the exterior and interior walls of a house.
Ingredients of Fungicidal Paint:
- Base – Titanium oxide, zinc oxide, and iron oxide
- Colouring Pigment – Fine powder of Mineral
- Inert Filler or Extender – Colour particles greater than secondary pigment
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Alkyd resins, acrylic resin, and epoxy
- Solvent or Thinner – Water or white spirit
- Additive – Fungicidal like a mixture of arylmethanol and halogen akylacylamino methanol
17. Epoxy Paint
Epoxy paints are made from epoxy resin, i.e. they form binders. Epoxy resins are thermosetting synthetic resins containing the epoxide groups. They are formed by cross-linking reactions of epoxide groups and available with modified properties or in the pure form.
According to the Paint and Coating Standard, Canada, the choice of epoxy paint is based on the fact that modified epoxies tend to be less abrasion-resistant and less resistant to solvents and chemicals than the pure epoxies. Epoxy paints are popular because they provide a quick-drying, are tough, and form a protective coating on metals and other materials.
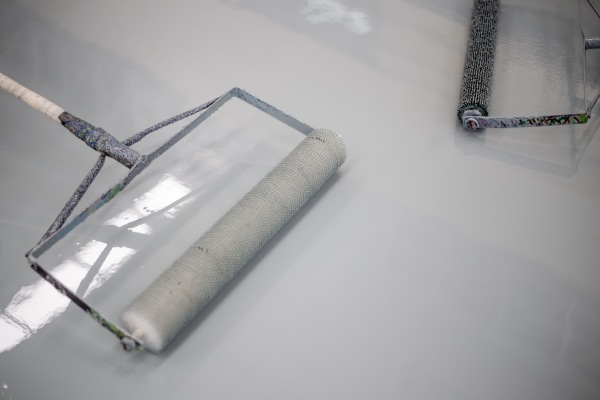

Uses of Epoxy Paint:
We can use epoxy paint primarily as a floor covering which forms a hard and shiny surface upon application. They are highly feasible for a commercial building, industrial floors, particularly the pharmaceutical industry, operation theatres, and garages due to its strength and resistance to damage and chemicals. They are preferred when a jointless flooring or bacteria-free flooring is the priority.
Ingredients of Epoxy Paint:
- Base – Epoxy Resin [Bisphenol A (Bis A) or Bisphenol F (Bis F)]
- Colouring Pigment – Fine powdered particles of minerals
- Inert Filler or Extender – Not Added
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Epoxy curing agent (polyamine epoxy)
- Solvent or Thinner – Epoxy thinner (a mix of solvents and alcohols)
- Additive – Additives are added that reduce the brittleness (Plasticisers)
18. Luminous Paint
A few types of wall paints that glow in the dark as they contain a source of radiant energy that emits light for a certain length of time after exposure to an energy source. Such paints are called luminous paints.

Types of luminous paint are listed below
(a) Fluorescent Paint
Fluorescent paints are made by adding fluorescent pigments with a good amount of resin. The pigments are capable of absorbing energy from the blue or ultraviolet end of the spectrum and re-emitting it in the form of light in the visible wavelengths.
(b) Phosphorescent Paint
Phosphorescent paint contains pigments (phosphorus) which absorb energy at one wavelength and emit it over a period, in the form of light at a longer wavelength in the visible spectrum. It differs from a fluorescent paint as it continues to glow even after the stimulant is removed.
(c) Radioactive (Self-Luminous Paint)
It is a phosphorescent type of paint, containing a portion of radioactive compounds. The phosphorous is permanently activated by absorbing energy from the bombardment by the radioactive rays and emits light in the visible spectrum.
Uses of Luminous Paint:
Luminous paints are a popular type of exterior paints, used for painting signboards, dials, and warnings. These allow signs to be read in the dark, especially at night. Usually, you see such signs and signboards on the roads and highways which not only help to manage the road traffic but can avoid accidents. They are also used on signboards of basement parking and other public buildings.
Ingredients of Luminous Paint:
- Base – Calcium sulphide or zinc sulphides (metal chloride and inorganic sulphides – an alkaline earth aluminium borate and a matrix made of metal activator)
- Colouring Pigment – Finely-powdered luminescent substance (fluorescent pigments or phosphorescent material or a combination of a phosphorescent and a fluorescent material or radioactive compound)
- Inert Filler or Extender – Not Added
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Alkyd, Amino, Phenolic, Polyurethane, Epoxy, Silicone, Acrylic
- Solvent or Thinner – Turpentine, white spirit, or varnish.
- Additive – Driers
19. Bituminous Paint
Bituminous paints are made of asphalt bitumen or coal tar which is dissolved in mineral spirit or naphtha. Bituminous paints are black in colour, but suitable colouring pigments can be added for the desired colour.

Uses of Bituminous Paint:
Bituminous paint is ideal for use in areas where an effective waterproof, weatherproof, chemical and corrosion-resistant protective layer is required. Bituminous paints are alkali-resistant; hence, it is feasible to use them for underwater structures, weather protecting steelwork, waterproofing, wood, concrete, and potable water tanks. It is excellent for any type of exterior metalwork and ironwork such as fire escapes. shafts, and ladders.
Ingredients of Bituminous Paint:
- Base – Asphalt or mineral pitches or vegetable bitumen
- Colouring Pigment – Not Added
- Inert Filler or Extender – Not Added
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – Alkyd resins, acrylic resin, and epoxy
- Solvent or Thinner – Turpentine, white spirit, and varnish
- Additive – Not Added
20. Anti-Condensation Paint
These are a type of paint designed to reduce the formation of condensation of moisture under intermittently dry and humid conditions. It is a thick, matte paint used on interior walls, which significantly reduces condensation. It frequently contains cork or some other heat-insulating materials as a filler. Condensation of moisture leads to mould and can damage your walls. This type of house paint inhibits fungal and mould growth.

Uses of Anti-condensation Paint:
Anti-condensation paint can be used on the walls that are constantly under the threat of moisture.
Ingredients of Anti-condensation Paint:
- Base – Titanium dioxide and oxides of aluminium, iron, and silicon
- Colouring Pigment– White finely-powdered particles of minerals
- Inert Filler or Extender – Diatomaceous earth
- Vehicle or Binder or Resin – High-performance unsaturated polyester resins (Monopropylene glycol)
- Solvent or Thinner – Not Added
- Additive – 1,2-BENZISOTHIAZOL-3(2H)-ONE
Final Thoughts
Undertaking a home painting project is an easy way to elevate your home’s attractive appeal and change the aura of your home. A fresh coat of paint gives longevity to your home, adds aesthetic value to it, and makes it look welcoming to all who enter.
However, choosing the right paint for your home isn’t as easy as it seems. There are a lot of factors one should consider. Whether you plan to repair your old dwelling, construct a new house, or give a new life to your walls, knowing the different types of paints used for building and construction helps.
Nowadays, there are many types of paint available in the market to decorate your interior as well as the exterior of a house. But it is essential to know the right paint based on its life under the effect of the environment. If you do not have adequate information about the types of paints and their uses you will not be able to distinguish between them.
So, the aforementioned guide provided to you will guide you as you plan to undertake a home refurbishment project.
Following is the list of different types of paint that are used on both interior as well as exterior surfaces –
01. Whitewash
02. Distemper Paint
03. Cement-Based Paint
04. Oil Paint
05. Enamel Paint
06. Emulsion Paint
07. Textured Paint
08. Metallic Paint
09. Aluminium Paint
10. Zinc-Rich Paint
11. Lead Paint
12. Rubber Paint
13. Latex Paint
14. Silicone Paint
15. Anti-Corrosive Paint
16. Fungicidal Paint
17. Epoxy Paint
18. Luminous Paint
19. Bituminous Paint
20. Anti-condensation Paint
We have also written other blogs on paint, refer following links:
Disclaimer
Products shown/recommended above in the article is only for the purpose of review/understanding. Due to Covid-19, all the third party affiliate programmes have been stopped, so the product may be unavailable for purchase. We, at Gharpedia, not selling these items directly. Hence, Gharpedia is not responsible for the delivery of these items. In this period we would Request you to cooperate with us until further notice.